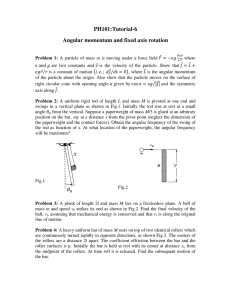
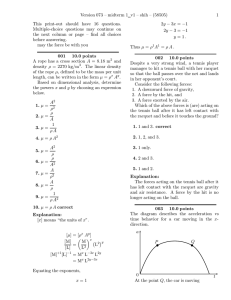
Chapter 5 – Work and Energy
... Why Isn’t Work Done On The Bucket of Water? • Work is only done when COMPONENTS of a force are parallel to a displacement. • Since Kim exerts an upward force on the bucket of water, which is perpendicular to the displacement, there is no work done on the bucket of water. ...
... Why Isn’t Work Done On The Bucket of Water? • Work is only done when COMPONENTS of a force are parallel to a displacement. • Since Kim exerts an upward force on the bucket of water, which is perpendicular to the displacement, there is no work done on the bucket of water. ...
Inertial and Non-Inertial Frames of Reference - K
... Your new weight in this accelerated, non-inertial reference frame is called the ‘apparent weight’. On a roller coaster, when you are in free fall down a large hill, the acceleration of the ride is equal to g (9.81 m/s2) and the normal force between you and your seat becomes zero. This makes your app ...
... Your new weight in this accelerated, non-inertial reference frame is called the ‘apparent weight’. On a roller coaster, when you are in free fall down a large hill, the acceleration of the ride is equal to g (9.81 m/s2) and the normal force between you and your seat becomes zero. This makes your app ...
Unit 4 vocabulary - Riverdale Middle School
... 2. position – an object’s location compared to other things. 3. motion – a change in an object’s position compared to a fixed object. 4. apparent motion – when things appear to an observer to be moving but are not actually changing position. 5. speed – how fast an object’s position changes with time ...
... 2. position – an object’s location compared to other things. 3. motion – a change in an object’s position compared to a fixed object. 4. apparent motion – when things appear to an observer to be moving but are not actually changing position. 5. speed – how fast an object’s position changes with time ...
Section 1
... from an object, then the motion of that object would not change. This was Newton's first law of motion. In our study of motion, we need to start clarifying the concept of mass. In effect, we will find that mass is a measure of how hard it is to get an object moving. Applying a force to a light obje ...
... from an object, then the motion of that object would not change. This was Newton's first law of motion. In our study of motion, we need to start clarifying the concept of mass. In effect, we will find that mass is a measure of how hard it is to get an object moving. Applying a force to a light obje ...
Ball launcher
... The final speed is different from the average speed. After all, it was going more slowly at first, so it didn’t go as far in a small time interval than it did later. It turns out that for this system the average speed actually is the average of the initial speed and the final speed average speed = ½ ...
... The final speed is different from the average speed. After all, it was going more slowly at first, so it didn’t go as far in a small time interval than it did later. It turns out that for this system the average speed actually is the average of the initial speed and the final speed average speed = ½ ...
torque
... a linear system, we can show the relationship between torque and angular momentum Angular momentum is defined as L = I ω ...
... a linear system, we can show the relationship between torque and angular momentum Angular momentum is defined as L = I ω ...
Chapter 10.3-10.5
... • What does Newton’s 1st Law of motion state? – An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Why is Newton’s 1st law of motion sometimes called the law of intertia? – Inertia is a measure of an object’s tendency to r ...
... • What does Newton’s 1st Law of motion state? – An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • Why is Newton’s 1st law of motion sometimes called the law of intertia? – Inertia is a measure of an object’s tendency to r ...
Physics 130 - UND: University of North Dakota
... vSYS = 875/mTotal = 875/135 = 6.5m/s pSYS,i = 0 in the same direction as pSYS,f pSYS,f = 875kg m/s May seem odd that v is less now but = Arctan (450/750) = 31° above there is more mass in the system! horizontal, to the right ...
... vSYS = 875/mTotal = 875/135 = 6.5m/s pSYS,i = 0 in the same direction as pSYS,f pSYS,f = 875kg m/s May seem odd that v is less now but = Arctan (450/750) = 31° above there is more mass in the system! horizontal, to the right ...
integrated-science-5th-edition-tillery-solution
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. The change of momentum from hitting the ground, or impulse, is the product of the applied force and time that the force is applied. The product of the force and the time is always the same, bu ...
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. The change of momentum from hitting the ground, or impulse, is the product of the applied force and time that the force is applied. The product of the force and the time is always the same, bu ...
Ph201_CH4_worksheet
... 11. Consider the same pulley system in Problem 10. In this case, there is friction (static and/or kinetic) between M2 and the horizontal surface. a. Draw free body diagrams for each mass. ...
... 11. Consider the same pulley system in Problem 10. In this case, there is friction (static and/or kinetic) between M2 and the horizontal surface. a. Draw free body diagrams for each mass. ...
Force (or free-body) diagrams
... •We know F = m * a, where “a” is acceleration. •If a = 0, then F = m * 0 = 0. •When F = 0, the object is not accelerating. •We we can then say that the forces acting on the object cancel each other out and it is in a state of ...
... •We know F = m * a, where “a” is acceleration. •If a = 0, then F = m * 0 = 0. •When F = 0, the object is not accelerating. •We we can then say that the forces acting on the object cancel each other out and it is in a state of ...
South Pasadena A.P. Physics Name Chapter 8 Rotational Motion
... 9. Find the moment of inertia (I) of two 5 kg bowling balls joined by a 1-meter long rod of negligible mass when rotated about the center of the rod. Compare this to the moment of inertia of the object when rotated about one of the masses. (The moment of inertia of each ball will be considered as mr ...
... 9. Find the moment of inertia (I) of two 5 kg bowling balls joined by a 1-meter long rod of negligible mass when rotated about the center of the rod. Compare this to the moment of inertia of the object when rotated about one of the masses. (The moment of inertia of each ball will be considered as mr ...