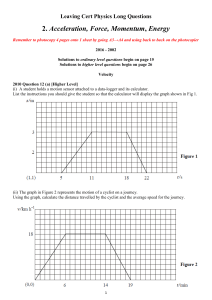
Parallel axis theorem
... motion. It appears in the relationships for the dynamics of rotational motion. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. For a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of perpendicular distance to the rotation axis, I = mr2. That poi ...
... motion. It appears in the relationships for the dynamics of rotational motion. The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. For a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of perpendicular distance to the rotation axis, I = mr2. That poi ...
PROBLEMS
... on the frequency of oscillation. 0.120 m. (a) Find the force constant of the spring. The fish is now 13.22. A harmonic oscillator has angular frequency w and ampli pulled down 5.00 cm and released. (b) What is the period of oscil tude A. (a) What are the magnitudes of the displacement and lation of ...
... on the frequency of oscillation. 0.120 m. (a) Find the force constant of the spring. The fish is now 13.22. A harmonic oscillator has angular frequency w and ampli pulled down 5.00 cm and released. (b) What is the period of oscil tude A. (a) What are the magnitudes of the displacement and lation of ...
Physics 231 Topic 7: Oscillations Wade Fisher October 5-10 2012
... Earth travels at constant speed throughout its orbit: x/t = S. It must traverse the circumference of the orbit: D = 2 π R Thus, the speed S = D/T = 2 π R / T We can also express this in terms of an angular frequency: The angular frequency = / t = 2 π / T = the speed at which the angle is ...
... Earth travels at constant speed throughout its orbit: x/t = S. It must traverse the circumference of the orbit: D = 2 π R Thus, the speed S = D/T = 2 π R / T We can also express this in terms of an angular frequency: The angular frequency = / t = 2 π / T = the speed at which the angle is ...
5 The Physics of Rotating Bodies
... piece of masking tape on the brass disk of the gyroscope (if none is already present) to assist in later measurement of the spin rate. Spin up the gyroscope and restore it to the crane and add the hanging weight. At this time the gyroscope should have no net forces and no net torques on it, and so s ...
... piece of masking tape on the brass disk of the gyroscope (if none is already present) to assist in later measurement of the spin rate. Spin up the gyroscope and restore it to the crane and add the hanging weight. At this time the gyroscope should have no net forces and no net torques on it, and so s ...
Momentum - ClassZone
... A moving object has a property that is called momentum (moh-MEHN-tuhm). Momentum is a measure of mass in motion; the momentum of an object is the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mas ...
... A moving object has a property that is called momentum (moh-MEHN-tuhm). Momentum is a measure of mass in motion; the momentum of an object is the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mas ...
Newton`s Law of motion 2
... Inelastic collision: stick together after collision (same velocity) RReem maarrkk:: PPhhyyssiiccaall m meeaanniinngg ooff ““m moom meennttuum m”” In our textbook (Physics Today) said: “the amount of MOTION of an object depends on both its mass and velocity”. I am not total agree with him. In my opin ...
... Inelastic collision: stick together after collision (same velocity) RReem maarrkk:: PPhhyyssiiccaall m meeaanniinngg ooff ““m moom meennttuum m”” In our textbook (Physics Today) said: “the amount of MOTION of an object depends on both its mass and velocity”. I am not total agree with him. In my opin ...
AP Physics 1 Investigation 5: Impulse and Momentum
... in terms of linear momentum and kinetic energy, how the outcome of a collision between two objects changes depending on whether the collision is elastic or inelastic. (Science Practices 6.4 and 7.2) 5.D. 2.4 The student is able to analyze data that verify conservation of momentum in collisions with ...
... in terms of linear momentum and kinetic energy, how the outcome of a collision between two objects changes depending on whether the collision is elastic or inelastic. (Science Practices 6.4 and 7.2) 5.D. 2.4 The student is able to analyze data that verify conservation of momentum in collisions with ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... velocity – change in position as a function of time acceleration – change in velocity as a function of time centripetal acceleration – Quotient of the velocity squared and the distance from the center of rotation momentum – product of mass and velocity change in momentum = Impulse = change in the pr ...
... velocity – change in position as a function of time acceleration – change in velocity as a function of time centripetal acceleration – Quotient of the velocity squared and the distance from the center of rotation momentum – product of mass and velocity change in momentum = Impulse = change in the pr ...
Practice Final
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...
... A) 0.654 mph B) 39.2 mph C) 780 mph D) 1430 mph E) 2350 mph 5) How fast will a motorcycle starting at rest go after 5 seconds if its acceleration is 3 m/s2? A) 7 m/s B) 12 m/s C) 15 m/s D) 18 m/s E) none of these 6) How long does it take for a sport car at rest to reach 27 m/s if its acceleration is ...