File
... simulation allows you to change the force at four different time intervals, but there are also four target circles. ...
... simulation allows you to change the force at four different time intervals, but there are also four target circles. ...
Symbols a = acceleration t = time d = distance s = speed Ѵ = velocity
... Definition: universal force of the attraction of the mass of an object Context: The motion of objects has long been a fascination, but it was the Italian physicist Galileo who first began a scientific inquiry into the behavior of moving objects. He studied the speed of falling bodies and determined ...
... Definition: universal force of the attraction of the mass of an object Context: The motion of objects has long been a fascination, but it was the Italian physicist Galileo who first began a scientific inquiry into the behavior of moving objects. He studied the speed of falling bodies and determined ...
Motion and Forces
... 4. You push a friend on a sled. Your friend and the sled together has a mass of 70 kg. If the net force on the sled is 35 N, what is it’s acceleration? ...
... 4. You push a friend on a sled. Your friend and the sled together has a mass of 70 kg. If the net force on the sled is 35 N, what is it’s acceleration? ...
Physics Review
... quantity. An object has mass regardless of whether gravity or any other force is acting upon it. Weight, on the other hand, changes depending on the influence of gravity. The relation between weight, W, and mass, m, can be written as the following. In this equation, g represents the acceleration due ...
... quantity. An object has mass regardless of whether gravity or any other force is acting upon it. Weight, on the other hand, changes depending on the influence of gravity. The relation between weight, W, and mass, m, can be written as the following. In this equation, g represents the acceleration due ...
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
... reaches a height of 0.12 meters with each jump, and that the average net force acting on the stick during contact with the ground is 330 N upward. The speed of the man and pogo stick when they strike the ground is1.53 m/s. (a) What is the time of contact with the ground between the jumps? Assume tha ...
... reaches a height of 0.12 meters with each jump, and that the average net force acting on the stick during contact with the ground is 330 N upward. The speed of the man and pogo stick when they strike the ground is1.53 m/s. (a) What is the time of contact with the ground between the jumps? Assume tha ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
... 9.4 Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis 2nd law for linear motion of crate ...
... 9.4 Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis 2nd law for linear motion of crate ...
Name
... What two things can you say about an object’s motion if the net forces on the object are zero? Which of these objects are accelerating? a. A ball that is falling. b. A rocket flying at a constant velocity through space. c. A car traveling down the road at a constant velocity. d. A book resting on a ...
... What two things can you say about an object’s motion if the net forces on the object are zero? Which of these objects are accelerating? a. A ball that is falling. b. A rocket flying at a constant velocity through space. c. A car traveling down the road at a constant velocity. d. A book resting on a ...
Chapter 5-6
... 1. Walker3 5.P.045. [544707] Show Details In a tennis serve, a 0.070 kg ball can be accelerated from rest to 35 m/s over a distance of 0.70 m. Find the magnitude for the average force exerted by the racket on the ball during the serve. 61.3 N [Answer] Newton’s second law: F = m a To find F, we need ...
... 1. Walker3 5.P.045. [544707] Show Details In a tennis serve, a 0.070 kg ball can be accelerated from rest to 35 m/s over a distance of 0.70 m. Find the magnitude for the average force exerted by the racket on the ball during the serve. 61.3 N [Answer] Newton’s second law: F = m a To find F, we need ...
Ph211_CH6_worksheet-f06
... 1) The motion of a 0.1 kg ball tossed vertically into the air was recorded using a motion detector. The initial velocity for the ball was 5 m/s (see Graph 1). Analysis of the velocity vs. time graph yielded the acceleration of the ball during 3 phases of the motion: upward, near the top and downward ...
... 1) The motion of a 0.1 kg ball tossed vertically into the air was recorded using a motion detector. The initial velocity for the ball was 5 m/s (see Graph 1). Analysis of the velocity vs. time graph yielded the acceleration of the ball during 3 phases of the motion: upward, near the top and downward ...
Physics 106b/196b – Problem Set 9 – Due Jan 19,... Version 3: January 18, 2007
... (b) Now, place the cone on a tilted plane as indicated in the figure. Using the results from above, write down the Lagrangian for the problem and find the equations of motion. Find the frequency of small oscillations about the equilibrium point θ = 0. ...
... (b) Now, place the cone on a tilted plane as indicated in the figure. Using the results from above, write down the Lagrangian for the problem and find the equations of motion. Find the frequency of small oscillations about the equilibrium point θ = 0. ...
Dynamics
... Friction depends on two things 1. The nature of the surfaces in contact, every different pair of surfaces will act differently with respect to friction. Every surface has a different amount of “grippeness”. This grippeness can be measured, and then for every pair of surfaces an associated value is ...
... Friction depends on two things 1. The nature of the surfaces in contact, every different pair of surfaces will act differently with respect to friction. Every surface has a different amount of “grippeness”. This grippeness can be measured, and then for every pair of surfaces an associated value is ...
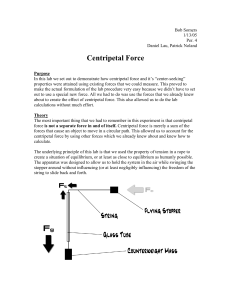
Centripetal Force
... There were a ton of possible sources of error in this lab, all of which were rather significant, lending towards the somewhat high percent difference numbers in the calculations. Just for these trials alone we can see a span of -8.30 % to +5.58 %, which is almost a 14 % span of difference, just in b ...
... There were a ton of possible sources of error in this lab, all of which were rather significant, lending towards the somewhat high percent difference numbers in the calculations. Just for these trials alone we can see a span of -8.30 % to +5.58 %, which is almost a 14 % span of difference, just in b ...
The Nature of Force and Motion Notes
... An object will not start moving unless a __________ acts on it. An object will not ________________ moving unless a force acts on it. An object will not change ________________ unless a force acts on it. An object will not change ________________unless a force acts on it. Newton’s first law of m ...
... An object will not start moving unless a __________ acts on it. An object will not ________________ moving unless a force acts on it. An object will not change ________________ unless a force acts on it. An object will not change ________________unless a force acts on it. Newton’s first law of m ...
Newton`s First Law WebPkt.
... push. Discuss how the process of pushing the bricks will allow Shirley to determine which of the two bricks is most massive. What difference will Shirley observe and how can this observation lead to the necessary conclusion? _________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... push. Discuss how the process of pushing the bricks will allow Shirley to determine which of the two bricks is most massive. What difference will Shirley observe and how can this observation lead to the necessary conclusion? _________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
Chapter 10 - UCF Physics
... can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
... can say that SF = 0 • An object in rotational equilibrium does not change its rotational speed. In this case we can say that there is no net torque or in other words that: ...
mechanics - Hertfordshire Grid for Learning
... If there is a second string attached to the mass underneath, its tension must be included in the vertical and horizontal equations. If the speed slows down then the tension in the bottom string reduces to a critical value ie zero. At this point the situation is the same as the diagram above. If the ...
... If there is a second string attached to the mass underneath, its tension must be included in the vertical and horizontal equations. If the speed slows down then the tension in the bottom string reduces to a critical value ie zero. At this point the situation is the same as the diagram above. If the ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
... • The force of gravity causes the speed of an object in a vertical circular path to vary. The object accelerates on the downward portion of its circular path and decelerates on the upward portion of the circular path. • At the top and bottom of a vertical circular path, the weight and the normal for ...
... • The force of gravity causes the speed of an object in a vertical circular path to vary. The object accelerates on the downward portion of its circular path and decelerates on the upward portion of the circular path. • At the top and bottom of a vertical circular path, the weight and the normal for ...
Year 11 Biomechanics
... ‘A body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it.’ In other words, a body will remain at rest or in motion unless acted upon by a force. In order to get a body moving, a force must overcome the body’s tendency to remain at rest or inertia. The amount o ...
... ‘A body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it.’ In other words, a body will remain at rest or in motion unless acted upon by a force. In order to get a body moving, a force must overcome the body’s tendency to remain at rest or inertia. The amount o ...
Torque, Atwood Machines, Angular M.
... When the force is applied, the bolt itself moves in or out of the page. In other words, the FORCE and DISPLACEMENT (lever arm) are in the X/Y plane, but the actual displacement of the BOLT is on the "Z“ axis. We therefore have what is called, CROSS PRODUCT. Counterclockwise rotation is considered t ...
... When the force is applied, the bolt itself moves in or out of the page. In other words, the FORCE and DISPLACEMENT (lever arm) are in the X/Y plane, but the actual displacement of the BOLT is on the "Z“ axis. We therefore have what is called, CROSS PRODUCT. Counterclockwise rotation is considered t ...
____The Force Table
... A vector quantity is one that has direction as well as amount or magnitude. Take force as an example. To be properly described, the direction of a force, as well as its magnitude, must be given. The same is true for velocity also. An object may be acted upon several forces at one time, each varying ...
... A vector quantity is one that has direction as well as amount or magnitude. Take force as an example. To be properly described, the direction of a force, as well as its magnitude, must be given. The same is true for velocity also. An object may be acted upon several forces at one time, each varying ...