Phys 111 CE1 2013 Fall
... First, write your name and section number on both the Scantron card and this exam sheet. Use the formula sheet (last exam booklet page) and no other materials. Budget your time. There are 18 multiple choice problems. For most, if not all, of the multiple choice problems, it will be difficult to arri ...
... First, write your name and section number on both the Scantron card and this exam sheet. Use the formula sheet (last exam booklet page) and no other materials. Budget your time. There are 18 multiple choice problems. For most, if not all, of the multiple choice problems, it will be difficult to arri ...
Uniform Circular Motion
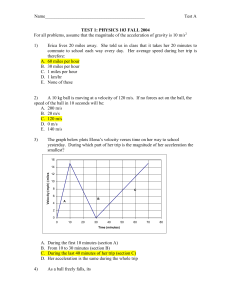
... • A 1.5 kg cart moves in a circular path of 1.3 meter radius at a constant speed of 2.0 m/s. – Determine the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. – Determine the magnitude of the centripetal force. – Determine the period. ...
... • A 1.5 kg cart moves in a circular path of 1.3 meter radius at a constant speed of 2.0 m/s. – Determine the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration. – Determine the magnitude of the centripetal force. – Determine the period. ...
1 PY105 Uniform and Vertical Circular Motions
... Two identical coins are placed on a flat turntable that is initially at rest. One coin is closer to the center than the other disk is. There is some friction between the coins and the turntable. We start spinning the turntable, steadily increasing the speed. Which coin starts sliding on the ...
... Two identical coins are placed on a flat turntable that is initially at rest. One coin is closer to the center than the other disk is. There is some friction between the coins and the turntable. We start spinning the turntable, steadily increasing the speed. Which coin starts sliding on the ...
Goal #2 – Motion and Forces
... If the net force on the object is zero, then all the forces are balanced, and the object will not change its motion. (3rd Law) When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first object. (Action-reaction) As an object falls freely, if w ...
... If the net force on the object is zero, then all the forces are balanced, and the object will not change its motion. (3rd Law) When one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first object. (Action-reaction) As an object falls freely, if w ...
01 - Edmodo
... a. It is described in Newton’s first law of motion. b. It is a property of motion. c. It is measured by weight. d. all of the above _____ 3. Two forces act on an object. The magnitude of the net force acting on the object a. equals the sum of the magnitudes of the two forces. b. equals the differenc ...
... a. It is described in Newton’s first law of motion. b. It is a property of motion. c. It is measured by weight. d. all of the above _____ 3. Two forces act on an object. The magnitude of the net force acting on the object a. equals the sum of the magnitudes of the two forces. b. equals the differenc ...
Chapter 2 Review WS Name ______Answer Key Date ______
... when an unbalanced force acts upon it -Both deal with forces. ...
... when an unbalanced force acts upon it -Both deal with forces. ...
Chapter 4: Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion The first two laws deal with a single object and the net forces applied to it - but not what is applying the force(s) The third law deals with how two objects interact with each other Whenever one object exerts a force on ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion The first two laws deal with a single object and the net forces applied to it - but not what is applying the force(s) The third law deals with how two objects interact with each other Whenever one object exerts a force on ...
Two Dimensional Motion 2
... that when added to a group of forces, produces Equilibrium. The Equilibrant (-R) is equal and opposite to the Resultant Force (R). ...
... that when added to a group of forces, produces Equilibrium. The Equilibrant (-R) is equal and opposite to the Resultant Force (R). ...
speed
... The second law states that unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes mor ...
... The second law states that unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes mor ...
Causes of circular motion
... The scaffold weighs 200.0 N and is 3.00 m long. What is the tension in each rope when the window washer stands 1.00 m from one end? ...
... The scaffold weighs 200.0 N and is 3.00 m long. What is the tension in each rope when the window washer stands 1.00 m from one end? ...
PreAP_Physics_Spring_Semester_Practice_Final
... 11. A flight attendant pulls a 65.0 N flight bag a distance of 100.0 m along a level airport floor at a constant speed. A 36.0 N force is exerted on the bag at an angle of 45.0 ...
... 11. A flight attendant pulls a 65.0 N flight bag a distance of 100.0 m along a level airport floor at a constant speed. A 36.0 N force is exerted on the bag at an angle of 45.0 ...
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... 2) A cannonball is positioned at the edge of a cliff 80 m high. If the cannon is positioned at an angle of 45 degrees above the ground and the initial velocity of the cannonball is 125 m/s, how far from the base of the cliff will the cannonball land? A. 80 m B. 120 m C. 483 m D. 354 m E. Cannot be d ...
... 2) A cannonball is positioned at the edge of a cliff 80 m high. If the cannon is positioned at an angle of 45 degrees above the ground and the initial velocity of the cannonball is 125 m/s, how far from the base of the cliff will the cannonball land? A. 80 m B. 120 m C. 483 m D. 354 m E. Cannot be d ...
AP Physics IB
... Problem solving strategies • Draw a free body diagram. • Is the object in equilibrium (at rest or constant velocity)or is it accelerating? If in equilibrium: the sum of the upward forces = the sum of the downward forces and the sum of the forces to the right = the sum of the forces to the left. If ...
... Problem solving strategies • Draw a free body diagram. • Is the object in equilibrium (at rest or constant velocity)or is it accelerating? If in equilibrium: the sum of the upward forces = the sum of the downward forces and the sum of the forces to the right = the sum of the forces to the left. If ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... We’ve been learning kinematics; describing motion without understanding what the cause of the motion is. Now we are going to learn dynamics!! FORCE is what cause an object to move. Can someone tell me The above statement is not entirely correct. Why? what FORCE is? Because when an object is moving w ...
... We’ve been learning kinematics; describing motion without understanding what the cause of the motion is. Now we are going to learn dynamics!! FORCE is what cause an object to move. Can someone tell me The above statement is not entirely correct. Why? what FORCE is? Because when an object is moving w ...
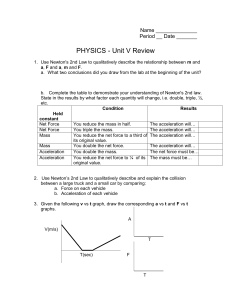
Unit V review
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
newton`s laws of motion
... 1) Newton’s second law is a “law of nature”-- experimentally proven, not the result of an analytical proof. 2) Mass (property of an object) is a measure of the resistance to a change in velocity of the object. 3) Weight (a force) depends on the local gravitational field. Calculating the weight of an ...
... 1) Newton’s second law is a “law of nature”-- experimentally proven, not the result of an analytical proof. 2) Mass (property of an object) is a measure of the resistance to a change in velocity of the object. 3) Weight (a force) depends on the local gravitational field. Calculating the weight of an ...