pg 165 - Denton ISD
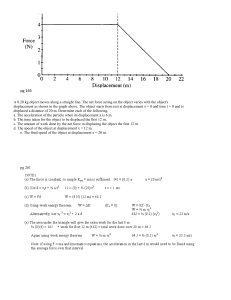
... pg 164 1992B1. A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of an 0.80 meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown in the diagram above. Point P, the lowest point of the circle, is 0.20 meter above the floor. The speed of the ball at the top of the cir ...
... pg 164 1992B1. A 0.10-kilogram solid rubber ball is attached to the end of an 0.80 meter length of light thread. The ball is swung in a vertical circle, as shown in the diagram above. Point P, the lowest point of the circle, is 0.20 meter above the floor. The speed of the ball at the top of the cir ...
AP Physics – Work and Energy - Ms. Gamm
... and then that gets you into the whole speed/kinetic energy thing. You can also work backwards – kinetic energy to change in speed to acceleration to force. 2. Conservative Forces and Potential Energy a. You should understand the concept of conservative forces so you can: (1) Write an expression for ...
... and then that gets you into the whole speed/kinetic energy thing. You can also work backwards – kinetic energy to change in speed to acceleration to force. 2. Conservative Forces and Potential Energy a. You should understand the concept of conservative forces so you can: (1) Write an expression for ...
ExamView - Newton`s Laws Review.tst
... 39. A distance-time graph indicates an object moves 20 km in 4 h. The average speed of the object is ____________________ km/h. 40. Because its ____________________ is always changing, an object moving in a circular path experiences a continuous change in velocity. 41. A moving object does not _____ ...
... 39. A distance-time graph indicates an object moves 20 km in 4 h. The average speed of the object is ____________________ km/h. 40. Because its ____________________ is always changing, an object moving in a circular path experiences a continuous change in velocity. 41. A moving object does not _____ ...
Chapter AA
... Let’s take some concrete values, mass=1, damp=2 and we shall take the time interval to be 1 second. So each second, the speed changes by -2 units. If we start with an initial speed of 10, then here’s how the speed will decrease: ...
... Let’s take some concrete values, mass=1, damp=2 and we shall take the time interval to be 1 second. So each second, the speed changes by -2 units. If we start with an initial speed of 10, then here’s how the speed will decrease: ...
Force motion and machines powerpoint
... can be summarized by the equation F=ma. • More mass takes more force to move. (Kick a wall or a ball?) • Newtons second law of motion explains why an unbalanced forces cause an object to accelerate in the direction of the greatest force. • Balanced forced lead to NO acceleration – or constant speed ...
... can be summarized by the equation F=ma. • More mass takes more force to move. (Kick a wall or a ball?) • Newtons second law of motion explains why an unbalanced forces cause an object to accelerate in the direction of the greatest force. • Balanced forced lead to NO acceleration – or constant speed ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
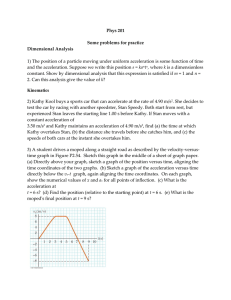
... Masses m1 = 4.00 kg and m2 = 9.00 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. As shown in the diagram, m1 is held at rest on the floor and m2 rests on a fixed incline of angle 40 degrees. The masses are released from rest, and m2 slides1.00 m down the incline in 4 seco ...
... Masses m1 = 4.00 kg and m2 = 9.00 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. As shown in the diagram, m1 is held at rest on the floor and m2 rests on a fixed incline of angle 40 degrees. The masses are released from rest, and m2 slides1.00 m down the incline in 4 seco ...
x - WordPress.com
... Therefore, the kinematic equations cannot be applied. If the block is released from some position x = A, then the initial acceleration is –kA/m. When the block passes through the equilibrium position, a = ...
... Therefore, the kinematic equations cannot be applied. If the block is released from some position x = A, then the initial acceleration is –kA/m. When the block passes through the equilibrium position, a = ...
Forces
... conditions: 1 total force=0; 2 total torque=0 (rotational force). Torque is just a easier way to deal with the forces that one experiences on objects that have length, width and height. If you ...
... conditions: 1 total force=0; 2 total torque=0 (rotational force). Torque is just a easier way to deal with the forces that one experiences on objects that have length, width and height. If you ...
Revision Semester 2 Physics test File
... 2. As a rocket takes off to the sky, it’s speed increases. Explain why. F = m × a; Newton second law states that acceleration of an object is directly proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, i ...
... 2. As a rocket takes off to the sky, it’s speed increases. Explain why. F = m × a; Newton second law states that acceleration of an object is directly proportional and in the same direction as the applied force, and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the rocket takes off to the sky, i ...
Circular Motion A rotation of an object about some axis, whether
... A rotation of an object about some axis, whether inside the object or outside the object leads to circular motion. Just like in linear motion, an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in rotational motion about an axis continues to be in that motion unless interfered with some external ...
... A rotation of an object about some axis, whether inside the object or outside the object leads to circular motion. Just like in linear motion, an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in rotational motion about an axis continues to be in that motion unless interfered with some external ...
ALL PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET NAME: 1. Change .0005 m to milli
... 53.A fisherman’s scale stretches 3.5cm when a 2.7kg fish hangs from it. What is the spring constant and what will be the frequency is the fish is pulled down and released? 54.A small fly .8g is caught in a spider’s web and vibrates at 10hz. What is the spring constant? At what frequency would it vib ...
... 53.A fisherman’s scale stretches 3.5cm when a 2.7kg fish hangs from it. What is the spring constant and what will be the frequency is the fish is pulled down and released? 54.A small fly .8g is caught in a spider’s web and vibrates at 10hz. What is the spring constant? At what frequency would it vib ...
WORK and ENERGY - Cloudfront.net
... a) How much work does the passenger do? b) The same passenger carries the same suitcase back down the same stairs. How much work does the passenger do now? ...
... a) How much work does the passenger do? b) The same passenger carries the same suitcase back down the same stairs. How much work does the passenger do now? ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.