Presentation - ScienceScene
... Tension - Tension force is the force exerted by a string, spring, beam or other object which is being stretched compressed. The electric forces among the molecules give rise to the force. ...
... Tension - Tension force is the force exerted by a string, spring, beam or other object which is being stretched compressed. The electric forces among the molecules give rise to the force. ...
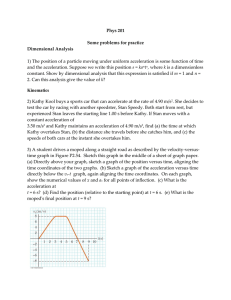
POSITION-TIME GRAPHS WORKSHEET #2
... 1. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its greatest speed? 2. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its least (nonzero) speed? 3. During which time interval(s) (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart at rest? 4. During w ...
... 1. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its greatest speed? 2. During which time interval (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart traveling at its least (nonzero) speed? 3. During which time interval(s) (AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG) was the cart at rest? 4. During w ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - pams
... What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When ...
... What happens if you are standing on a skateboard or a slippery floor and push against a wall? You slide in the opposite direction (away from the wall), because you pushed on the wall but the wall pushed back on you with equal and opposite force. Why does it hurt so much when you stub your toe? When ...
Forces and Motion
... – Strength • Length represents strength or magnitude – The scale with more apples, greater mass, has a longer arrow. The arrow is pointed downward due to mass is below the balance pulling downwards. ...
... – Strength • Length represents strength or magnitude – The scale with more apples, greater mass, has a longer arrow. The arrow is pointed downward due to mass is below the balance pulling downwards. ...
Chapter 10-Forces - Solon City Schools
... (weight=mass x acceleration due to gravity) Which object will hit the ground first if dropped from the same height at the same time, a crumpled sheet of paper or an uncrumpled sheet of paper? (crumpled sheet of paper) What is the formula for calculating force? (force = mass x acceleration) ...
... (weight=mass x acceleration due to gravity) Which object will hit the ground first if dropped from the same height at the same time, a crumpled sheet of paper or an uncrumpled sheet of paper? (crumpled sheet of paper) What is the formula for calculating force? (force = mass x acceleration) ...
Chapter 3
... 2. Now you slow down and go from 40 miles per hour to 35 to 30 each second. What is the acceleration? What is this type of acceleration often called? a. -5 mph/sec b. deceleration ...
... 2. Now you slow down and go from 40 miles per hour to 35 to 30 each second. What is the acceleration? What is this type of acceleration often called? a. -5 mph/sec b. deceleration ...
Force
... A person weighs a fish on a spring scale attached to the ceiling of an elevator, as shown in Figure 4.14. Show that if the elevator accelerates, the spring scale reads an apparent weight different from the fish’s true weight. ...
... A person weighs a fish on a spring scale attached to the ceiling of an elevator, as shown in Figure 4.14. Show that if the elevator accelerates, the spring scale reads an apparent weight different from the fish’s true weight. ...
Circular motion and rotation Uniform circular motion
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
12.2 Newton`s 1st and 2nd Laws of Motion
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
... continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a nonzero net force ...
12 Outline Small
... Gravity: is a force that acts between any 2 masses. o Gravity is an attractive force that pulls object together. o Earth’s gravitational force exerts a force of attraction on every other object that is near Earth. o The force of gravity does not require objects to be in contact for it to act on them ...
... Gravity: is a force that acts between any 2 masses. o Gravity is an attractive force that pulls object together. o Earth’s gravitational force exerts a force of attraction on every other object that is near Earth. o The force of gravity does not require objects to be in contact for it to act on them ...
Newton`s 1st Law
... Then they accelerate around the bend (leaning sideways) : changing direction but not speed. ...
... Then they accelerate around the bend (leaning sideways) : changing direction but not speed. ...
Physics Toolkit - Effingham County Schools
... An apparent force that seems to cause deflection to an object in a horizontal motion when the observer is in a rotating frame of reference is known as the Coriolis “force” ...
... An apparent force that seems to cause deflection to an object in a horizontal motion when the observer is in a rotating frame of reference is known as the Coriolis “force” ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review_9
... (C) The force of motion is proportional to the speed of the puck. (D) The force to the right must be equal to the force from friction. (26) ___________ True or False: A force is required to keep objects moving. (27) Using Newton’s 1st Law, explain why it is important for students to wear seat belts. ...
... (C) The force of motion is proportional to the speed of the puck. (D) The force to the right must be equal to the force from friction. (26) ___________ True or False: A force is required to keep objects moving. (27) Using Newton’s 1st Law, explain why it is important for students to wear seat belts. ...
TWGHs. Kap Yan Directors` College
... D. The coin falls faster than the feather, but both take a shorter time than if they were falling from the same height on Earth. 31. A bullet of mass 0.02 kg travelling horizontally at 100 m s-1 is stopped by 0.1 m of concrete. What is the resistive force on the bullet by the concrete? A. 2 N ...
... D. The coin falls faster than the feather, but both take a shorter time than if they were falling from the same height on Earth. 31. A bullet of mass 0.02 kg travelling horizontally at 100 m s-1 is stopped by 0.1 m of concrete. What is the resistive force on the bullet by the concrete? A. 2 N ...
Newton"s 1st
... The force exerted by air is a ____________ force. (small, balanced, or negative) The equation F= _____ is a mathematical model of Newton’s 2nd Law. ...
... The force exerted by air is a ____________ force. (small, balanced, or negative) The equation F= _____ is a mathematical model of Newton’s 2nd Law. ...