02-5-net-force-with
... 1. Apply the Momentum Principle to find the net force. 2. Sketch all forces acting on the system. 3. Apply the Principle of Superposition, by summing the forces acting on the system. 4. Solve for the unknown force. ...
... 1. Apply the Momentum Principle to find the net force. 2. Sketch all forces acting on the system. 3. Apply the Principle of Superposition, by summing the forces acting on the system. 4. Solve for the unknown force. ...
Physics 11 exam outline
... There are cases when forces or displacements are present yet no work is done. 1. F=0, d ≠0 2. F≠0, d=0 3. F is perpendicular to d Energy (E) Energy is defined as the ability to do work. If something can apply a force to another object (resulting in a displacement of that object) then that somethi ...
... There are cases when forces or displacements are present yet no work is done. 1. F=0, d ≠0 2. F≠0, d=0 3. F is perpendicular to d Energy (E) Energy is defined as the ability to do work. If something can apply a force to another object (resulting in a displacement of that object) then that somethi ...
Work, Energy & Power
... THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! " The net WORK done on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of t ...
... THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! " The net WORK done on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of t ...
J S U
... 1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string? 2. What is Archimedes’ principle .What do you mean by buoyancy? 3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water. ? 4. What is known as up thrust or buoyant force? At what factors it d ...
... 1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string? 2. What is Archimedes’ principle .What do you mean by buoyancy? 3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water. ? 4. What is known as up thrust or buoyant force? At what factors it d ...
Objective: Conservation of Energy I
... For a closed path, the total work done by a non-conservative force is NOT ZERO - as it is for a conservative force. For instance, a frictional force would oppose the motion and “slow” the car down. Unlike gravity, friction would do negative work on the car through out the entire trip, on both the up ...
... For a closed path, the total work done by a non-conservative force is NOT ZERO - as it is for a conservative force. For instance, a frictional force would oppose the motion and “slow” the car down. Unlike gravity, friction would do negative work on the car through out the entire trip, on both the up ...
P4: Explaining Motion
... floor surface slightly causing an equal force upwards (the reaction of the surface) ...
... floor surface slightly causing an equal force upwards (the reaction of the surface) ...
Chapter 3: Forces and Motion
... ex hitting a ball with a bat, the result is a change in velocity (direction) *an interaction can lead to a change in magnitude or direction A force is any influence that can change the velocity of an object. *this definition agrees with the idea of forces as “pushes” or “pulls” contact force arise ...
... ex hitting a ball with a bat, the result is a change in velocity (direction) *an interaction can lead to a change in magnitude or direction A force is any influence that can change the velocity of an object. *this definition agrees with the idea of forces as “pushes” or “pulls” contact force arise ...
2017WorkEnergyandPowerworksheet
... 8. A 500 kg roller coaster starts from rest 60 m above the ground. How fast will it be going when it gets to the ground? 34.6 m/s 9. A box car at the top of a 500 m hill has a gravitational potential energy of 11050 Joules. a. What is the mass of the car? 2.26 kg ...
... 8. A 500 kg roller coaster starts from rest 60 m above the ground. How fast will it be going when it gets to the ground? 34.6 m/s 9. A box car at the top of a 500 m hill has a gravitational potential energy of 11050 Joules. a. What is the mass of the car? 2.26 kg ...
Name: Chapter 2 Guided Notes P.S. Teacher: Price Motion and
... 2. Positive acceleration - speed is increasing 3. Negative acceleration - speed is decreasing 4. When an object changes speed or direction, it is accelerating B. Calculating Acceleration 1. ___________________= final velocity - initial velocity over time a = v f – vi / t 2. Units of acceleration – m ...
... 2. Positive acceleration - speed is increasing 3. Negative acceleration - speed is decreasing 4. When an object changes speed or direction, it is accelerating B. Calculating Acceleration 1. ___________________= final velocity - initial velocity over time a = v f – vi / t 2. Units of acceleration – m ...
1) A car starts to accelerate from rest with a=0
... unknown what the relative angle between the two vectors is. What are the minimum and maximum magnitude of the resultant vector? a) 2m and 4m b) 2m and 6m c) 0.5m and 8m d) 3.5m and 4.5 m e) 0m and 6m 5) A block is launched up an incline plane. After going up, it slides back down to its starting posi ...
... unknown what the relative angle between the two vectors is. What are the minimum and maximum magnitude of the resultant vector? a) 2m and 4m b) 2m and 6m c) 0.5m and 8m d) 3.5m and 4.5 m e) 0m and 6m 5) A block is launched up an incline plane. After going up, it slides back down to its starting posi ...
Unit 4 SG
... stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 seconds. ...
... stops for 4 seconds to drink water, and then takes off running at 4 m/s for 2 seconds. ...
Practice - People Server at UNCW
... l. Can the cyclist coast to the top of the hill? If so, how fast will she be moving? If not, then how high will she get? ...
... l. Can the cyclist coast to the top of the hill? If so, how fast will she be moving? If not, then how high will she get? ...
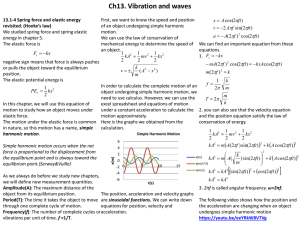
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Frequency(f): The number of complete cycles or a ...
... object from its equilibrium position. The position, acceleration and velocity graphs Period(T): The time it takes the object to move are sinusoidal functions. We can write down through one complete cycle of motion. equations for position, velocity and Frequency(f): The number of complete cycles or a ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.