Economics Defined - Ajadaf
... Resources can only be used for one purpose at a time Scarcity thus requires that choices must be made The cost of any good, service, or activity is the value of what must be given up to get it. This is opportunity cost. This is a most important concept which we will refer to over and over. ...
... Resources can only be used for one purpose at a time Scarcity thus requires that choices must be made The cost of any good, service, or activity is the value of what must be given up to get it. This is opportunity cost. This is a most important concept which we will refer to over and over. ...
Financial Operations - International Business (Our Global Economy).
... produce both shoes and shirts at 6 per hour, and a worker in a country with less machinery can produce either 2 shoes or 4 shirts in an hour, each country can gain from trade because their internal trade-offs between shoes and shirts are different. The lessefficient country has a comparative advanta ...
... produce both shoes and shirts at 6 per hour, and a worker in a country with less machinery can produce either 2 shoes or 4 shirts in an hour, each country can gain from trade because their internal trade-offs between shoes and shirts are different. The lessefficient country has a comparative advanta ...
economics and politics.ppt
... Business cycle fluctuations result from imbalances between aggregate demand and productive capacity • Aggregate demand is the total amount of money available in the economy to be spent on goods and services • Productive capacity is the total value of goods and services that can be produced by the ec ...
... Business cycle fluctuations result from imbalances between aggregate demand and productive capacity • Aggregate demand is the total amount of money available in the economy to be spent on goods and services • Productive capacity is the total value of goods and services that can be produced by the ec ...
Economics Fall 2013 Objectives: Student will be able to relate the
... 8. Make-up work is the student’s responsibility and must be turned in two days post absence. It is the student’s responsibility to collect missed assignments on their own time, not during class, and the same late policy applies after the two days grace period. 9. Cheating is not tolerated and parent ...
... 8. Make-up work is the student’s responsibility and must be turned in two days post absence. It is the student’s responsibility to collect missed assignments on their own time, not during class, and the same late policy applies after the two days grace period. 9. Cheating is not tolerated and parent ...
Introduction
... It is indeed important to keep in mind why we have undertaken the exercise of reinforcing economic governance. It is because our policy framework failed to prevent unsustainable fiscal and economic developments in many member states, with devastating consequences for their economies, and the risk of ...
... It is indeed important to keep in mind why we have undertaken the exercise of reinforcing economic governance. It is because our policy framework failed to prevent unsustainable fiscal and economic developments in many member states, with devastating consequences for their economies, and the risk of ...
Chapter 17
... Germans and Italians helped Franco take over • Soviet Union allied with loyalists • Popular Front – Americans and others ...
... Germans and Italians helped Franco take over • Soviet Union allied with loyalists • Popular Front – Americans and others ...
International Business
... takes place within a nation’s borders, without regard to whether the production is done by domestic or foreign factors of production Example • Both a Ford and Toyota manufactured in ...
... takes place within a nation’s borders, without regard to whether the production is done by domestic or foreign factors of production Example • Both a Ford and Toyota manufactured in ...
The Role of Government in the Economy The government provides
... which the volatility of economic activity is automatically suppressed as it moves through the business cycle. Other stabilizers require a conscious policy choice. So-called active stabilization policies were very popular in the period immediately following World War II, influenced by the conventiona ...
... which the volatility of economic activity is automatically suppressed as it moves through the business cycle. Other stabilizers require a conscious policy choice. So-called active stabilization policies were very popular in the period immediately following World War II, influenced by the conventiona ...
grade_10_HSS_released_CSTs
... A string of decisive military victories gained land from the Central Powers. B. Russia’s sale of supplies to its western allies ...
... A string of decisive military victories gained land from the Central Powers. B. Russia’s sale of supplies to its western allies ...
Major Schools of Economic Theory
... •The Marxist School challenged Classical theory. Karl Marx saw capitalism as an “evolutionary” phase in economic development. He believed capitalism would eventually destroy itself. •Marx believed in the labor theory of value which states that all production belongs to labor because workers produce ...
... •The Marxist School challenged Classical theory. Karl Marx saw capitalism as an “evolutionary” phase in economic development. He believed capitalism would eventually destroy itself. •Marx believed in the labor theory of value which states that all production belongs to labor because workers produce ...
Lesson 1 Visuals - Focus: Understanding Economics in Civics and
... Yes. Article 126 states clearly that private enterprises may not be nationalized. In other words, they are to be privately owned. ...
... Yes. Article 126 states clearly that private enterprises may not be nationalized. In other words, they are to be privately owned. ...
Economic Policymaking
... Policies for Controlling the Economy Fiscal Policy of Presidents and Parties Fiscal Policy: the policy that describes the impact of the federal budget on the economy (How much is the government taxing, borrowing and spending?) Fiscal policy is controlled by the President and the ...
... Policies for Controlling the Economy Fiscal Policy of Presidents and Parties Fiscal Policy: the policy that describes the impact of the federal budget on the economy (How much is the government taxing, borrowing and spending?) Fiscal policy is controlled by the President and the ...
The Economic Problem
... simplify economic reality show how dependent variables are affected by independent variables include inverse and/or direct relationships incorporate a variety of assumptions such as ...
... simplify economic reality show how dependent variables are affected by independent variables include inverse and/or direct relationships incorporate a variety of assumptions such as ...
Global Economy - Georgia State University
... abroad and their impact on the domestic economy is therefore an important aspect of modern economics. Course Learning Objectives: This is an overview course and the students should expect to learn the basics of international trade, international finance and development economics. The students are al ...
... abroad and their impact on the domestic economy is therefore an important aspect of modern economics. Course Learning Objectives: This is an overview course and the students should expect to learn the basics of international trade, international finance and development economics. The students are al ...
Macroeconomic instability
... • Appear to fight deficits; do so is political suicide. • “[M]arket fluctuations, in turn, provide rhetorical ammunition for politicians wanting to inject the government still more into economic life.” ...
... • Appear to fight deficits; do so is political suicide. • “[M]arket fluctuations, in turn, provide rhetorical ammunition for politicians wanting to inject the government still more into economic life.” ...
economics - Mr Bello`s Blog
... Why is per capita GDP a better measure of development than GDP? Per capita GDP shows how much of the nation’s product is being created per person rather than the total production in the country. It can also indicate people’s living standard, depending on income distribution within the country. ...
... Why is per capita GDP a better measure of development than GDP? Per capita GDP shows how much of the nation’s product is being created per person rather than the total production in the country. It can also indicate people’s living standard, depending on income distribution within the country. ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... international human capital; • Chronic instability of legal solutions, which causes substantial uncertainty as to level of the fiscal burden and the basic cost accounting components; • Low efficiency and unfriendly attitude of public administration with respect to enterprises, which increases busine ...
... international human capital; • Chronic instability of legal solutions, which causes substantial uncertainty as to level of the fiscal burden and the basic cost accounting components; • Low efficiency and unfriendly attitude of public administration with respect to enterprises, which increases busine ...
Download pdf | 1612 KB |
... • Abundant labour (refugees) plus wartime investment in capital stock gave Germans an advantage • Reduction of class conflict compared with 1920s— the success of ‘corporatism’ (Maier) – Unemployment down from 10% (1950) to 1% (1960) – Lower labour radicalism, e.g. Germany ...
... • Abundant labour (refugees) plus wartime investment in capital stock gave Germans an advantage • Reduction of class conflict compared with 1920s— the success of ‘corporatism’ (Maier) – Unemployment down from 10% (1950) to 1% (1960) – Lower labour radicalism, e.g. Germany ...
SS6E5 6 7 Notes
... A quota is when a country limits the amount of a product that can be sold to another country. Quotas can cause shortages that cause prices to rise, but also protect domestic production of a product by restricting foreign competition. An embargo is when one country completely refuses to trade w ...
... A quota is when a country limits the amount of a product that can be sold to another country. Quotas can cause shortages that cause prices to rise, but also protect domestic production of a product by restricting foreign competition. An embargo is when one country completely refuses to trade w ...
2 Peter 1:2 - Joe Griffin Media Ministries
... feudalism into oblivion, Smith’s policies, including free trade, sound money (the gold standard), balanced budgets, and minimum levels of poor relief, were increasingly put into practice. World War I marked a turning point in the development of capitalism. After the war, international markets shrank ...
... feudalism into oblivion, Smith’s policies, including free trade, sound money (the gold standard), balanced budgets, and minimum levels of poor relief, were increasingly put into practice. World War I marked a turning point in the development of capitalism. After the war, international markets shrank ...
What Is A Political Economy?
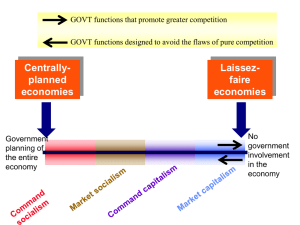
... “the good of society” because there is little incentive to control costs and be efficient, command economies tend to stagnate Mixed economies - certain sectors of the economy are left to private ownership and free market mechanisms while other sectors have significant state ownership and governmen ...
... “the good of society” because there is little incentive to control costs and be efficient, command economies tend to stagnate Mixed economies - certain sectors of the economy are left to private ownership and free market mechanisms while other sectors have significant state ownership and governmen ...
Chapter 2
... “the good of society” because there is little incentive to control costs and be efficient, command economies tend to stagnate Mixed economies - certain sectors of the economy are left to private ownership and free market mechanisms while other sectors have significant state ownership and governmen ...
... “the good of society” because there is little incentive to control costs and be efficient, command economies tend to stagnate Mixed economies - certain sectors of the economy are left to private ownership and free market mechanisms while other sectors have significant state ownership and governmen ...
Chapter 1: The Economic Way of Thinking Section 4: The Economist
... interested in identifying trends in statistics, they often use graphs, or visual representations of numerical relationships. • The most common type is the line graph, which are good to show changes over time. • Line graphs use at least two sets of numbers. • Bar graphs are useful for comparing items ...
... interested in identifying trends in statistics, they often use graphs, or visual representations of numerical relationships. • The most common type is the line graph, which are good to show changes over time. • Line graphs use at least two sets of numbers. • Bar graphs are useful for comparing items ...
Crisis Theory For Complex Societies - Brian Holmes
... developing and guiding Keynesian welfare policies on different scales. This reflects the more general importance of national economies and national states in the 'thirty glorious years' of postwar growth. For the national not only dominated the circuits of Atlantic Fordism, but also the mercantilist ...
... developing and guiding Keynesian welfare policies on different scales. This reflects the more general importance of national economies and national states in the 'thirty glorious years' of postwar growth. For the national not only dominated the circuits of Atlantic Fordism, but also the mercantilist ...