Monday, Sept. 22, 2008
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintaine ...
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintaine ...
chapter12_PC
... oscillate between 1, we can find the maximum values of velocity and acceleration for an object in SHM ...
... oscillate between 1, we can find the maximum values of velocity and acceleration for an object in SHM ...
f (x) - mrdsample
... equilibrium: Points of equilibrium are where the force is zero (slope = zero). x3 and x5 are points of stable equilibrium or energy wells. If the system is slightly displaced to either side the forces on either side will return the object back to these positions. x6 is a position of neutral equilibr ...
... equilibrium: Points of equilibrium are where the force is zero (slope = zero). x3 and x5 are points of stable equilibrium or energy wells. If the system is slightly displaced to either side the forces on either side will return the object back to these positions. x6 is a position of neutral equilibr ...
Conservation - mackenziekim
... the apple struck his stomach. It then bounced straight back up, having lost 10% of its kinetic energy in the collision. How high did it rise on the first bounce if it had originally dropped from a branch 1.0 m above Isaac's stomach? (SIN '72) (0.90 m) 3. Realizing that he could not drive up a 30°, i ...
... the apple struck his stomach. It then bounced straight back up, having lost 10% of its kinetic energy in the collision. How high did it rise on the first bounce if it had originally dropped from a branch 1.0 m above Isaac's stomach? (SIN '72) (0.90 m) 3. Realizing that he could not drive up a 30°, i ...
How Can I Build a Rollercoaster?
... The first hill in a rollercoaster is always the biggest. Starting the rollercoaster on top of a high place allows the coaster to gain a lot of gravitational potential energy. That is, the amount of work an object will be able to do with the energy it gets from falling. Luckily, the coaster will be " ...
... The first hill in a rollercoaster is always the biggest. Starting the rollercoaster on top of a high place allows the coaster to gain a lot of gravitational potential energy. That is, the amount of work an object will be able to do with the energy it gets from falling. Luckily, the coaster will be " ...
Astronomy
... Symmetry in Forces 4.5. Normal, Tension, and Other Examples of Forces Define normal and tension forces. Apply Newton's laws of motion to solve problems involving a variety of forces. Use trigonometric identities to resolve weight into components. Practice - 4.5 Incline Planes Without Friction ...
... Symmetry in Forces 4.5. Normal, Tension, and Other Examples of Forces Define normal and tension forces. Apply Newton's laws of motion to solve problems involving a variety of forces. Use trigonometric identities to resolve weight into components. Practice - 4.5 Incline Planes Without Friction ...
circular motion
... PROBLEM The moon has a mass of 7.3 x 1022 kg and orbits the Earth at a radius of 3.8 x 108 m once every 27.4 days. Find a) The orbital speed of the moon, b) The acceleration of the moon towards the Earth, and c) The gravitational force the Earth exerts on the moon. ...
... PROBLEM The moon has a mass of 7.3 x 1022 kg and orbits the Earth at a radius of 3.8 x 108 m once every 27.4 days. Find a) The orbital speed of the moon, b) The acceleration of the moon towards the Earth, and c) The gravitational force the Earth exerts on the moon. ...
work, energy, and simple machines
... Work - the product of the force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves in the direction of the force. W = F d cos θ W: work F: magnitude of force d: magnitude of displacement Units are Joules (J = Nm) If a 1 N force moves an object 1 m, 1 Joule of work is done. Work is only done on a ...
... Work - the product of the force exerted on an object and the distance the object moves in the direction of the force. W = F d cos θ W: work F: magnitude of force d: magnitude of displacement Units are Joules (J = Nm) If a 1 N force moves an object 1 m, 1 Joule of work is done. Work is only done on a ...
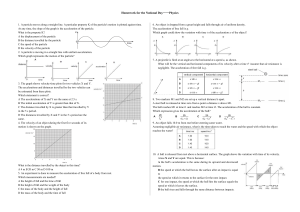
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... 14. In the absence of air resistance, a stone is thrown from P and follows a parabolic path in which the highest point reached is T. The stone reaches point Q just before landing. The vertical component of acceleration of the stone is A zero at T. B greatest at T. C greatest at Q. D the same at Q as ...
... 14. In the absence of air resistance, a stone is thrown from P and follows a parabolic path in which the highest point reached is T. The stone reaches point Q just before landing. The vertical component of acceleration of the stone is A zero at T. B greatest at T. C greatest at Q. D the same at Q as ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... Example: A Satellite in an Elliptical Orbit An artificial satellite is placed in an elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at ...
... Example: A Satellite in an Elliptical Orbit An artificial satellite is placed in an elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at ...
Chapter 2 Lessons 1 - 3 slides
... Kinematics in 1 dimension with constant acceleration Lesson Objective: The ‘suvat’ equations Consider a point mass moving along a line with a constant acceleration. What does its velocity time graph look like? ...
... Kinematics in 1 dimension with constant acceleration Lesson Objective: The ‘suvat’ equations Consider a point mass moving along a line with a constant acceleration. What does its velocity time graph look like? ...
Problem set 13
... 1. h12i Consider force free motion of a symmetric top with I1 = I2 , as discussed in the lecture. Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle ...
... 1. h12i Consider force free motion of a symmetric top with I1 = I2 , as discussed in the lecture. Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.