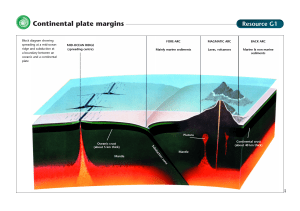
File - Mr. Snelgrove
... Europe) were tested their ancient magnetism no longer lines up with the modern magnetic poles. Therefore, the continents (and the plates they are on) must have moved. ...
... Europe) were tested their ancient magnetism no longer lines up with the modern magnetic poles. Therefore, the continents (and the plates they are on) must have moved. ...
What is an Earthquake? Seismicity Faults and Earthquakes
... – Energy buildup due tectonic stresses. – Cause rocks to break. – Energy moves outward as an expanding sphere of waves. – This waveform energy can be measured around the globe. ...
... – Energy buildup due tectonic stresses. – Cause rocks to break. – Energy moves outward as an expanding sphere of waves. – This waveform energy can be measured around the globe. ...
Results from the iMUSH Active Source Seismic
... understand the deformation associated with active volcanism. This is the largest dense array over a volcano at this scale anywhere in the world, so should play an important role in addressing GeoPRISMS science goals associated with magmatic processes. As of summer 2015 we have one year of data from ...
... understand the deformation associated with active volcanism. This is the largest dense array over a volcano at this scale anywhere in the world, so should play an important role in addressing GeoPRISMS science goals associated with magmatic processes. As of summer 2015 we have one year of data from ...
Jeopardy
... The reason the continental drift hypothesis was initially rejected by the scientific ...
... The reason the continental drift hypothesis was initially rejected by the scientific ...
Morganfest brochure
... spreading ocean floor. This insight was fundamental to Meteor Seamount. Today, Jason Morgan, with other the revolutionary theory then developing, and sharing hotspot theorists, is not only prepared to suggest its that office with Fred Vine drew Morgan into the subject general origin but to indicate ...
... spreading ocean floor. This insight was fundamental to Meteor Seamount. Today, Jason Morgan, with other the revolutionary theory then developing, and sharing hotspot theorists, is not only prepared to suggest its that office with Fred Vine drew Morgan into the subject general origin but to indicate ...
Chapter 10: Plate Tectonics
... Climate Clues Wegener used continental drift to explain evidence of changing climates. For example, fossils of warm-weather plants were found on the island of Spitsbergen in the Arctic Ocean. To explain this, Wegener hypothesized that Spitsbergen drifted from tropical regions to the arctic. Wegener ...
... Climate Clues Wegener used continental drift to explain evidence of changing climates. For example, fossils of warm-weather plants were found on the island of Spitsbergen in the Arctic Ocean. To explain this, Wegener hypothesized that Spitsbergen drifted from tropical regions to the arctic. Wegener ...
Bedrock - NH Division of Forests and Lands
... relative to one another. It is through various plate tectonic processes that we will tell an important part of the story of the geologic history of the Monadnock Region. However, in order to understand plate tectonic processes, we must first preface our story with a look at the interior of the earth ...
... relative to one another. It is through various plate tectonic processes that we will tell an important part of the story of the geologic history of the Monadnock Region. However, in order to understand plate tectonic processes, we must first preface our story with a look at the interior of the earth ...
Geologica: Earth`s Dynamic Forces by Robert Coenraads and John I
... Large forces can change the Earth's surface rapidly or slowly Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes can cause rapid changes on Earth’s surface such as creating new land, making cracks in the crust, or changing landforms. Mass movement of material can cause rapid change to Earth’s surface such as rocks ...
... Large forces can change the Earth's surface rapidly or slowly Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes can cause rapid changes on Earth’s surface such as creating new land, making cracks in the crust, or changing landforms. Mass movement of material can cause rapid change to Earth’s surface such as rocks ...
Unit: tectonic patterns and processes
... plate movements. It should include broader explanations, including human actions and the continued human occupation of hazardous locations. The topic teaches about human response to perceived risk, and the idea of preparedness for natural hazards. ...
... plate movements. It should include broader explanations, including human actions and the continued human occupation of hazardous locations. The topic teaches about human response to perceived risk, and the idea of preparedness for natural hazards. ...
Uncharted Territory (1170L)
... to zero, Gakkel Ridge is the best bet, says marine geochemist and Healy cochief scientist Charles Langmuir of Harvard University. Nearly 20,000 km, or one-third, of the total midocean-ridge system is likely to fall into the new, ultraslow category, and Gakkel Ridge is "the slowest-spreading major po ...
... to zero, Gakkel Ridge is the best bet, says marine geochemist and Healy cochief scientist Charles Langmuir of Harvard University. Nearly 20,000 km, or one-third, of the total midocean-ridge system is likely to fall into the new, ultraslow category, and Gakkel Ridge is "the slowest-spreading major po ...
Exploring the Earth`s Magnetic Field
... What are magnetic fields? In physical science, a "field of force " is a region or space in which an object can cause a push or pull. This field extends infinitely in all directions but gets weaker as you get farther from the source of the field. Magnetic lines of force show the strength and directio ...
... What are magnetic fields? In physical science, a "field of force " is a region or space in which an object can cause a push or pull. This field extends infinitely in all directions but gets weaker as you get farther from the source of the field. Magnetic lines of force show the strength and directio ...
Plate Tectonics: What Happens when Plates Collide
... As the 12 major plates of the earth’s crust move due to the convection of heated magma in the mantle, this causes many events. Where two plates slide past one another laterally enormous amounts of built up pressure is released in the form of earthquakes. This is illustrated by the TRANSFORM fault ab ...
... As the 12 major plates of the earth’s crust move due to the convection of heated magma in the mantle, this causes many events. Where two plates slide past one another laterally enormous amounts of built up pressure is released in the form of earthquakes. This is illustrated by the TRANSFORM fault ab ...
File
... Before a volcanic eruption, seismic activity seems to do what considering frequency and ...
... Before a volcanic eruption, seismic activity seems to do what considering frequency and ...
Plate Tectonics Introduction Boundaries between crustal plates
... drifted great distances (not to mention the fact that Wegener was a meteorologist) his ideas were widely rejected. In the subsequently developed hypotheses of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics, however, there was no problem of continents plowing through oceanic rock. Instead, rigid plates, incl ...
... drifted great distances (not to mention the fact that Wegener was a meteorologist) his ideas were widely rejected. In the subsequently developed hypotheses of seafloor spreading and plate tectonics, however, there was no problem of continents plowing through oceanic rock. Instead, rigid plates, incl ...
Precambrian Time
... operated at precisely the same rate. Moreover, some important geologic processes are not currently observable, but evidence that they occur is well established. For example, we know that Earth has been hit by large meteorites even though we have no human witnesses. Such events altered Earth’s crust, ...
... operated at precisely the same rate. Moreover, some important geologic processes are not currently observable, but evidence that they occur is well established. For example, we know that Earth has been hit by large meteorites even though we have no human witnesses. Such events altered Earth’s crust, ...
Continental Drift Reading
... coastlines of South America and Africa looked as though they would fit like adjacent pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. Although his formal profession was meteorology, Wegener had always been curious about the remarkable fit of the coastlines. Was it just a coincidence? He speculated that perhaps the contin ...
... coastlines of South America and Africa looked as though they would fit like adjacent pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. Although his formal profession was meteorology, Wegener had always been curious about the remarkable fit of the coastlines. Was it just a coincidence? He speculated that perhaps the contin ...
The Birth of Plate Tectonics
... oceanic Nazca Plate is pushed toward and beneath the continental portion of the South American Plate, is an example of a convergent plate boundary. ...
... oceanic Nazca Plate is pushed toward and beneath the continental portion of the South American Plate, is an example of a convergent plate boundary. ...
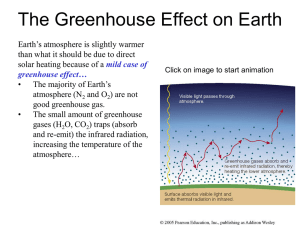
The Greenhouse Effect on Earth
... – The wearing away of bedrock and transport of loosened particles by a fluid, such as water – Example: Sediment moved along the bottom of a ...
... – The wearing away of bedrock and transport of loosened particles by a fluid, such as water – Example: Sediment moved along the bottom of a ...
Nature of Earthquakes - mcdonough-mbvm
... About 15% of all earthquakes take place in the Mediterranean-Asiatic belt. The convergent plate boundaries in the region are shrinking the Mediterranean Sea. The convergence is also causing the Himalayas to grow. The remaining 5% of earthquakes are scattered around the other plate boundaries. A few ...
... About 15% of all earthquakes take place in the Mediterranean-Asiatic belt. The convergent plate boundaries in the region are shrinking the Mediterranean Sea. The convergence is also causing the Himalayas to grow. The remaining 5% of earthquakes are scattered around the other plate boundaries. A few ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.