Forces in Mechanical Systems
... Line of action – line along the applied force that extends in both directions. ...
... Line of action – line along the applied force that extends in both directions. ...
Chapter 4: Forces and the Laws of Motion Name Use Chapter 4 in
... 48) Explain how the cross sectional area of an object and the speed of an object affect the force of air resistance on an object if it is falling in air. As both the speed increases and the cross sectional area increases, the object moves through more air molecules and increases the air resistance. ...
... 48) Explain how the cross sectional area of an object and the speed of an object affect the force of air resistance on an object if it is falling in air. As both the speed increases and the cross sectional area increases, the object moves through more air molecules and increases the air resistance. ...
PhysicsMidtermREV
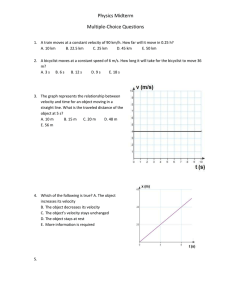
... 8. Starting from the origin, a car travels 4 km east and then 7 km west. What is the net displacement of the car from the initial point? A. 3 km, west B. 3 km, east C. 4 km, east D. 7 km, west E. 7 km east 9. An object moves with a constant acceleration of 6 m/s2. Which of the following statements i ...
... 8. Starting from the origin, a car travels 4 km east and then 7 km west. What is the net displacement of the car from the initial point? A. 3 km, west B. 3 km, east C. 4 km, east D. 7 km, west E. 7 km east 9. An object moves with a constant acceleration of 6 m/s2. Which of the following statements i ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... As stated, Newton’s first law of motion governs the properties of inertia that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion remain in motion in the absence of an external force. However, it is observed that an object that tends to move comes to rest at a certain point as well as objects t ...
... As stated, Newton’s first law of motion governs the properties of inertia that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion remain in motion in the absence of an external force. However, it is observed that an object that tends to move comes to rest at a certain point as well as objects t ...
Name of Model - BHS Physics Class
... a. On the diagram, draw a path that the ball might follow after the hit. Explain your reasoning for the path you drew. Prior to the hit, there was no net force acting on the ball, so it moved with constant velocity to the right (east). The applied force acted on the ball toward the top of the page ( ...
... a. On the diagram, draw a path that the ball might follow after the hit. Explain your reasoning for the path you drew. Prior to the hit, there was no net force acting on the ball, so it moved with constant velocity to the right (east). The applied force acted on the ball toward the top of the page ( ...
Circular Motion
... It seems to go all the way back to the Mesopotamians over 6,000 years ago, who liked to work with the number 60, partly probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And f ...
... It seems to go all the way back to the Mesopotamians over 6,000 years ago, who liked to work with the number 60, partly probably because it could be divided up so many different ways, i.e. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 24 and 30. This got picked up by the Babylonians and passed on to the Egyptians. And f ...
Force and Newtons Laws
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
... • What is the force required to push a 25kg girl in a 100kg wagon with an acceleration of 3m/s2? ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion What it says: An object at rest will
... This means that a force of 1 N will cause a 1 kg mass to accelerate at a speed of 1 m/sec2 Unless force is applied to an object, that object will never move. This force must be in sufficient quantity or strength to overcome the mass of the object that is being moved. Nothing moves on its own. The fo ...
... This means that a force of 1 N will cause a 1 kg mass to accelerate at a speed of 1 m/sec2 Unless force is applied to an object, that object will never move. This force must be in sufficient quantity or strength to overcome the mass of the object that is being moved. Nothing moves on its own. The fo ...
Viscous force
... • Law 1: Bodies in motion remain in motion with the same velocity, and bodies at rest remain at rest, unless acted upon by unbalanced forces. • Law 2: The rate of change of momentum of a body with time is equal to the vector sum of all forces acting upon the body and is the same direction. • Law 3: ...
... • Law 1: Bodies in motion remain in motion with the same velocity, and bodies at rest remain at rest, unless acted upon by unbalanced forces. • Law 2: The rate of change of momentum of a body with time is equal to the vector sum of all forces acting upon the body and is the same direction. • Law 3: ...