Exam sample
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
... 7. “No two electrons in the same atom may have the same values for all four quantum numbers” is a statement of: a. Hund’s Rule. b. deBroglie’s Hypothesis. c. the Pauli Exclusion Principle. d. the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. 8. All s orbitals are: a. shaped like four-leaf clovers. b. dumbbell- ...
Lecture 27: Quantum Mechanics (Continued)
... illustrate the basic ideas of quantum mechanics. More realistic cases involve potentials that are not infinite but finite. The walls in the particle in box problem denote an extremely hard or impenetrable barrier. If we reduce the magnitude of potential, i.e. make the walls bit softer, the strict re ...
... illustrate the basic ideas of quantum mechanics. More realistic cases involve potentials that are not infinite but finite. The walls in the particle in box problem denote an extremely hard or impenetrable barrier. If we reduce the magnitude of potential, i.e. make the walls bit softer, the strict re ...
Atom and Light
... Particle Properties of Light • Max Planck (1900) – Blackbody Radiation – Electromagnetic energy (radiation) is emitted in discrete, particlelike packet. ...
... Particle Properties of Light • Max Planck (1900) – Blackbody Radiation – Electromagnetic energy (radiation) is emitted in discrete, particlelike packet. ...
Group and phase velocity
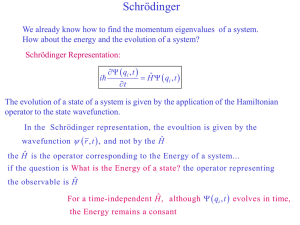
... We already know how to find the momentum eigenvalues of a system. How about the energy and the evolution of a system? Schrödinger Representation: ...
... We already know how to find the momentum eigenvalues of a system. How about the energy and the evolution of a system? Schrödinger Representation: ...
Document
... Occurs in problems with cylindrical symmetry involving electric fields, vibrations, heat conduction, optical diffraction. Spherical Bessel functions arise in problems with spherical symmetry. de Broglie’s concept of an atom… Legendre’s equation: ...
... Occurs in problems with cylindrical symmetry involving electric fields, vibrations, heat conduction, optical diffraction. Spherical Bessel functions arise in problems with spherical symmetry. de Broglie’s concept of an atom… Legendre’s equation: ...
Quantum Theory and Molecular Energy
... The Born Interpretation introduces the major differences between the results of Classical and Quantum Mechanics. ...
... The Born Interpretation introduces the major differences between the results of Classical and Quantum Mechanics. ...
$doc.title
... i.e. emits radiation with a continuous spectrum. e.g Infrared imaging of people, planet etc. ...
... i.e. emits radiation with a continuous spectrum. e.g Infrared imaging of people, planet etc. ...
Atomic Structure
... Light is a wave…right? • Einstein’s interpretation of the photoelectric effect (1905) was that light is quantized in packets of set energy called photons. (He won the Nobel Prize for this.) • This meant that light had characteristics of particles! ...
... Light is a wave…right? • Einstein’s interpretation of the photoelectric effect (1905) was that light is quantized in packets of set energy called photons. (He won the Nobel Prize for this.) • This meant that light had characteristics of particles! ...
Practice Quiz
... A. Spontaneous emission emits photons in random directions at random times B. Stimulated emission emits photons in random directions and random times C. Both spontaneous emission and stimulated emission emit photons in random directions and random times D. Both spontaneous emission and stimulated em ...
... A. Spontaneous emission emits photons in random directions at random times B. Stimulated emission emits photons in random directions and random times C. Both spontaneous emission and stimulated emission emit photons in random directions and random times D. Both spontaneous emission and stimulated em ...
Chapter 6 review
... Do particles have wave characteristics? • If a photon has mass m=h/c while it is moving… • Then a particle moving at a velocity v has a wavelength using the equation m=h/v • Solve for and =h/mv • This is de Broglie’s equation. ...
... Do particles have wave characteristics? • If a photon has mass m=h/c while it is moving… • Then a particle moving at a velocity v has a wavelength using the equation m=h/v • Solve for and =h/mv • This is de Broglie’s equation. ...
Electronic structure and spectroscopy
... where A depends on the quality of the metal plate (called work function). Explanation was given again by Einstein using the quantization introduced by Planck: the light consist of tiny particles which can have energy of hν only. (Note that Planck opposed the use of his „uncompleted” theory!!) ...
... where A depends on the quality of the metal plate (called work function). Explanation was given again by Einstein using the quantization introduced by Planck: the light consist of tiny particles which can have energy of hν only. (Note that Planck opposed the use of his „uncompleted” theory!!) ...