Newton`s Second Law
... If you know the acceleration of an object, you can determine the net force acting on it. ...
... If you know the acceleration of an object, you can determine the net force acting on it. ...
waves
... One object might change momentum, say losing some momentum, as another object changes momentum in an opposite manner, picking up the momentum that was lost by the first. ...
... One object might change momentum, say losing some momentum, as another object changes momentum in an opposite manner, picking up the momentum that was lost by the first. ...
FALL 2016 2 1 mV 2 1 mV − mgR − 1 t 5 4 3 2 + − = x x Fx
... a) The kinetic and potential energies both increase b) The kinetic and potential energies both decrease c) Both remain constant d) The kinetic energy remains constant but the potential energy does not e) The potential energy remains constant but the kinetic energy does not. ...
... a) The kinetic and potential energies both increase b) The kinetic and potential energies both decrease c) Both remain constant d) The kinetic energy remains constant but the potential energy does not e) The potential energy remains constant but the kinetic energy does not. ...
v mf - Yimg
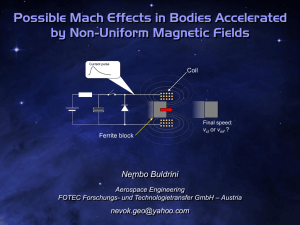
... The experimental method used so far to investigate the existence of Mach effects is to subject capacitors to charge and discharge cycles while they are accelerated. Two main types of devices have been build, which differs from the method used to accelerate the active mass (AM). In the piezo-actuator ...
... The experimental method used so far to investigate the existence of Mach effects is to subject capacitors to charge and discharge cycles while they are accelerated. Two main types of devices have been build, which differs from the method used to accelerate the active mass (AM). In the piezo-actuator ...
Lecture 18.Collision..
... Because the total momentum of the system is conserved, that means that p = 0 for the car and truck combined. Therefore, pcar must be equal and opposite to that of the truck (–ptruck) in order for the total momentum change to be zero. Note that this conclusion also follows from Newton’s Third Law. ...
... Because the total momentum of the system is conserved, that means that p = 0 for the car and truck combined. Therefore, pcar must be equal and opposite to that of the truck (–ptruck) in order for the total momentum change to be zero. Note that this conclusion also follows from Newton’s Third Law. ...
laws of motion
... In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is (a) Zero (b) 0.75 kg m s–1 (c) 1.5 kg m s–1 (d) 14 kg m s –1. ...
... In the previous problem (5.3), the magnitude of the momentum transferred during the hit is (a) Zero (b) 0.75 kg m s–1 (c) 1.5 kg m s–1 (d) 14 kg m s –1. ...
F r i c t i o n - Southgate Community School District
... Acceleration = change in velocity/change in time Symbol is a Units: m/s2 “meters per second squared” Vector Quantity: value has magnitude AND direction (N,S, up, down, etc.) • Ex. You accelerated at 4 m/s2 eastbound this morning on Eureka Rd • Can be positive or negative, accels = positive, decels = ...
... Acceleration = change in velocity/change in time Symbol is a Units: m/s2 “meters per second squared” Vector Quantity: value has magnitude AND direction (N,S, up, down, etc.) • Ex. You accelerated at 4 m/s2 eastbound this morning on Eureka Rd • Can be positive or negative, accels = positive, decels = ...




![06 Momentum WS 08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017198328_1-636fbdb6d6c62db5233df770cc2cf61d-300x300.png)