Electromagnetic Delay Lines
... impedance can be connected input-to-output (cascaded) to optimize rise time and/or obtain specific delay values. The rise time of the grouped lines is given by ...
... impedance can be connected input-to-output (cascaded) to optimize rise time and/or obtain specific delay values. The rise time of the grouped lines is given by ...
nemmani_paper
... radiation both single event and total ionization dose on the phase-locked loops are briefly described. The constituent parts of digital phase-locked loops (DPLLs) are described and their impact on the overall radiation tolerance is reviewed. Single event hardening design techniques were additionally ...
... radiation both single event and total ionization dose on the phase-locked loops are briefly described. The constituent parts of digital phase-locked loops (DPLLs) are described and their impact on the overall radiation tolerance is reviewed. Single event hardening design techniques were additionally ...
Automatic control systems
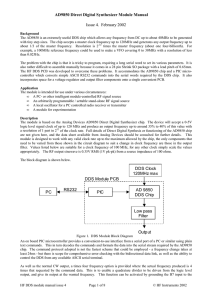
... • The Local Oscillator is adapted to the actual line frequency in this wiring. As a second variant the control circuit can control the transmitters frequency instead of the LO frequency! In this case the transmitterfrequency would regulated to the more stable LO-frequency. ...
... • The Local Oscillator is adapted to the actual line frequency in this wiring. As a second variant the control circuit can control the transmitters frequency instead of the LO frequency! In this case the transmitterfrequency would regulated to the more stable LO-frequency. ...
Diode Laser Control Electronics Diode Laser Locking and Linewidth
... frequency deviations, the diode current can be changed. This has an influence on the index of refraction in the diode, and therefore again on the optical cavity length of the laser. TOPICA’s diode laser systems are available with a current modulation board, DLMod, that is designed for this purpose. ...
... frequency deviations, the diode current can be changed. This has an influence on the index of refraction in the diode, and therefore again on the optical cavity length of the laser. TOPICA’s diode laser systems are available with a current modulation board, DLMod, that is designed for this purpose. ...
H48034249
... frequencies between 90 GHz and 125 GHz were demonstrated. The generated signals had low phase noise less than -75dBc/Hz at 100Hz offset. In the first setup, optical filters and optical couplers were connected through optical fibers. The measured signals showed phase fluctuations and high phase noise ...
... frequencies between 90 GHz and 125 GHz were demonstrated. The generated signals had low phase noise less than -75dBc/Hz at 100Hz offset. In the first setup, optical filters and optical couplers were connected through optical fibers. The measured signals showed phase fluctuations and high phase noise ...
PPS - Institut Mihajlo Pupin
... program PSPICE This generated model can be applied as an integral part of the simulation circuits of the power converters with phase and switch mode control, for driving vibratory actuator ...
... program PSPICE This generated model can be applied as an integral part of the simulation circuits of the power converters with phase and switch mode control, for driving vibratory actuator ...
LTC1069-1 - Low Power, 8th Order Progressive Elliptic, Lowpass Filter
... Consult LTC Marketing for parts specified with wider operating temperature ranges. *The temperature grade is identified by a label on the shipping container. Consult LTC Marketing for information on non-standard lead based finish parts. For more information on lead free part marking, go to: http://www. ...
... Consult LTC Marketing for parts specified with wider operating temperature ranges. *The temperature grade is identified by a label on the shipping container. Consult LTC Marketing for information on non-standard lead based finish parts. For more information on lead free part marking, go to: http://www. ...
Chirp spectrum

The spectrum of a chirp pulse describes its characteristics in terms of its frequency components. This frequency-domain representation is an alternative to the more familiar time-domain waveform, and the two versions are mathematically related by the Fourier transform. The spectrum is of particular interest when pulses are subject to signal processing. For example, when a chirp pulse is compressed by its matched filter, the resulting waveform contains not only a main narrow pulse but, also, a variety of unwanted artifacts many of which are directly attributable to features in the chirp's spectral characteristics. The simplest way to derive the spectrum of a chirp, now computers are widely available, is to sample the time-domain waveform at a frequency well above the Nyquist limit and call up an FFT algorithm to obtain the desired result. As this approach was not an option for the early designers, they resorted to analytic analysis, where possible, or to graphical or approximation methods, otherwise. These early methods still remain helpful, however, as they give additional insight into the behavior and properties of chirps.