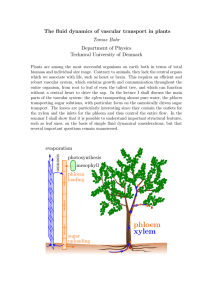
The actual equation that is provided you is where would be some
... a) You should understand that the difference in the pressure on the upper and lower surfaces of an object immersed in a liquid results in an upward force on the object. We went through this when the Physics Kahuna derived the buoyancy equation for you. Because the pressure depends on depth, the pres ...
... a) You should understand that the difference in the pressure on the upper and lower surfaces of an object immersed in a liquid results in an upward force on the object. We went through this when the Physics Kahuna derived the buoyancy equation for you. Because the pressure depends on depth, the pres ...
29006_L14
... the weight of the fluid which it displaces. Anything less dense than water will float in water water weighs 10N/liter each liter of displaced water provides 10 N of buoyant force –helium balloons: (density of He = 0.18 kg/m3) –hot air balloons: the density of hot air is lower than the density o ...
... the weight of the fluid which it displaces. Anything less dense than water will float in water water weighs 10N/liter each liter of displaced water provides 10 N of buoyant force –helium balloons: (density of He = 0.18 kg/m3) –hot air balloons: the density of hot air is lower than the density o ...
Lecture-21-11
... The same force applied over a smaller area results in greater pressure – think of poking a balloon with your finger and then with a needle. Pressure is a useful concept for discussing fluids, because fluids distribute their force over an area ...
... The same force applied over a smaller area results in greater pressure – think of poking a balloon with your finger and then with a needle. Pressure is a useful concept for discussing fluids, because fluids distribute their force over an area ...
Middle Ear Fluid and Tubes
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
... Normally, the middle ear is filled with fluid. In young children, the eustachian tube can become swollen, usually as a result of a cold or allergies. The swollen eustachian tube prevents air from being equalized behind the eardrum and may lead to fluid building up behind the eardrum. Fluid alone usu ...
Fluid Power
... Force means a total push or pull. It is push or pull exerted against the total area of a particular surface and is expressed in pounds or grams. Pressure means the amount of push or pull (force) applied to each unit area of the surface. Pressure may be exerted in one direction, in several direct ...
... Force means a total push or pull. It is push or pull exerted against the total area of a particular surface and is expressed in pounds or grams. Pressure means the amount of push or pull (force) applied to each unit area of the surface. Pressure may be exerted in one direction, in several direct ...
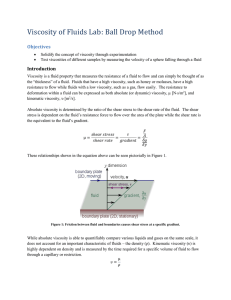
Viscosity of Fluids Lab (Ball Drop Method)
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
... the “thickness” of a fluid. Fluids that have a high viscosity, such as honey or molasses, have a high resistance to flow while fluids with a low viscosity, such as a gas, flow easily. The resistance to deformation within a fluid can be expressed as both absolute (or dynamic) viscosity, µ [Ns/m2], a ...
Project 1: Computational Modeling of Flow and Surfactant Transport
... Short Abstract: This project is part of a optofluidics project to be done though a European network within FP7 comprising research groups in England, France, Switzerland and Koç University. In this project, we will explore mechanisms of deforming droplets using an external electric field. It is well ...
... Short Abstract: This project is part of a optofluidics project to be done though a European network within FP7 comprising research groups in England, France, Switzerland and Koç University. In this project, we will explore mechanisms of deforming droplets using an external electric field. It is well ...
CHAPTER 3 HYDRAULICS OF SEWERS
... The classification of the fluid flow based on the variation of the fluid flow parameters with time characterizes the flow in two categories, steady and unsteady flow. If the flow parameters, such as velocity, pressure, density and discharge do not vary with time or are independent of time then the f ...
... The classification of the fluid flow based on the variation of the fluid flow parameters with time characterizes the flow in two categories, steady and unsteady flow. If the flow parameters, such as velocity, pressure, density and discharge do not vary with time or are independent of time then the f ...
Electric Current and Circuits Guided Notes
... 1) Friction (when an object whose electrons are _________________ rubs against another object) 2) Conduction (when an object with an excess of electrons _________________ a neutral object) 3) Induction (a neutral object acquires a charge from a charged object ________________________________________ ...
... 1) Friction (when an object whose electrons are _________________ rubs against another object) 2) Conduction (when an object with an excess of electrons _________________ a neutral object) 3) Induction (a neutral object acquires a charge from a charged object ________________________________________ ...
ATM 316 - Balanced flow
... Recall V is a nonnegative speed and R > 0 for CCW motion. Thus, Vg > V for cyclonic flow since the fVR term is positive in the Northern Hemisphere. Similarly, for CW motion, R < 0 and V > Vg . For the same pressure gradient, anticyclonic flow is supergeostrophic. That was the math, now let’s look a ...
... Recall V is a nonnegative speed and R > 0 for CCW motion. Thus, Vg > V for cyclonic flow since the fVR term is positive in the Northern Hemisphere. Similarly, for CW motion, R < 0 and V > Vg . For the same pressure gradient, anticyclonic flow is supergeostrophic. That was the math, now let’s look a ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.