Two Interpretations of Rigidity in Rigid Body Collisions
... time, the relative displacement between pairs of points that are not in the contact-deformation regions (say points R and P) can be accurately calculated by treating the spheres as rigid everywhere except in a small, localized contact region governed by the Hertz relations. In general point-contact ...
... time, the relative displacement between pairs of points that are not in the contact-deformation regions (say points R and P) can be accurately calculated by treating the spheres as rigid everywhere except in a small, localized contact region governed by the Hertz relations. In general point-contact ...
Chapter 6 Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems
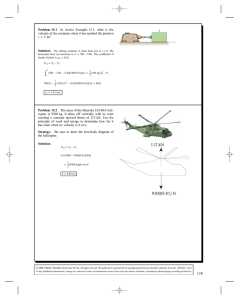
... nearly uniform and thus the effect of the momentum-flux correction factor is negligible, β ≅ 1. Analysis We take the plate as the control volume. The relative velocity between the plate and the jet is V when the plate is stationary, and 1.5V when the plate is moving with a velocity ½V towards the pl ...
... nearly uniform and thus the effect of the momentum-flux correction factor is negligible, β ≅ 1. Analysis We take the plate as the control volume. The relative velocity between the plate and the jet is V when the plate is stationary, and 1.5V when the plate is moving with a velocity ½V towards the pl ...
Chapter 7 LINEAR MOMENTUM
... propelling it forward. Similarly, a rocket engine expels exhaust from burning fuel to propel itself forward. 9. First law: The momentum of an object is constant unless acted upon by an external force. Second law: The net force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of the object’s moment ...
... propelling it forward. Similarly, a rocket engine expels exhaust from burning fuel to propel itself forward. 9. First law: The momentum of an object is constant unless acted upon by an external force. Second law: The net force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of the object’s moment ...
to the file
... gravity is broken down into components, one acting perpendicular to the inclined ramp and one acting parallel to the inclined ramp. The component of the force of gravity that is parallel to the inclined ramp causes the object (vehicle in this case) to move down the ramp, if that component is greater ...
... gravity is broken down into components, one acting perpendicular to the inclined ramp and one acting parallel to the inclined ramp. The component of the force of gravity that is parallel to the inclined ramp causes the object (vehicle in this case) to move down the ramp, if that component is greater ...
Document
... Any other use of the materials is governed by the general copyright statement that follows. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, without written permission from the publisher. Heriot-Watt Universi ...
... Any other use of the materials is governed by the general copyright statement that follows. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, without written permission from the publisher. Heriot-Watt Universi ...