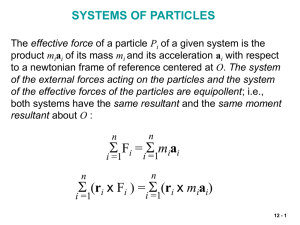
Conservation of mechanical energy
... mechanical energy. In a closed system, one where there are no external dissipative forces acting, the mechanical energy will remain constant. In other words, it will not change (become more or less). This is called the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. ...
... mechanical energy. In a closed system, one where there are no external dissipative forces acting, the mechanical energy will remain constant. In other words, it will not change (become more or less). This is called the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. ...
Ch 2 outline - Huber Heights City Schools
... 1. A bowling ball with a negative initial velocity slows down as it rolls down the lane toward the pins. Is the bowling ball’s acceleration positive or negative? 2. As the shuttle bus comes to a sudden stop to avoid hitting a dog, it accelerates uniformly at -4.1 m/s2 as it slows from 9.0 m/s to 0 m ...
... 1. A bowling ball with a negative initial velocity slows down as it rolls down the lane toward the pins. Is the bowling ball’s acceleration positive or negative? 2. As the shuttle bus comes to a sudden stop to avoid hitting a dog, it accelerates uniformly at -4.1 m/s2 as it slows from 9.0 m/s to 0 m ...
Experiment 5U: Kinetic Friction
... 3. Put enough mass on the hanger so that the friction block will begin to slide on the track without an initial push. 4. Pull the block back until the hanging mass is just below the pulley. Note the position of the block so you can start each trial at the same place. 5. Click “Record” to begin data ...
... 3. Put enough mass on the hanger so that the friction block will begin to slide on the track without an initial push. 4. Pull the block back until the hanging mass is just below the pulley. Note the position of the block so you can start each trial at the same place. 5. Click “Record” to begin data ...
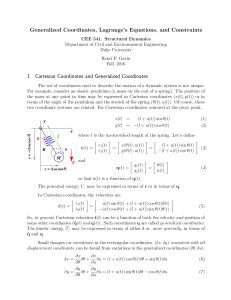
Newtonian Mechanics - University of Iowa Physics
... Thus the principle of Galilean relativity applied to a Newtonian force in an inertial coordinate system requires the the force has no explicit time dependence, is a function of coordinate and velocity differences, and is a vector constructed out of the coordinate and velocity differences. This princ ...
... Thus the principle of Galilean relativity applied to a Newtonian force in an inertial coordinate system requires the the force has no explicit time dependence, is a function of coordinate and velocity differences, and is a vector constructed out of the coordinate and velocity differences. This princ ...
AP Physics - Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
Lecture 3a - Work & Energy
... much work is required to compress it from its uncompressed length (x = 0) to x = 11.0 cm? (b) If a 1.85-kg block is placed against the spring and the spring is released, what will be the speed of the block when it separates from the spring at x = 0? Ignore friction. (c) Repeat part (b) but assume th ...
... much work is required to compress it from its uncompressed length (x = 0) to x = 11.0 cm? (b) If a 1.85-kg block is placed against the spring and the spring is released, what will be the speed of the block when it separates from the spring at x = 0? Ignore friction. (c) Repeat part (b) but assume th ...
Solving Trajectory Optimization Problems as Large-Scale NLPs
... • v(t) = (vx (t), vy (t), vz (t))—velocity. • a(t) = (ax (t), ay (t), az (t))—acceleration. • T —time at which ball arrives at hole. ...
... • v(t) = (vx (t), vy (t), vz (t))—velocity. • a(t) = (ax (t), ay (t), az (t))—acceleration. • T —time at which ball arrives at hole. ...
IPS Sem 2 Review Activity Ch 8 to 14
... A. Both poles must be south poles B. Both poles must be north poles C. One pole is a south pole and the other is a north pole D. The poles are the same type ...
... A. Both poles must be south poles B. Both poles must be north poles C. One pole is a south pole and the other is a north pole D. The poles are the same type ...
gravitational potential energy
... ball, reducing its kinetic energy until it reaches zero. On the way back down, the force of gravity increases the ball’s kinetic energy by the same amount it lost on the way up. ...
... ball, reducing its kinetic energy until it reaches zero. On the way back down, the force of gravity increases the ball’s kinetic energy by the same amount it lost on the way up. ...
2.Work and Energy Solutions
... Student A lifts a 50.newton box from the floor to a height of 0.40 meter in 2.0 seconds. Student B lifts a 40.newton box from the floor to a height of 0.50 meter in 1.0 second. Compared to student A, student B does 1. the same work but develops more power 2. the same work but develops less powe ...
... Student A lifts a 50.newton box from the floor to a height of 0.40 meter in 2.0 seconds. Student B lifts a 40.newton box from the floor to a height of 0.50 meter in 1.0 second. Compared to student A, student B does 1. the same work but develops more power 2. the same work but develops less powe ...
Lecture slides with notes
... (KE+PE) of the system is also conserved. If not a vertical collision, then PEi = PEf and KE1i + KE2i = KE1f + KE2f ...
... (KE+PE) of the system is also conserved. If not a vertical collision, then PEi = PEf and KE1i + KE2i = KE1f + KE2f ...
CAS English 1
... used to describe all the forces used in determining the net force acting on an object. Key 2: An object will continue to move at a constant speed, in a straight line, without a net force acting on it. Key 3: If a net force acts on an object, it will cause the object to speed up, slow down, or change ...
... used to describe all the forces used in determining the net force acting on an object. Key 2: An object will continue to move at a constant speed, in a straight line, without a net force acting on it. Key 3: If a net force acts on an object, it will cause the object to speed up, slow down, or change ...
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity`
... passing through the wheel's center. How can we measure the distance traveled by an object on the edge of the Ferris wh~ A point on an object that rotates about a single axis undergoes circular motion around that axis. In other words, regardless of the shape of the object, any single point on the obj ...
... passing through the wheel's center. How can we measure the distance traveled by an object on the edge of the Ferris wh~ A point on an object that rotates about a single axis undergoes circular motion around that axis. In other words, regardless of the shape of the object, any single point on the obj ...
I - Mathphysics.com
... has commanded attention, and in this context the study of dynamical systems has a claim on the title of the oldest mathematical science, next to geometry: The Chaldeans predicted eclipses about 3000 years ago, and there is some evidence that earlier civilizations performed the same feat 1000 years b ...
... has commanded attention, and in this context the study of dynamical systems has a claim on the title of the oldest mathematical science, next to geometry: The Chaldeans predicted eclipses about 3000 years ago, and there is some evidence that earlier civilizations performed the same feat 1000 years b ...
1-newtons_laws_homew..
... An inclined plane is tilted at an angle α above the horizontal. A ball is launched (initial velocity v0 ) into the air directly up the inclined plane, launched at an additional angle β above the plane’s surface. (a) Draw the situation here, and roughly sketch a predicted path of the ball for some in ...
... An inclined plane is tilted at an angle α above the horizontal. A ball is launched (initial velocity v0 ) into the air directly up the inclined plane, launched at an additional angle β above the plane’s surface. (a) Draw the situation here, and roughly sketch a predicted path of the ball for some in ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.