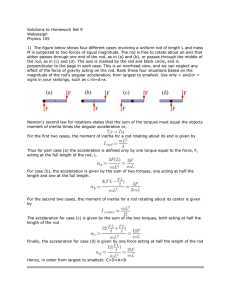
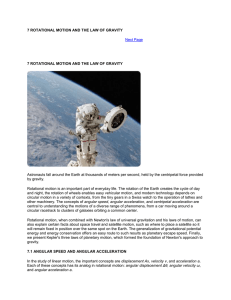
Rotational Kinematics (Part I from chapter 10)
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
Document
... 14- Calculate the acceleration from each slope using equations of motion. 15- Find the real value of the carts acceleration using Newton’s second law which states that the force is proportional to the acceleration. F=ma where F could be found from the mass causing the motion of the cart. 16- Find th ...
... 14- Calculate the acceleration from each slope using equations of motion. 15- Find the real value of the carts acceleration using Newton’s second law which states that the force is proportional to the acceleration. F=ma where F could be found from the mass causing the motion of the cart. 16- Find th ...
141S13-NotesCh8a-June13
... The role of torque in rotational motion is analogous to the role of force in translational motion. Any non-zero net torque will result in an angular acceleration, just as any non-zero net force results in a linear acceleration. Examples 8.2 and 8.3 of the text (pp. 270-272) discuss the concept of to ...
... The role of torque in rotational motion is analogous to the role of force in translational motion. Any non-zero net torque will result in an angular acceleration, just as any non-zero net force results in a linear acceleration. Examples 8.2 and 8.3 of the text (pp. 270-272) discuss the concept of to ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 06.
... • A curve that is banked changes the direction of the normal force. • The normal force, which is perpendicular to the surface of the road, can provide the force required for circular motion. • In this way, you can round the curve even when there is no friction ……. but only if you drive with exactly ...
... • A curve that is banked changes the direction of the normal force. • The normal force, which is perpendicular to the surface of the road, can provide the force required for circular motion. • In this way, you can round the curve even when there is no friction ……. but only if you drive with exactly ...
S - Nuffield Foundation
... They can also be used to find the position, velocity or acceleration of a particle at a specified time. Think about What can you say about the direction of a, at, and at2? What about u and ut? ...
... They can also be used to find the position, velocity or acceleration of a particle at a specified time. Think about What can you say about the direction of a, at, and at2? What about u and ut? ...
conceptual physics ch.4
... Ans. Since there are no unbalance forces acting on the planets, Newton’s fist law of motion tells us that they would travel in a straight line at constant speed. All the planets, including the Earth, would stop revolving around the Sun, and we would not continue to live happily ever after. Extra: A ...
... Ans. Since there are no unbalance forces acting on the planets, Newton’s fist law of motion tells us that they would travel in a straight line at constant speed. All the planets, including the Earth, would stop revolving around the Sun, and we would not continue to live happily ever after. Extra: A ...
Ch. 4 Newton`s Second Law of Motion p.65 Review Questions
... Ans. Since there are no unbalance forces acting on the planets, Newton’s fist law of motion tells us that they would travel in a straight line at constant speed. All the planets, including the Earth, would stop revolving around the Sun, and we would not continue to live happily ever after. Extra: A ...
... Ans. Since there are no unbalance forces acting on the planets, Newton’s fist law of motion tells us that they would travel in a straight line at constant speed. All the planets, including the Earth, would stop revolving around the Sun, and we would not continue to live happily ever after. Extra: A ...
Physics1
... defined as the ratio of the change in the angular speed to the time interval t : ...
... defined as the ratio of the change in the angular speed to the time interval t : ...
textbook_week_3
... To derive Equation 7.13, consider Figure 7.7a. An object is first at point with velocity i at time ti and then at point with velocity f at a later time tf. We assume i and f differ only in direction; their magnitudes are the same (vi = vf = v). To calculate the acceleration, we begin with Equation ...
... To derive Equation 7.13, consider Figure 7.7a. An object is first at point with velocity i at time ti and then at point with velocity f at a later time tf. We assume i and f differ only in direction; their magnitudes are the same (vi = vf = v). To calculate the acceleration, we begin with Equation ...
Book 2
... rest and is made to move. A force is clearly needed. For example, we need to give a chair a push to start it moving on the floor. When we start a car, the force is the friction from the road surface. This force is forward because the wheels begin to spin in a direction such that the tires tend to sl ...
... rest and is made to move. A force is clearly needed. For example, we need to give a chair a push to start it moving on the floor. When we start a car, the force is the friction from the road surface. This force is forward because the wheels begin to spin in a direction such that the tires tend to sl ...
L3 ROTATIONAL MOTION
... Use your slowest object for these calculations: • Calculate the cylinders final speed, v, using v = 2d/t, which is the final speed of the cylinder. • Calculate its final linear kinetic energy, Ek(linear) • Calculate the initial gravitational potential energy, Ep(grav) • Hence find the final rotatio ...
... Use your slowest object for these calculations: • Calculate the cylinders final speed, v, using v = 2d/t, which is the final speed of the cylinder. • Calculate its final linear kinetic energy, Ek(linear) • Calculate the initial gravitational potential energy, Ep(grav) • Hence find the final rotatio ...
10 Circular Motion
... • A point on the outer edge of the turntable travels a greater distance in one rotation than a point near the center. • The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • The speed of something moving along a circular path can be called tangential spe ...
... • A point on the outer edge of the turntable travels a greater distance in one rotation than a point near the center. • The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of a rotating object than it is closer to the axis. • The speed of something moving along a circular path can be called tangential spe ...