Chapter 6 | Thermochemistry
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
Coleman progress - Rutgers Physics
... and the crystal melts. Yet research into condensed matter over the past decade has revealed a new kind of phase transition that is driven, not by thermal motion, but by the quantum fluctuations associated with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. These quantum fluctuations are called ‘zero-point moti ...
... and the crystal melts. Yet research into condensed matter over the past decade has revealed a new kind of phase transition that is driven, not by thermal motion, but by the quantum fluctuations associated with Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. These quantum fluctuations are called ‘zero-point moti ...
Systems of particles
... simplifications in the equations and a greater level of understanding, but we have to be careful: the centre of mass may be accelerating (in fact, it must if Fe 6= 0), so the new axes may not be inertial. The main results of this section show that the motion of the system can be very conveniently de ...
... simplifications in the equations and a greater level of understanding, but we have to be careful: the centre of mass may be accelerating (in fact, it must if Fe 6= 0), so the new axes may not be inertial. The main results of this section show that the motion of the system can be very conveniently de ...
CHAPTER Work and Energy
... 35 ·· Force A does 5 J of work in 10 s. Force B does 3 J of work in 5 s. Which force delivers greater power? PA = (5/10) W = 0.5 W; PB = (3/5) W = 0.6 W; PB > PA. 36 · A 5-kg box is lifted by a force equal to the weight of the box. The box moves upward at a constant velocity of 2 m/s. (a) What is th ...
... 35 ·· Force A does 5 J of work in 10 s. Force B does 3 J of work in 5 s. Which force delivers greater power? PA = (5/10) W = 0.5 W; PB = (3/5) W = 0.6 W; PB > PA. 36 · A 5-kg box is lifted by a force equal to the weight of the box. The box moves upward at a constant velocity of 2 m/s. (a) What is th ...
circular motion
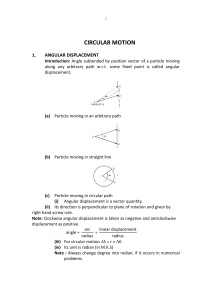
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
... A train is moving towards North. At one place it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that (A) the radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner rail (B) the radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater (C) the radius of curvature of inner rail will be grea ...
Meson spectroscopy - KVI - Center for Advanced Radiation
... - Quantum numbers that cannot be explained by the quark model. (JPC) - Formed by a q q pair plus one explicit gluon. - If kinematics and other conservation laws allow, the production cross section for hybrids, is expected to be the same as that for ordinary mesons. - Hybrid mesons and ordinary meson ...
... - Quantum numbers that cannot be explained by the quark model. (JPC) - Formed by a q q pair plus one explicit gluon. - If kinematics and other conservation laws allow, the production cross section for hybrids, is expected to be the same as that for ordinary mesons. - Hybrid mesons and ordinary meson ...
tc mani̇sa celal bayar university physics i laboratory manuals 2016
... a straight path in the direction of v ⃗ i . Therefore, the vertical distance 2 ⃗gt 2 through which the particle “falls” off the straight-line path is the same distance that an object dropped from rest would fall during the same time interval. Two-dimensional motion with constant acceleration can be ...
... a straight path in the direction of v ⃗ i . Therefore, the vertical distance 2 ⃗gt 2 through which the particle “falls” off the straight-line path is the same distance that an object dropped from rest would fall during the same time interval. Two-dimensional motion with constant acceleration can be ...
One-Dimensional Mass-Spring Chains Supporting Elastic Waves
... Mass-spring composite structures are introduced as metaphors for more complex phononic crystals with non-conventional topology. The elastic wave equation of motion of an intrinsic phononic structure composed of two coupled one-dimensional (1D) harmonic chains can be factored into a Dirac-like equati ...
... Mass-spring composite structures are introduced as metaphors for more complex phononic crystals with non-conventional topology. The elastic wave equation of motion of an intrinsic phononic structure composed of two coupled one-dimensional (1D) harmonic chains can be factored into a Dirac-like equati ...
Chapter 4 The Two Slit Experiment
... number of flashes in a region of size δx to give the fraction of flashes that occur in the range x to x + δx, as in the case of the bullets. As there, we will call the result P1 (x). Now do the same with slit 1 closed and slit 2 opened. The result is a distribution described by the curve P2 (x). The ...
... number of flashes in a region of size δx to give the fraction of flashes that occur in the range x to x + δx, as in the case of the bullets. As there, we will call the result P1 (x). Now do the same with slit 1 closed and slit 2 opened. The result is a distribution described by the curve P2 (x). The ...
Gravity as a fluid dynamic phenomenon in a superfluid
... This hypothesis starts from considering the physical vacuum as a super uid quantum medium, that we call super uid quantum space (SQS), close to the previous concepts of quantum vacuum, quantum foam, super uid vacuum etc. We usually believe that quantum vacuum is populated by an enormous amount of pa ...
... This hypothesis starts from considering the physical vacuum as a super uid quantum medium, that we call super uid quantum space (SQS), close to the previous concepts of quantum vacuum, quantum foam, super uid vacuum etc. We usually believe that quantum vacuum is populated by an enormous amount of pa ...