notes - MADD Physical Science
... a) The mass of an object is dependent upon the value of the acceleration of gravity. b) The standard metric unit of mass is the kilogram. c) Mass depends on how much stuff is present in an object. d) The mass of an object is variable and dependent upon its location. e) An object would have more mass ...
... a) The mass of an object is dependent upon the value of the acceleration of gravity. b) The standard metric unit of mass is the kilogram. c) Mass depends on how much stuff is present in an object. d) The mass of an object is variable and dependent upon its location. e) An object would have more mass ...
Worked solutions Chapter 2: Collisions and
... The horizontal displacement of the ball at t = 1.0 s = 11.3 × 1.0 = 11.3 m, while the vertical displacement at t = 1.0 s using x = ut + 0.5at2 = 11.3 × 1.0 – 0.5 × 9.8 × 1.02 = 6.41 m The resultant displacement after 1.0 s = [(11.3)2 + (6.41)2] ½ = 13.0 m The angle of the displacement from the hor ...
... The horizontal displacement of the ball at t = 1.0 s = 11.3 × 1.0 = 11.3 m, while the vertical displacement at t = 1.0 s using x = ut + 0.5at2 = 11.3 × 1.0 – 0.5 × 9.8 × 1.02 = 6.41 m The resultant displacement after 1.0 s = [(11.3)2 + (6.41)2] ½ = 13.0 m The angle of the displacement from the hor ...
Unit 2
... force and the head of the arrow pointing in the direction of the force. Using such arrows, the resulting force (net force) and direction can be ...
... force and the head of the arrow pointing in the direction of the force. Using such arrows, the resulting force (net force) and direction can be ...
Chapter 4 Powerpoint
... beams. A significant hazard for the driver is that the load may slide forward, crushing the cab, if the truck stops suddenly in an accident or even in braking. Assume, for example, that a 10 000-kg load sits on the flat bed of a 20 000-kg truck moving at 12.0 m/s. Assume the load is not tied down to ...
... beams. A significant hazard for the driver is that the load may slide forward, crushing the cab, if the truck stops suddenly in an accident or even in braking. Assume, for example, that a 10 000-kg load sits on the flat bed of a 20 000-kg truck moving at 12.0 m/s. Assume the load is not tied down to ...
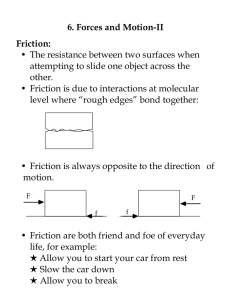
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
008 Newton`s Second Law Explored
... • For most practical situations in biomechanics, velocity has more meaning than acceleration. • Further, practitioners such as coaches are usually interested in the velocity after a net force has acted. ...
... • For most practical situations in biomechanics, velocity has more meaning than acceleration. • Further, practitioners such as coaches are usually interested in the velocity after a net force has acted. ...
Static Equilibrium - University of Colorado Boulder
... Torque is always computed with respect to some axis or pivot point. If the object is not moving at all, we can pick any point as the axis. We can always pretend that the object is about to rotate about that point. Let us choose the right end of the bar as our pivot point. Then the tension force does ...
... Torque is always computed with respect to some axis or pivot point. If the object is not moving at all, we can pick any point as the axis. We can always pretend that the object is about to rotate about that point. Let us choose the right end of the bar as our pivot point. Then the tension force does ...
Newton`s Second Law
... harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? What does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter ...
... harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. Is the cart’s velocity related to the force you apply? Or does the force just change the velocity? What does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter ...
A Question about Vectors
... A general method for solving circular motion problems Follow the method for force problems! ...
... A general method for solving circular motion problems Follow the method for force problems! ...
Physical-Science-8th-Edition-Bill-Tillery-Solution
... 3. A single force never occurs alone; a force is always produced by the interaction of two or more objects. There is always a matched and opposite force that occurs at the same time, and Newton's second law of motion is a statement of this relationship. ...
... 3. A single force never occurs alone; a force is always produced by the interaction of two or more objects. There is always a matched and opposite force that occurs at the same time, and Newton's second law of motion is a statement of this relationship. ...
Ch 2 Motion - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. Bending your knees as you hit the ground extends the stopping time. This is important since the change of momentum is equal to the impulse, which is force times the time. A greater time theref ...
... unbalanced force occurs on a single object as the result of one or more interactions with other objects. 7. Bending your knees as you hit the ground extends the stopping time. This is important since the change of momentum is equal to the impulse, which is force times the time. A greater time theref ...
Document
... object's speed! But which part of F really causes the object to increase in speed? It is |F|Cos θ ! Because it is parallel to the displacement d In fact if you apply the dot product, you get (|F|Cos θ)d, which happens to be defined as "WORK" (check your equation sheet!) ...
... object's speed! But which part of F really causes the object to increase in speed? It is |F|Cos θ ! Because it is parallel to the displacement d In fact if you apply the dot product, you get (|F|Cos θ)d, which happens to be defined as "WORK" (check your equation sheet!) ...