Question #3, p
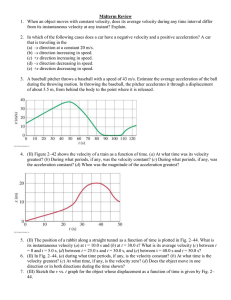
... falling rock. However, this time we will consider the position (x). Consistently with the choice of the reference frame, (the vertical components of) the rock's initial position (x0) and velocity (v0) are zero, While the (vertical component of the) acceleration is 3.71m/s2. Thus from the equation fo ...
... falling rock. However, this time we will consider the position (x). Consistently with the choice of the reference frame, (the vertical components of) the rock's initial position (x0) and velocity (v0) are zero, While the (vertical component of the) acceleration is 3.71m/s2. Thus from the equation fo ...
P221_2009_week4
... The coefficient of static friction between a 12.5 kg block and table is 0.34 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.22. The block is at rest on the table when a horizontal force of 30 N is applied to it. A). What is the force of friction at this point in time? B). The block is now set in motio ...
... The coefficient of static friction between a 12.5 kg block and table is 0.34 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.22. The block is at rest on the table when a horizontal force of 30 N is applied to it. A). What is the force of friction at this point in time? B). The block is now set in motio ...
here
... For the following problems, solve for any unknowns. Show all work and box all answers. Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a ...
... For the following problems, solve for any unknowns. Show all work and box all answers. Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a ...
AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the speed of the bullet. ...
... A bullet (mass m1 = 0.0100 kg) is fired with a speed v01. Just after the bullet collides with it, the block (now containing the bullet) has a speed vf and then swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the speed of the bullet. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
... Recall Newton’s Second Law Thus, in uniform circular motion there must be a net force to produce the centripetal acceleration. The centripetal force is the name given to the net force required to keep an object moving on a circular path. The direction of the centripetal force always points to ...
Section 6.2 Circular Motion Acceleration
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Circular Motion - juan
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
... Rather than labeling this axis x or y, call it c, for centripetal acceleration. The other axis is in the direction of the velocity, tangent to the circle. It is labeled tang for tangential. Centripetal force is just another name for the net force in the centripetal direction. It is the sum of all th ...
Document
... Gravitational force is proportional to mass F = ma gives an object’s responding acceleration Divide both sides of the equation by “m” a = F/m Both numerator and denominator are proportional to “m”, if force is gravity • SO....acceleration is the same, regardless of the mass • We’ll return to this po ...
... Gravitational force is proportional to mass F = ma gives an object’s responding acceleration Divide both sides of the equation by “m” a = F/m Both numerator and denominator are proportional to “m”, if force is gravity • SO....acceleration is the same, regardless of the mass • We’ll return to this po ...