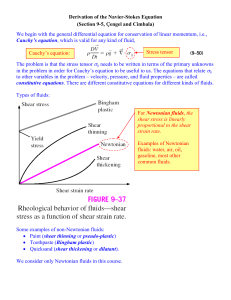
Control surface Control Volume
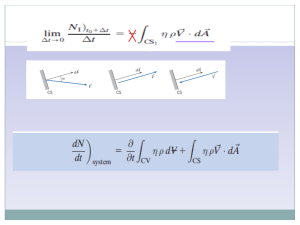
... EXP1)The balloon is being filled through section 1, where the area is A1, velocity is V1,and fluid density is ρ1. The average density within the balloon is ρb(t). Find an expression for the rate of change of system mass within the balloon at this instant. ...
... EXP1)The balloon is being filled through section 1, where the area is A1, velocity is V1,and fluid density is ρ1. The average density within the balloon is ρb(t). Find an expression for the rate of change of system mass within the balloon at this instant. ...
Water Movement
... • Viscosity: resistance of a liquid to change of form. • Inertia: resistance of an object (body) to a change in its state of motion. • These two forces together influences an organism’s ability to move in water and how water flows. • The ratio of inertial force to viscous force is Re. ...
... • Viscosity: resistance of a liquid to change of form. • Inertia: resistance of an object (body) to a change in its state of motion. • These two forces together influences an organism’s ability to move in water and how water flows. • The ratio of inertial force to viscous force is Re. ...
Electric Potential - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Bernoulli’s Equation: work and energy in fluids Conditions: steady flow, incompressible fluid. Look at energy balance along a streamline: Change in (kinetic energy/volume) + change in (potential energy/volume) = (net work by pressure)/volume then, or, ...
... Bernoulli’s Equation: work and energy in fluids Conditions: steady flow, incompressible fluid. Look at energy balance along a streamline: Change in (kinetic energy/volume) + change in (potential energy/volume) = (net work by pressure)/volume then, or, ...
Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio
... Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio of work done to the time interval required to do the work. You can also calculate power using the product of the prime mover and a rate. The equations for calculating power in mechanical, fluid, and electrical systems are listed ...
... Power is the rate of doing work (or transferring energy), or the ratio of work done to the time interval required to do the work. You can also calculate power using the product of the prime mover and a rate. The equations for calculating power in mechanical, fluid, and electrical systems are listed ...
Chapter 9
... piston of circular cross section having a radius of 5.00 cm. This pressure is transmitted by an incompressible liquid to a second piston of radius 15.0 cm. (a) what force must the compressed air exert in order to lift a car weighing 13,300 N? (b) What air pressure will produce this force? (c) Show t ...
... piston of circular cross section having a radius of 5.00 cm. This pressure is transmitted by an incompressible liquid to a second piston of radius 15.0 cm. (a) what force must the compressed air exert in order to lift a car weighing 13,300 N? (b) What air pressure will produce this force? (c) Show t ...
Fluids-powerpoint - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Matter is anything that has mass and volume The Particle Theory of Matter is a theory that describes matter. It explains the behaviour of solids, liquids and gasses. Copy the 6 postulates of the theory into your booklet from page 198 in your textbook. ...
... Matter is anything that has mass and volume The Particle Theory of Matter is a theory that describes matter. It explains the behaviour of solids, liquids and gasses. Copy the 6 postulates of the theory into your booklet from page 198 in your textbook. ...
Types of Flow
... particles get together and form a flowing stream. These particles, while moving, group themselves in a variety of ways, e.g., they move in a regular formation, just as disciplined soldiers do; or they may swirl, like the individuals, in a disorderly crowd. The type of flow of a liquid depends upon t ...
... particles get together and form a flowing stream. These particles, while moving, group themselves in a variety of ways, e.g., they move in a regular formation, just as disciplined soldiers do; or they may swirl, like the individuals, in a disorderly crowd. The type of flow of a liquid depends upon t ...
Problem 1. Water flows steadily from a large closed tank as shown in
... Solution. We have 6 variables and all 3 reference dimensions, so we choose 6-3=3 non-repeating variables and Pi-terms. Non-repeating variables: d, µ, ρ Repeating variables: σ, V, D I will choose F, T, L as few of my variables will look simpler in terms of force. Please recall, I have to choose d as ...
... Solution. We have 6 variables and all 3 reference dimensions, so we choose 6-3=3 non-repeating variables and Pi-terms. Non-repeating variables: d, µ, ρ Repeating variables: σ, V, D I will choose F, T, L as few of my variables will look simpler in terms of force. Please recall, I have to choose d as ...
A force is a push or a pull on an object in a direction. In mechanical
... an object feels when it is immersed in the fluid. In fluid systems, a pressure difference can cause fluid to move or change its motion. When electric charges are separated, each charge feels a force of attraction or repulsion because of the presence of the other charges. The space surrounding the el ...
... an object feels when it is immersed in the fluid. In fluid systems, a pressure difference can cause fluid to move or change its motion. When electric charges are separated, each charge feels a force of attraction or repulsion because of the presence of the other charges. The space surrounding the el ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.