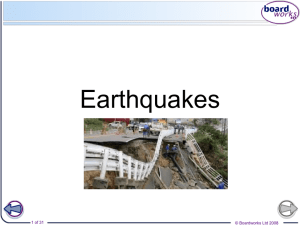
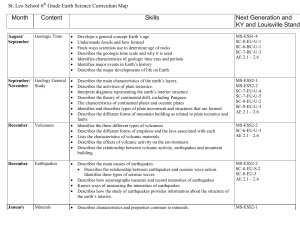
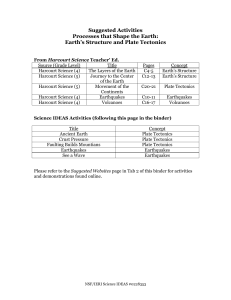
Plate Tectonics
... These boundaries are created when plates move apart and new material is added to the Earth’s crust. An example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
... These boundaries are created when plates move apart and new material is added to the Earth’s crust. An example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
Chapter 2 Whole Notes
... Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago and is made mostly of rock. Approximately 70% of the surface is covered with water. Earth is an oblate sphere, or a slightly flattened sphere. Earth’s pole-to-pole circumference is 24,804 miles. Its equatorial circumference is 24,845 miles. Earth’s average di ...
... Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago and is made mostly of rock. Approximately 70% of the surface is covered with water. Earth is an oblate sphere, or a slightly flattened sphere. Earth’s pole-to-pole circumference is 24,804 miles. Its equatorial circumference is 24,845 miles. Earth’s average di ...
PowerPoint slides from lecture
... Milankovitch cycles- Eccentricity • Earth’s orbit changes from nearly circular to more elliptical. • The present difference in light intensity between summer and winter is about 6%. During very elliptical orbit, can be as much as 30% different. • Cycle is ~95,000 years ...
... Milankovitch cycles- Eccentricity • Earth’s orbit changes from nearly circular to more elliptical. • The present difference in light intensity between summer and winter is about 6%. During very elliptical orbit, can be as much as 30% different. • Cycle is ~95,000 years ...
Science Enhanced Scope Sequence
... thick beneath the continents and only about 6.5 miles thick beneath the oceans. The crust is light and brittle compared to the other layers of the Earth, and most earthquakes occur within the crust. Procedure 1. Hand out the attached diagram of “The Layers of the Earth,” and ask them if they can ...
... thick beneath the continents and only about 6.5 miles thick beneath the oceans. The crust is light and brittle compared to the other layers of the Earth, and most earthquakes occur within the crust. Procedure 1. Hand out the attached diagram of “The Layers of the Earth,” and ask them if they can ...
Day 11 - Ch. 5
... The tides cause the Earth to slow down and the Moon’s orbit to increase in radius (4 cm per century). Also, the Moon’s rotation is synchronous with its orbit. ...
... The tides cause the Earth to slow down and the Moon’s orbit to increase in radius (4 cm per century). Also, the Moon’s rotation is synchronous with its orbit. ...
Earth`s Structure
... drilled was in Russia. It took 24 years, and it is less than 13 kilometers (about 7.6 miles) deep. – This is less than halfway through Earth’s crust. ...
... drilled was in Russia. It took 24 years, and it is less than 13 kilometers (about 7.6 miles) deep. – This is less than halfway through Earth’s crust. ...
June 2008
... Layer 2 is younger than layer 1, but is older than layer 4. Layer 2 is younger than layer 3, but is older than layer 1. Layer 3 is older than layer 2, but is younger than layer 1. Layer 3 is older than layer 4, but is younger than layer 2. ...
... Layer 2 is younger than layer 1, but is older than layer 4. Layer 2 is younger than layer 3, but is older than layer 1. Layer 3 is older than layer 2, but is younger than layer 1. Layer 3 is older than layer 4, but is younger than layer 2. ...
Unit 4 - College Guild
... So far we have been studying rocks and the Earth’s structure. But now we will focus on the evolution of the Earth, starting from its early age until the present. As mentioned earlier, rocks record time and information. The oldest rocks are at the bottom of the rock layers, or strata, each representi ...
... So far we have been studying rocks and the Earth’s structure. But now we will focus on the evolution of the Earth, starting from its early age until the present. As mentioned earlier, rocks record time and information. The oldest rocks are at the bottom of the rock layers, or strata, each representi ...
Rocks & Landforms
... coastlines of continents such as South America & Africa show that they could fix together like a jig-saw puzzle Rare & identical fossils are found in rocks in South America & Africa mountain chains of Europe & Africa & the Americas are geologically related, but separated by the Atlantic Ocean In the ...
... coastlines of continents such as South America & Africa show that they could fix together like a jig-saw puzzle Rare & identical fossils are found in rocks in South America & Africa mountain chains of Europe & Africa & the Americas are geologically related, but separated by the Atlantic Ocean In the ...
Earth`s Interior
... • When it first formed , it was a spinning mass of rocks and dust that was loosely held together. • Over time, many comets and asteroids crashed into its surface and added to its mass. • Impacts, radioactive decay and gravity produced intense heat. • It was a young planet, a glowing ball of melted r ...
... • When it first formed , it was a spinning mass of rocks and dust that was loosely held together. • Over time, many comets and asteroids crashed into its surface and added to its mass. • Impacts, radioactive decay and gravity produced intense heat. • It was a young planet, a glowing ball of melted r ...
Plate Tectonics - BSHYear7Geography
... explain continental drift with the theory of plate tectonics. The Earth's surface is made up of a number of large plates that are in constant, slow motion. The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. The edges of these plates – plate boundaries – are ...
... explain continental drift with the theory of plate tectonics. The Earth's surface is made up of a number of large plates that are in constant, slow motion. The ocean floors are continually moving, spreading from the centre and sinking at the edges. The edges of these plates – plate boundaries – are ...
Earth`s Structure Is Affected by Density
... Southern) Country that you picked out was probably greatly distorted in size on the flat map. It is also hard to see the relationship between two countries on a map when they are on opposite sides of the paper. Web link: http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/core/7thgrd/sciber7/EARTH/HTML/MODEL.HTM ...
... Southern) Country that you picked out was probably greatly distorted in size on the flat map. It is also hard to see the relationship between two countries on a map when they are on opposite sides of the paper. Web link: http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/core/7thgrd/sciber7/EARTH/HTML/MODEL.HTM ...
What Is Inside Earth?
... • The lithosphere is the top part of the mantle and the crust together. It is a rigid layer. • The asthenosphere is a soft layer underneath the lithosphere. This layer is hotter and under increasing pressure but still solid. • The lower mantle is solid. This solid material extends all the way to Ear ...
... • The lithosphere is the top part of the mantle and the crust together. It is a rigid layer. • The asthenosphere is a soft layer underneath the lithosphere. This layer is hotter and under increasing pressure but still solid. • The lower mantle is solid. This solid material extends all the way to Ear ...
orbiting the sun - MIT Haystack Observatory
... 2. Does the orbital period depend on the planet’s distance from the sun (orbital radius)? How? yes, the greater the orbital radius, the greater the orbital period 3. Does the orbital velocity depend on the planet’s orbital radius? How? yes, the greater the orbital radius, the lower the orbital veloc ...
... 2. Does the orbital period depend on the planet’s distance from the sun (orbital radius)? How? yes, the greater the orbital radius, the greater the orbital period 3. Does the orbital velocity depend on the planet’s orbital radius? How? yes, the greater the orbital radius, the lower the orbital veloc ...
What are Earth`s physical layers?
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
... mantle made of solid rock that moves very slowly. • The asthenosphere is located below the lithosphere and is often described as “plastic like” • Tectonic plates move on top of the asthenosphere. ...
History of geodesy
Geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɨsi/), also named geodetics, is the scientific discipline that deals with the measurement and representation of the Earth. The history of geodesy began in antiquity and blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment.Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat (see flat earth), and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses were seen as circular shadows which could only be caused by a spherical Earth, and that Polaris is seen lower in the sky as one travels South.