AP Physics C IB
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
Force And Work
... a greater acceleration? • We can see that there is an inverse relationship between the mass and acceleration. The greater the mass is for a certain force, the smaller will be its acceleration • Formula Fnet = ma where Fnet => force (N, Newtons) m => mass (kg) a => acceleration (m/s2) • The unit of f ...
... a greater acceleration? • We can see that there is an inverse relationship between the mass and acceleration. The greater the mass is for a certain force, the smaller will be its acceleration • Formula Fnet = ma where Fnet => force (N, Newtons) m => mass (kg) a => acceleration (m/s2) • The unit of f ...
Day 3
... • Hot summer day. Swimmers jump from a bridge into the river below. They hit the water 1.5 s after they stepped off the bridge. ? How high was the bridge ? ? How fast were the swimmers moving when the hit the water ? ? What would be swimmers’ drop time be if the bridge were twice as high ? ...
... • Hot summer day. Swimmers jump from a bridge into the river below. They hit the water 1.5 s after they stepped off the bridge. ? How high was the bridge ? ? How fast were the swimmers moving when the hit the water ? ? What would be swimmers’ drop time be if the bridge were twice as high ? ...
TAKE OUT SWING EXAMPLE IF DOING PIG LAB
... Newton reasoned that if you fired a projectile fast enough horizontally, it would continually fall from its straight-line path but never hit the earth…”falling around” or orbiting the earth. ...
... Newton reasoned that if you fired a projectile fast enough horizontally, it would continually fall from its straight-line path but never hit the earth…”falling around” or orbiting the earth. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion Notes
... a. The forces on the wall and the ice skater are equal in size and opposite in direction. Although there are two objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward forc ...
... a. The forces on the wall and the ice skater are equal in size and opposite in direction. Although there are two objects involved, each object exerts one force and experiences one force. The wall does not move because it has a lot of inertia. b. When the fuel burns, the engine exerts a downward forc ...
8th 2014 midterm
... continues at the same average speed for another 4 hours, how far will it have traveled from its starting point? Show your work. 55) Suppose that the average speed your dog can run is 2 m/s. Remember, average speed = total distance/total time. How much time will it take your dog to run 120 m? 56) Cal ...
... continues at the same average speed for another 4 hours, how far will it have traveled from its starting point? Show your work. 55) Suppose that the average speed your dog can run is 2 m/s. Remember, average speed = total distance/total time. How much time will it take your dog to run 120 m? 56) Cal ...
small - UNSW
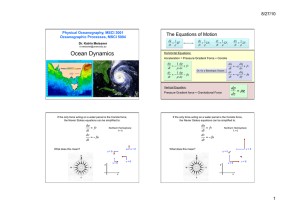
... Most of the motion in the ocean can be understood in terms of Newton’s Law that the acceleration of a parcel of water (how fast its velocity changes with time – du/dt) is related to the sum of forces acting on that parcel of water. We can split the forces, velocities and accelerations into south-nor ...
... Most of the motion in the ocean can be understood in terms of Newton’s Law that the acceleration of a parcel of water (how fast its velocity changes with time – du/dt) is related to the sum of forces acting on that parcel of water. We can split the forces, velocities and accelerations into south-nor ...
Motion, Forces &Machines PowerPoint presentation
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
... the rocket or how fast it went? • Both of those questions can be related to motion , forces and mechanics. ...
Dynamics Exam Extra Credit
... b) What is the net force when the object encounters 15 N of air resistance? c) What is the force of air resistance the object encounters if it is accelerating at a rate of 3.8 m/s 2 downward? d) What is the force of air resistance if the object has reached terminal velocity? 9. A boy applies a 12N h ...
... b) What is the net force when the object encounters 15 N of air resistance? c) What is the force of air resistance the object encounters if it is accelerating at a rate of 3.8 m/s 2 downward? d) What is the force of air resistance if the object has reached terminal velocity? 9. A boy applies a 12N h ...
true or false questions
... If you slide a hockey puck across a frictionless ice rink, there must be a horizontal force on the puck to keep it in motion. Excluding the force due to air pressure, there is only one force acting on a book lying at rest on a tabletop. If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the for ...
... If you slide a hockey puck across a frictionless ice rink, there must be a horizontal force on the puck to keep it in motion. Excluding the force due to air pressure, there is only one force acting on a book lying at rest on a tabletop. If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the for ...
05. RotationalReg
... 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. 2. A line from the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in a given period of time. 3. The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of its average distance from the sun. (T2 ~ r3) (can be derived for circula ...
... 1. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. 2. A line from the sun to a planet sweeps out equal areas in a given period of time. 3. The square of the orbital period of a planet is proportional to the cube of its average distance from the sun. (T2 ~ r3) (can be derived for circula ...
Types of Force
... that cause the motion. It is therefore important to understand the different types of forces which commonly occur in mechanics. The purpose of this leaflet is to explain these types. What is a force? A force is an influence on a system or object which, acting alone, will cause the motion of the syst ...
... that cause the motion. It is therefore important to understand the different types of forces which commonly occur in mechanics. The purpose of this leaflet is to explain these types. What is a force? A force is an influence on a system or object which, acting alone, will cause the motion of the syst ...