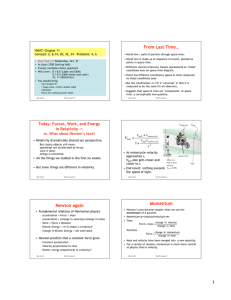
Questions – Impulse and Momentum
... Questions – Impulse and Momentum 1. A 6.00 N force acts on a 1.50 kg mass for 5.00 seconds. Find: a) The impulse which acted upon the mass. b) what change in momentum is produced? c) Calculate the final velocity of the object, if it was initially at rest. 2. For how many seconds would a force of 8.0 ...
... Questions – Impulse and Momentum 1. A 6.00 N force acts on a 1.50 kg mass for 5.00 seconds. Find: a) The impulse which acted upon the mass. b) what change in momentum is produced? c) Calculate the final velocity of the object, if it was initially at rest. 2. For how many seconds would a force of 8.0 ...
ppt
... consider one component of the wave equation and express the solution as a product of functions like (travelling wave case) ...
... consider one component of the wave equation and express the solution as a product of functions like (travelling wave case) ...
78AM-1
... 3. A shell bursts on contact with the ground and pieces fly off in all directions with speeds up to 30 m/s. A person is standing 40 m away. What is the time duration over which he can be hit by a piece? 4. A force given by F = 3t2 i + 5t j - (8t3 + 400) k N acts from t = 0 to t = 10 s. Determine the ...
... 3. A shell bursts on contact with the ground and pieces fly off in all directions with speeds up to 30 m/s. A person is standing 40 m away. What is the time duration over which he can be hit by a piece? 4. A force given by F = 3t2 i + 5t j - (8t3 + 400) k N acts from t = 0 to t = 10 s. Determine the ...
The fractional quantum Hall effect I
... response expression for the Hall conductance to the calculation of the Chern number of ground state wave function. The seminal experiment of Tsui et al. showed, however, that in a very clean sample, the Hall conductance develops a fractional plateau at one third of a quantum of conductance, see Fig ...
... response expression for the Hall conductance to the calculation of the Chern number of ground state wave function. The seminal experiment of Tsui et al. showed, however, that in a very clean sample, the Hall conductance develops a fractional plateau at one third of a quantum of conductance, see Fig ...
Document
... emits a flash of light toward the detector, the box recoils, because wave carries momentum. When the flash is received by the detector, the box will experience an equal and opposite impulse, and so the whole system will again come to rest. The CM of this isolated system seems not be fixed. Why? Cons ...
... emits a flash of light toward the detector, the box recoils, because wave carries momentum. When the flash is received by the detector, the box will experience an equal and opposite impulse, and so the whole system will again come to rest. The CM of this isolated system seems not be fixed. Why? Cons ...
SECTION B ( 48 marks )
... motion. By considering the collision of two objects, show that Newton’s third law can be derived from conservation of linear momentum. ( 5 marks ) c. For the following situations, briefly explain whether the total momentum is conserved and state the origin of the forces. i. The moon move in an orbit ...
... motion. By considering the collision of two objects, show that Newton’s third law can be derived from conservation of linear momentum. ( 5 marks ) c. For the following situations, briefly explain whether the total momentum is conserved and state the origin of the forces. i. The moon move in an orbit ...
PACING_GUIDE_HONORS_PHYSICS_10_12
... The Physics standards emphasize a complex understanding of experimentation, the analysis of data, and the use of reasoning and logic to evaluate evidence. The use of mathematics, including algebra and trigonometry, is important, but conceptual understanding of physical systems remains a primary conc ...
... The Physics standards emphasize a complex understanding of experimentation, the analysis of data, and the use of reasoning and logic to evaluate evidence. The use of mathematics, including algebra and trigonometry, is important, but conceptual understanding of physical systems remains a primary conc ...
CHAPTER 6: Quantum Mechanics II
... many measurements of a given quantity. The expectation value of x is denoted by
Any measurable quantity for which we can calculate the
expectation value is called a physical observable. The
expectation values of physical observables (for example,
position, linear momentum, angular momentum, and ...
... many measurements of a given quantity. The expectation value of x is denoted by
slides
... hits are centered (which are determined by the wave function trajectory) should themselves serve as the ``local beables of the theory. These are the mathematical counterparts in the theory to real events at definite places and times in the real world (as distinct from the many purely mathematical co ...
... hits are centered (which are determined by the wave function trajectory) should themselves serve as the ``local beables of the theory. These are the mathematical counterparts in the theory to real events at definite places and times in the real world (as distinct from the many purely mathematical co ...
Electron Corral
... above the threshold frequency causes electrons to leave the metal immediately; the greater the intensity of the incident radiation, the larger the flow of photoelectrons. The electromagnetic wave theory cannot explain all of these facts. According to the wave theory, it is the intensity of the radia ...
... above the threshold frequency causes electrons to leave the metal immediately; the greater the intensity of the incident radiation, the larger the flow of photoelectrons. The electromagnetic wave theory cannot explain all of these facts. According to the wave theory, it is the intensity of the radia ...
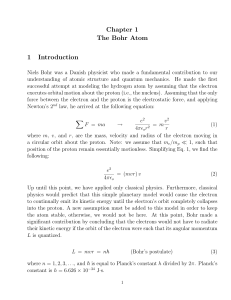
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... Up until this point, we have applied only classical physics. Furthermore, classical physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added t ...
... Up until this point, we have applied only classical physics. Furthermore, classical physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added t ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... gives a probability distribution Electron density map indicates the most probable distance from the nucleus Wave functions and probability maps do not describe How an electron arrived at its location Where an electron will go next When the electron will be in a particular location ...
... gives a probability distribution Electron density map indicates the most probable distance from the nucleus Wave functions and probability maps do not describe How an electron arrived at its location Where an electron will go next When the electron will be in a particular location ...