CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES
... Underwater mountain ranges where crust is spreading apart creating new ocean floor Continental Rifting The process that causes continental crust to extend and thin. Rift Valley deep valley formed on land where two plates move apart and magma rises to Earth's surface ...
... Underwater mountain ranges where crust is spreading apart creating new ocean floor Continental Rifting The process that causes continental crust to extend and thin. Rift Valley deep valley formed on land where two plates move apart and magma rises to Earth's surface ...
Plate Tectonics: Earthquake Epicenter
... the amplitude of the waves generated by it. Since there was such a broad range of values of amplitudes for earthquakes measured, Richter made the scale logarithmic. This means that each increase of one on the Richter scale corresponds to an increase of 10 in the amplitude of the waves. Thus, on the ...
... the amplitude of the waves generated by it. Since there was such a broad range of values of amplitudes for earthquakes measured, Richter made the scale logarithmic. This means that each increase of one on the Richter scale corresponds to an increase of 10 in the amplitude of the waves. Thus, on the ...
Pangaea and Seafloor Spreading Notes
... time ago, all the continents were connected as one large landmass. 1. Wegener formed the idea of Continental Drift based on his observations that many fossils of the same type were found on continents thousands of miles apart, that rock types and rock formations were the same on continents thousands ...
... time ago, all the continents were connected as one large landmass. 1. Wegener formed the idea of Continental Drift based on his observations that many fossils of the same type were found on continents thousands of miles apart, that rock types and rock formations were the same on continents thousands ...
Pangaea and Seafloor Spreading Notes
... ago, all the continents were connected as one large landmass. 1. Wegener formed the idea of Continental Drift based on his observations that many fossils of the same type were found on continents thousands of miles apart, that rock types and rock formations were the same on continents thousands of m ...
... ago, all the continents were connected as one large landmass. 1. Wegener formed the idea of Continental Drift based on his observations that many fossils of the same type were found on continents thousands of miles apart, that rock types and rock formations were the same on continents thousands of m ...
Ambient Noise Tomography
... seismic wave speeds in Earth’s interior in order to advance knowledge of temperature, composition, and fluid content which hold a key to the understanding of Earth processes. Recent studies based on TA data in the western US, such as that of Yang et al. (2008b), invert ambient noise and earthquake d ...
... seismic wave speeds in Earth’s interior in order to advance knowledge of temperature, composition, and fluid content which hold a key to the understanding of Earth processes. Recent studies based on TA data in the western US, such as that of Yang et al. (2008b), invert ambient noise and earthquake d ...
PLATE BOUNDARY LOCALIZATION: WHAT PROCESSES ACTIVE
... planet has adopted a global tectonic regime that appears unique in the solar system [1]. Deformation is localized in narrow deformation zones, some of which do no contribute to removing heat from the interior of the planet [2]. Because of the higher strain rate inside narrow deformation zones, energ ...
... planet has adopted a global tectonic regime that appears unique in the solar system [1]. Deformation is localized in narrow deformation zones, some of which do no contribute to removing heat from the interior of the planet [2]. Because of the higher strain rate inside narrow deformation zones, energ ...
Chapter 7, Section 4 Directed Reading A
... _____ 2. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called a. seismology. c. deformation. b. elasticity. d. re-formation. _____ 3. When stress squeezes an object it is called a. compression. c. convergence. b. re-formation. d. tension. _____ 4. When stress stretches an obj ...
... _____ 2. The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called a. seismology. c. deformation. b. elasticity. d. re-formation. _____ 3. When stress squeezes an object it is called a. compression. c. convergence. b. re-formation. d. tension. _____ 4. When stress stretches an obj ...
Chap-4-Sec-2-Evidence-Supporting-Continental
... was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate" refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift ...
... was developed in the mid 1960s by geophysicists. The term "plate" refers to large rigid blocks of the Earth's surface which appear to move as a unit. These plates may include both oceans and continents. When the plates move, the continents and ocean floor above them move as well. Continential Drift ...
Igneous Rocks - ElementaryScienceOlympiadBCS
... typical for silicon tetrahedra to form first, and they in turn join with each other and other ions to form the nuclei for crystal growth. The minerals with the highest melting points will crystalize first, and their crystal growth may continue unimpeded as long as the surrounding material remains mo ...
... typical for silicon tetrahedra to form first, and they in turn join with each other and other ions to form the nuclei for crystal growth. The minerals with the highest melting points will crystalize first, and their crystal growth may continue unimpeded as long as the surrounding material remains mo ...
Heat Flow in the Arctic - AINA Publications Server
... synchronous with the one in Barrow, although somewhat smaller. The mean surface temperature at Cape Thompson is again lower than the temperature predicted by the analysis, and a much more recent cooling is also indicated there. It is clear that any attempt to make heat-flow measurements in this regi ...
... synchronous with the one in Barrow, although somewhat smaller. The mean surface temperature at Cape Thompson is again lower than the temperature predicted by the analysis, and a much more recent cooling is also indicated there. It is clear that any attempt to make heat-flow measurements in this regi ...
Ocean Basins
... separate pieces of crust move due to convection of heat in underlying layer (Mantle) plates can move in different directions, and collide Collisions a) two continental plates collide, form high mountain ranges e.g., Himalayas b) two ocean plates collide, form island arc and submarine trench e.g., Al ...
... separate pieces of crust move due to convection of heat in underlying layer (Mantle) plates can move in different directions, and collide Collisions a) two continental plates collide, form high mountain ranges e.g., Himalayas b) two ocean plates collide, form island arc and submarine trench e.g., Al ...
2 Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era
... time. Scientists use the term evolution to describe this change. Evolution is the process in which new species develop from existing species. Scientists find evidence for evolution when they compare fossils to living organisms. This huge species existed from 110 million to 90 million ...
... time. Scientists use the term evolution to describe this change. Evolution is the process in which new species develop from existing species. Scientists find evidence for evolution when they compare fossils to living organisms. This huge species existed from 110 million to 90 million ...
Tasty Plate Tectonics
... asthenosphere: the region below the lithosphere, in which the rock is less rigid than that above. igneous rock: rock formed by the solidification of molten magma sedimentary rock: rock formed from consolidated clay sediments metamorphic rock: rock altered by pressure and heat Paleomagnetism: magneti ...
... asthenosphere: the region below the lithosphere, in which the rock is less rigid than that above. igneous rock: rock formed by the solidification of molten magma sedimentary rock: rock formed from consolidated clay sediments metamorphic rock: rock altered by pressure and heat Paleomagnetism: magneti ...
GRAVITY MODELING OF SUBDUCTION ON VENUS. S. M.
... trench region is much larger than other regions of the corona. The density anomalies at Quetzalpetlatl are consistent with a subducting slab in the presence of a hot mantle plume. This finding offers support to surface thermal emissivity data interpreted as indicating volcanism < 2.5 mya and probabl ...
... trench region is much larger than other regions of the corona. The density anomalies at Quetzalpetlatl are consistent with a subducting slab in the presence of a hot mantle plume. This finding offers support to surface thermal emissivity data interpreted as indicating volcanism < 2.5 mya and probabl ...
Seismicity, crustal structure, and morphology of the Louisville Ridge
... aftershocks associated with large earthquakes, together with the available marine seismic, swath bathymetry, gravity and magnetic data to determine the relationship between seismicity and the structure and morphology of the leading edges of overthrusting Indo-Australian and subducting Pacific plates ...
... aftershocks associated with large earthquakes, together with the available marine seismic, swath bathymetry, gravity and magnetic data to determine the relationship between seismicity and the structure and morphology of the leading edges of overthrusting Indo-Australian and subducting Pacific plates ...
Earthquake Hazards
... slippage of the boundary between two of the earth's tectonic plates – thick slabs of rock that carry the Earth's continents and seas on an underground ocean of much hotter, semi-solid material. ...
... slippage of the boundary between two of the earth's tectonic plates – thick slabs of rock that carry the Earth's continents and seas on an underground ocean of much hotter, semi-solid material. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Hot material rises while cool material sinks Cool material is dense The motion of sinking and rising material drags the tectonic plate away from mid-ocean ridge Flash Presentation ...
... Hot material rises while cool material sinks Cool material is dense The motion of sinking and rising material drags the tectonic plate away from mid-ocean ridge Flash Presentation ...
Hawaii Crustal Plate Lab
... The idea behind plate tectonics is that the crustal plates are moving with respect to one another over geologic time. The rates of movement of crustal plates can be determined by using data from the plate margins along the mid-ocean ridges, or at regions known as “HOTSPOTS” where the distance and ag ...
... The idea behind plate tectonics is that the crustal plates are moving with respect to one another over geologic time. The rates of movement of crustal plates can be determined by using data from the plate margins along the mid-ocean ridges, or at regions known as “HOTSPOTS” where the distance and ag ...
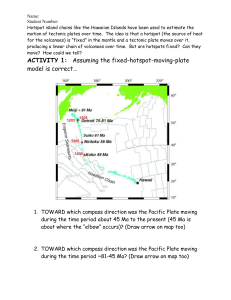
HotspotActivity_forSERC.v2
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
... Hotspot island chains like the Hawaiian Islands have been used to estimate the motion of tectonic plates over time. The idea is that a hotspot (the source of heat for the volcanoes) is “fixed” in the mantle and a tectonic plate moves over it, producing a linear chain of volcanoes over time. But are ...
Quaking, Shaking, Earth
... moving past each other without much upward or downward movement. • The San Andreas Fault is the boundary between two of Earth’s plates that are moving sideways past each other. ...
... moving past each other without much upward or downward movement. • The San Andreas Fault is the boundary between two of Earth’s plates that are moving sideways past each other. ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes
... •These earthquakes occur at a depth at which the subducted crust should no longer be brittle, due to the high temperature and pressure. A possible mechanism for the generation of deep focus earthquakes is faulting. • Earthquakes may also occur in volcanic regions and are caused there both by tectoni ...
... •These earthquakes occur at a depth at which the subducted crust should no longer be brittle, due to the high temperature and pressure. A possible mechanism for the generation of deep focus earthquakes is faulting. • Earthquakes may also occur in volcanic regions and are caused there both by tectoni ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.