PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... When a rigid body is suspended by a wire to a fixed support at the top and the body is twisted through some small angle q, the twisted wire can exert a restoring torque on the body that is proportional to the angular displacement. ...
... When a rigid body is suspended by a wire to a fixed support at the top and the body is twisted through some small angle q, the twisted wire can exert a restoring torque on the body that is proportional to the angular displacement. ...
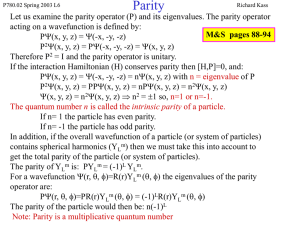
Lecture 6, Parity and Charge Conjugation
... b) We know (from experiment) that the p is captured by the d in an s-wave state. Thus the total angular momentum of the initial state is just that of the d (J=1). c) The isospin of the nn system is 1 since d is an isosinglet and the p- has I=|1,-1> note: a |1,-1> is symmetric under the interchange o ...
... b) We know (from experiment) that the p is captured by the d in an s-wave state. Thus the total angular momentum of the initial state is just that of the d (J=1). c) The isospin of the nn system is 1 since d is an isosinglet and the p- has I=|1,-1> note: a |1,-1> is symmetric under the interchange o ...
Syllabys for BSc(Major):
... Paper Name: Quantum Mechanics Total Marks: 60 Total No. of Lectures: 40 Unit I: Introduction (No. of Lectures: 14) (Marks: 22) Inadequacies of classical physics, Planck’s quantum hypothesis , wave particle duality , photoelectric effect, Compton effect, de-Broglie hypothesis , phase and group veloci ...
... Paper Name: Quantum Mechanics Total Marks: 60 Total No. of Lectures: 40 Unit I: Introduction (No. of Lectures: 14) (Marks: 22) Inadequacies of classical physics, Planck’s quantum hypothesis , wave particle duality , photoelectric effect, Compton effect, de-Broglie hypothesis , phase and group veloci ...
Balanced Forces Worksheet 1
... 4. Suppose that we could somehow succeed in making the floor completely frictionless. Just as in problems #1-3 the box sits at rest for a while, then is pushed so that it starts to move, and then loses contact with the person’s hands and moves across the now frictionless floor. a. Draw a qualitative ...
... 4. Suppose that we could somehow succeed in making the floor completely frictionless. Just as in problems #1-3 the box sits at rest for a while, then is pushed so that it starts to move, and then loses contact with the person’s hands and moves across the now frictionless floor. a. Draw a qualitative ...
Chapters 1–5 Schedule of Crisis Centre
... • Elastic collision: the total kinetic energy after collision is equal ! to the total before collision. • Inelastic collision: the total kinetic energy is not conserved. If ! objects stick together after collision, the collision is “perfectly ! inelastic” – no bounce of one object from the other. Ex ...
... • Elastic collision: the total kinetic energy after collision is equal ! to the total before collision. • Inelastic collision: the total kinetic energy is not conserved. If ! objects stick together after collision, the collision is “perfectly ! inelastic” – no bounce of one object from the other. Ex ...
UNIT 1 – FORCE AND MOTION (SEPUP Force and
... point, freezing/melting point, density [with density calculations], solubility, viscosity, and conductivity). PS-3.2 Infer the practical applications of organic and inorganic substances on the basis of their chemical and physical properties. PS-3.3 Illustrate the difference between a molecule and an ...
... point, freezing/melting point, density [with density calculations], solubility, viscosity, and conductivity). PS-3.2 Infer the practical applications of organic and inorganic substances on the basis of their chemical and physical properties. PS-3.3 Illustrate the difference between a molecule and an ...
The p orbital paradox
... states we may renunciate to the concept of trajectories in quantum mechanics [Messiah, 1999]. I dislike that kind of reply by two motives. The first reason is methodological. I think one would address the mistake being done during the early assumption, i.e. that a single electron finds in some point ...
... states we may renunciate to the concept of trajectories in quantum mechanics [Messiah, 1999]. I dislike that kind of reply by two motives. The first reason is methodological. I think one would address the mistake being done during the early assumption, i.e. that a single electron finds in some point ...
Group 2 Bhadouria, Arjun Singh Glave, Theodore Dean Han, Zhe
... u(x, t) = vertical displacement of the string from the x axis at position x and time t θ(x, t) = angle between the string and a horizontal line at position x and time t T(x, t) = tension in the string at position x and time t ρ(x) = mass density of the string at position x http://www.math.ubc.ca/~fe ...
... u(x, t) = vertical displacement of the string from the x axis at position x and time t θ(x, t) = angle between the string and a horizontal line at position x and time t T(x, t) = tension in the string at position x and time t ρ(x) = mass density of the string at position x http://www.math.ubc.ca/~fe ...
Physical Science Unit Analysis
... Compare various physical and chemical properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids such as state of matter at a given temperature, density, melting point, boiling point, luster, conductivity, ductility, malleability, color, reactivity, etc. Calculate the density of different substances using t ...
... Compare various physical and chemical properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids such as state of matter at a given temperature, density, melting point, boiling point, luster, conductivity, ductility, malleability, color, reactivity, etc. Calculate the density of different substances using t ...