Chapter 6 and 7 Review
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
Physics 211 Lab #2 – Forces
... why objects move. Our own human experience tells us that forces have something to do with causing motion. Aristotle developed a theory of motion based completely upon human experience and reason. He stated simply that all motion, even constant velocity, was caused by the existence of forces. Objects ...
... why objects move. Our own human experience tells us that forces have something to do with causing motion. Aristotle developed a theory of motion based completely upon human experience and reason. He stated simply that all motion, even constant velocity, was caused by the existence of forces. Objects ...
Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration: The Legacy of Sir Isaac Newton
... larger the force, the more an object will accelerate, in the direction of the applied force. • Mass is inertia, i.e., reluctance to accelerate, so for the same force, more massive objects experience smaller acceleration than less massive ones. ...
... larger the force, the more an object will accelerate, in the direction of the applied force. • Mass is inertia, i.e., reluctance to accelerate, so for the same force, more massive objects experience smaller acceleration than less massive ones. ...
Lesson 8
... motion a circle whose radius is the radius of curvature of the trajectory at that particular point. In the case of straight line motion, the radius of curvature is infinity so their is no centripetal acceleration. In the case of circular motion, the radius of curvature is constant! ...
... motion a circle whose radius is the radius of curvature of the trajectory at that particular point. In the case of straight line motion, the radius of curvature is infinity so their is no centripetal acceleration. In the case of circular motion, the radius of curvature is constant! ...
b. 4 m/s 2
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
... a. The car and the tree mutually exert equal forces in the same direction. b. The car and the tree mutually exert different forces in the same direction. c. The car and the tree mutually exert equal and opposite forces on each other. d. The car and the tree mutually exert different and opposite forc ...
Mechanics 105 chapter 10
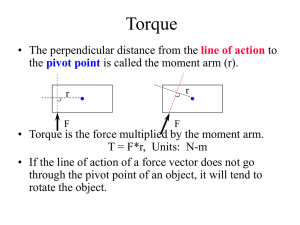
... formed by the two vectors forming the product, in a direction given using the right hand rule. ...
... formed by the two vectors forming the product, in a direction given using the right hand rule. ...
Chapter 12 Notes
... Gravitational force is an attractive force that acts between two masses. The bigger the masses and the closer they are, the more the attraction force. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object. ...
... Gravitational force is an attractive force that acts between two masses. The bigger the masses and the closer they are, the more the attraction force. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object. ...
Velocity and Acceleration presentation
... Perform a “sanity check”. Does your answer make sense? ...
... Perform a “sanity check”. Does your answer make sense? ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... than is necessary for students to know on the proficiency test, but is not as detailed as what would be discussed in a physics class. I made no effort to make this super-fancy because I just don’t know how. Sorry!! There are links to the RPDP site at the end of this presentation. There are also a fe ...
... than is necessary for students to know on the proficiency test, but is not as detailed as what would be discussed in a physics class. I made no effort to make this super-fancy because I just don’t know how. Sorry!! There are links to the RPDP site at the end of this presentation. There are also a fe ...
Review Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 57. At the very end of the race, a runner accelerates at 0.3 m/s2 for 12 s to attain a speed of 6.4 m/s. Determine the initial velocity of the runner. {3 m/s} 58. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1.6 m/s2 [down]. If a baseball was thrown with an initial velocity of 4.5 m/s [up], what ...
... 57. At the very end of the race, a runner accelerates at 0.3 m/s2 for 12 s to attain a speed of 6.4 m/s. Determine the initial velocity of the runner. {3 m/s} 58. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is 1.6 m/s2 [down]. If a baseball was thrown with an initial velocity of 4.5 m/s [up], what ...
chapter - 5 laws of motion
... acceleration is towards the centre and its magnitude is v2/R, where v is the speed. For vertical direction, acceleration = 0. Resolving the force in vertical and horizontal directions and applying Newton’s laws, we have ...
... acceleration is towards the centre and its magnitude is v2/R, where v is the speed. For vertical direction, acceleration = 0. Resolving the force in vertical and horizontal directions and applying Newton’s laws, we have ...
Lesson03 Newtons Second Law Worksheets
... net force acting on the car during this time? (2.31x103N south) A 1.08x103kg car uniformly accelerates from rest for 12.0s. During this time the car travels 132m north. What is the net force acting on the car? (1.98x103N north) A net force of 6.6N east acts on a 9.0kg object. If this object accelera ...
... net force acting on the car during this time? (2.31x103N south) A 1.08x103kg car uniformly accelerates from rest for 12.0s. During this time the car travels 132m north. What is the net force acting on the car? (1.98x103N north) A net force of 6.6N east acts on a 9.0kg object. If this object accelera ...
Unit 5 Powerpoint
... Forces always occur in pairs A single isolated force cannot exist The action force is equal in magnitude to the reaction force and opposite in direction ...
... Forces always occur in pairs A single isolated force cannot exist The action force is equal in magnitude to the reaction force and opposite in direction ...
PreAP Physics Extra Practice Unit 1: Uniform Motion and Graphing
... crawls the entire 1000 m distance at a speed of 0.2 m/s while the hare runs the first 200 m at 2 m/s. The hare then stops to take a nap for 1.3 hours and awakens to finish the last 800 m with an average speed of 3 m/s. Who wins the race and by how much time? Draw a graph of position vs. time for the ...
... crawls the entire 1000 m distance at a speed of 0.2 m/s while the hare runs the first 200 m at 2 m/s. The hare then stops to take a nap for 1.3 hours and awakens to finish the last 800 m with an average speed of 3 m/s. Who wins the race and by how much time? Draw a graph of position vs. time for the ...
CP7e: Ch. 7 Problems
... speed of 18.0 rad/s and rolls in a straight line without slipping. If the rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 1.90 rad/s2, how far does the coin roll before coming to rest? ...
... speed of 18.0 rad/s and rolls in a straight line without slipping. If the rotation slows with an angular acceleration of magnitude 1.90 rad/s2, how far does the coin roll before coming to rest? ...