Getting mathematical - Teaching Advanced Physics
... Equations of SHM These graphs can be represented by equations. For displacement: x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f) ...
... Equations of SHM These graphs can be represented by equations. For displacement: x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f) ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... push harder, is the change in motion smaller or larger? Do you think this is a direct or inverse relationship? 2. Assume that you have a bowling ball and a baseball, each suspended from a different rope. If you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will change its m ...
... push harder, is the change in motion smaller or larger? Do you think this is a direct or inverse relationship? 2. Assume that you have a bowling ball and a baseball, each suspended from a different rope. If you hit each of these balls with a full swing of a baseball bat, which ball will change its m ...
Chapter 1 Units and Problem Solving
... Answer: No. Gravity acts on the astronauts and the spacecraft, providing the necessary centripetal force for the orbit, so g is not zero and there is weight by definition (w=mg). The “floating” occurs because the spacecraft and astronauts are “falling” (“accelerating” toward Earth at the same rate). ...
... Answer: No. Gravity acts on the astronauts and the spacecraft, providing the necessary centripetal force for the orbit, so g is not zero and there is weight by definition (w=mg). The “floating” occurs because the spacecraft and astronauts are “falling” (“accelerating” toward Earth at the same rate). ...
Lecture 1: Rotation of Rigid Body
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
Welcome to Mrs. Sharp`s Classroom
... change in velocity (velocityf – velocityi) and its acceleration both have positive values. When an object moves in one dimension (along a straight line) in the positive direction, and its velocity increases over time (it speeds up), its acceleration is positive. Now imagine that same car slowing d ...
... change in velocity (velocityf – velocityi) and its acceleration both have positive values. When an object moves in one dimension (along a straight line) in the positive direction, and its velocity increases over time (it speeds up), its acceleration is positive. Now imagine that same car slowing d ...
Section 2.2
... The second law says that acceleration is proportional to force. If force is increased or decreased, acceleration will be increased or decreased by the same ...
... The second law says that acceleration is proportional to force. If force is increased or decreased, acceleration will be increased or decreased by the same ...
PPT
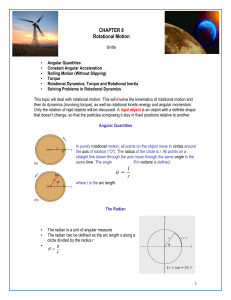
... When we say “moment of inertia” we’re not finished. We always have to say — or think — “moment of inertia about some particular axis of rotation”. ...
... When we say “moment of inertia” we’re not finished. We always have to say — or think — “moment of inertia about some particular axis of rotation”. ...
and the Normal Force
... abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
... abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
1 - Net Start Class
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
File
... What is a Force? A Push or Pull If an object is in motion and more force is applied to it, the object will begin moving faster. What is the RELATIONSHIP between force and mass? More mass requires more force Less mass requires less force If two objects have the same mass and a greater force i ...
... What is a Force? A Push or Pull If an object is in motion and more force is applied to it, the object will begin moving faster. What is the RELATIONSHIP between force and mass? More mass requires more force Less mass requires less force If two objects have the same mass and a greater force i ...
Part 1 - Go to webpages.dcu.ie
... thrust T of 180 kN. At the instant shown, its speed is 300 km/h and is increasing at a rate of 1.96 m/s2. Also is decreasing as the aircraft begins to level off. If the radius of curvature at this instant is 20 km, compute the lift L and the drag D. (Lift and drag are the aerodynamic forces normal ...
... thrust T of 180 kN. At the instant shown, its speed is 300 km/h and is increasing at a rate of 1.96 m/s2. Also is decreasing as the aircraft begins to level off. If the radius of curvature at this instant is 20 km, compute the lift L and the drag D. (Lift and drag are the aerodynamic forces normal ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion
... Identify all the forces acting directly on the object and the object exerting them. With the exception of gravity and certain other forces rarely used in first semester physics (magnetism, electric force), the two objects will be in direct contact. Do not include forces by an object acting through a ...
... Identify all the forces acting directly on the object and the object exerting them. With the exception of gravity and certain other forces rarely used in first semester physics (magnetism, electric force), the two objects will be in direct contact. Do not include forces by an object acting through a ...