Chapter_6_AP_Packet
... A particle moves in a circle in such a way that the x- and y- coordinates of its motion are given in meters as functions of time t in seconds by: X = 5 cos (3t) Y = 5 sin (3t) 1) What is the period of revolution of the particle? a) 1/3 sec b) 3 sec c) 2/3 sec ...
... A particle moves in a circle in such a way that the x- and y- coordinates of its motion are given in meters as functions of time t in seconds by: X = 5 cos (3t) Y = 5 sin (3t) 1) What is the period of revolution of the particle? a) 1/3 sec b) 3 sec c) 2/3 sec ...
Newton`s Laws Review
... Newton’s Laws Review Newton’s 1st 1. What is Newton’s 1st law? An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion. Objects do this because of their inertia. 2. Describe what inertia is. Inertia is the resistance of any object to a change in its state of motion (can be moving or ...
... Newton’s Laws Review Newton’s 1st 1. What is Newton’s 1st law? An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion. Objects do this because of their inertia. 2. Describe what inertia is. Inertia is the resistance of any object to a change in its state of motion (can be moving or ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... Sir Isaac Newton • Lived from 1642-1727 in England. • He was a dedicated physicist and mathematician, and is considered to be one of the most brilliant scientists of all time. • He is most famous for his three laws of motion and his universal law of gravitation, but did much more. ...
... Sir Isaac Newton • Lived from 1642-1727 in England. • He was a dedicated physicist and mathematician, and is considered to be one of the most brilliant scientists of all time. • He is most famous for his three laws of motion and his universal law of gravitation, but did much more. ...
Document
... • Force is a push or pull on an object In a particular direction…forces are used everyday to change the motion of objects; Forces cause changes in speed and direction (velocity) and acceleration • Contact forces are those that push or pull an object by touching it • Action-at-a-distance forces are a ...
... • Force is a push or pull on an object In a particular direction…forces are used everyday to change the motion of objects; Forces cause changes in speed and direction (velocity) and acceleration • Contact forces are those that push or pull an object by touching it • Action-at-a-distance forces are a ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant Acceleration
... state of rest or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force." For an object to change: speed, direction or shape there must be a resultant unbalanced force. No unbalanced force : things stay as they are ...
... state of rest or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force." For an object to change: speed, direction or shape there must be a resultant unbalanced force. No unbalanced force : things stay as they are ...
Name
... 3. You are standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is ascending at a constant rate. The reading on the scale would be ______________? a) equal to your mass b) equal to your weight c) greater than your mass d) greater than your weight e) less than your weight 4. You are standing on a scale i ...
... 3. You are standing on a scale in an elevator. The elevator is ascending at a constant rate. The reading on the scale would be ______________? a) equal to your mass b) equal to your weight c) greater than your mass d) greater than your weight e) less than your weight 4. You are standing on a scale i ...
Standard Physics Mid
... 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. ...
... 4. A train is traveling northward with a velocity of 100 km/hr. A child on this train walks southward with a velocity of 5 km/hr. The child’s velocity with respect to he ground is (a) 95 km/hr N (b) 95 km/hr S (c) 105 km/hr N (d) 105 km/hr S 5. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff. ...
Physics - Allen ISD
... c. it doesn’t matter which planet you are on. 6. Which has more mass, a kilogram of feathers or a kilogram of iron? a. the feathers b. the iron c. same masses 7. According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, the acceleration of an object ______ its mass. a. is directly proportional to b. is inversely ...
... c. it doesn’t matter which planet you are on. 6. Which has more mass, a kilogram of feathers or a kilogram of iron? a. the feathers b. the iron c. same masses 7. According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, the acceleration of an object ______ its mass. a. is directly proportional to b. is inversely ...
AP Physics IB
... blocks slides across a frictionless floor. a) What is the horizontal acceleration of the box? b) What is the normal force on the box? ...
... blocks slides across a frictionless floor. a) What is the horizontal acceleration of the box? b) What is the normal force on the box? ...
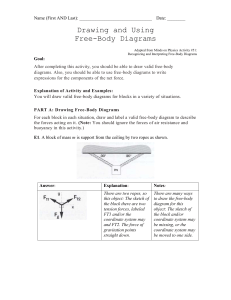
Drawing and Using
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
... First of all, you should make sure that the directions of all your forces are accurately drawn. This will help you find the components of the forces, which will help you find the net force, and ultimately, the acceleration of the object. Then, if the sizes of the force vectors are also drawn accurat ...
Force and Motion
... -When two surfaces touch you get friction; friction causes an object to slow down and eventually stop -Friction occurs in the opposite direction you are trying to move an object -Mass (the amount of matter that makes up an object) -Determines how much force is needed to change an object’s motion -Le ...
... -When two surfaces touch you get friction; friction causes an object to slow down and eventually stop -Friction occurs in the opposite direction you are trying to move an object -Mass (the amount of matter that makes up an object) -Determines how much force is needed to change an object’s motion -Le ...
4-1_to_4-3 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... • There are several ways to describe an inertial frame. Here are a few descriptions: – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference with constant velocity. – An inertial frame of reference is a non-accelerating frame of reference. – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference in ...
... • There are several ways to describe an inertial frame. Here are a few descriptions: – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference with constant velocity. – An inertial frame of reference is a non-accelerating frame of reference. – An inertial frame of reference is a frame of reference in ...
centripetal force
... Second Law says that if an object is accelerating, there must be a net force on it. For an object moving in a circle, this is called the centripetal force. centripetal force points toward the center of the circle. ...
... Second Law says that if an object is accelerating, there must be a net force on it. For an object moving in a circle, this is called the centripetal force. centripetal force points toward the center of the circle. ...
Reveiw PPT 2_Graphs and Equilibrium Forces
... • A net Force (Fnet) is the sum of all the forces on an object (direction determines + or -) ...
... • A net Force (Fnet) is the sum of all the forces on an object (direction determines + or -) ...