- ILM.COM.PK
... • Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. In order to possess kinetic energy an object must be moving. • As the speed (velocity) of an object increases its kinetic energy increases. The kinetic energy content of a body is also related to its mass. The most massive objects at the same speed contain t ...
... • Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. In order to possess kinetic energy an object must be moving. • As the speed (velocity) of an object increases its kinetic energy increases. The kinetic energy content of a body is also related to its mass. The most massive objects at the same speed contain t ...
Chapter 7
... explain the principles of how a telescope works discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of ...
... explain the principles of how a telescope works discover and describe total internal reflection. explain that tides are caused by the Moon. He tried to use stellar parallax caused by the Earth's orbit to measure the distance to the stars; the same principle as depth perception. Today this branch of ...
During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and
... 31. A stone is thrown with a speed v0 and returns to earth, as the drawing shows. Ignore friction and air resistance, and consider the initial and final locations of the stone. Which one of the following correctly describes the change ΔPE in the gravitational potential energy and the change ΔKE in ...
... 31. A stone is thrown with a speed v0 and returns to earth, as the drawing shows. Ignore friction and air resistance, and consider the initial and final locations of the stone. Which one of the following correctly describes the change ΔPE in the gravitational potential energy and the change ΔKE in ...
Review Questions
... 31. A stone is thrown with a speed v0 and returns to earth, as the drawing shows. Ignore friction and air resistance, and consider the initial and final locations of the stone. Which one of the following correctly describes the change ΔPE in the gravitational potential energy and the change ΔKE in ...
... 31. A stone is thrown with a speed v0 and returns to earth, as the drawing shows. Ignore friction and air resistance, and consider the initial and final locations of the stone. Which one of the following correctly describes the change ΔPE in the gravitational potential energy and the change ΔKE in ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes Formulas: a = aC + aT F = Gm1m2/r2
... Problem: What is the angle we need to bank a curve so that a car doesn’t need any friction to stay on the curve. FN y Note, here we use the normal x and x y axis because the acceleration is along the horizontal direction (which is toward the center of the circle). mg So, as an example, to design a r ...
... Problem: What is the angle we need to bank a curve so that a car doesn’t need any friction to stay on the curve. FN y Note, here we use the normal x and x y axis because the acceleration is along the horizontal direction (which is toward the center of the circle). mg So, as an example, to design a r ...
Newton`s Three Laws
... direction) is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). ...
... direction) is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). ...
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy
... Example: Potential energy changes for a roller coaster. A 1000-kg roller-coaster car moves from point 1 to point 2 and then to point 3. (a) What is the gravitational potential energy at points 2 and 3 relative to point 1? That is, take y = 0 at point 1. (b) What is the change in potential energy wh ...
... Example: Potential energy changes for a roller coaster. A 1000-kg roller-coaster car moves from point 1 to point 2 and then to point 3. (a) What is the gravitational potential energy at points 2 and 3 relative to point 1? That is, take y = 0 at point 1. (b) What is the change in potential energy wh ...
What are Newton`s laws of motion
... example to give at this point is riding on a bus. Students will feel the effects of inertia when standing on a stopped bus. When the bus begins to move forward they will fall backwards. If the bus suddenly stops, they would fall forward. Even though the bus stops the student keeps moving. Newton’s f ...
... example to give at this point is riding on a bus. Students will feel the effects of inertia when standing on a stopped bus. When the bus begins to move forward they will fall backwards. If the bus suddenly stops, they would fall forward. Even though the bus stops the student keeps moving. Newton’s f ...
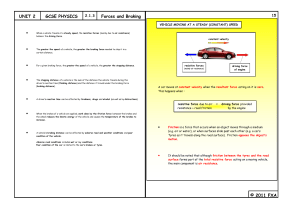
GCSE P2 2.1.3 Forces and Braking
... done by the friction force* between the brakes pads and the wheel discs reduces the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle and causes the temperature of the brakes to increase. Friction is a force that occurs when an object moves through a medium (e.g. air or water), or when surfaces (e.g. the brake p ...
... done by the friction force* between the brakes pads and the wheel discs reduces the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle and causes the temperature of the brakes to increase. Friction is a force that occurs when an object moves through a medium (e.g. air or water), or when surfaces (e.g. the brake p ...
Mechanical Energy
... Worked Example: Block Sliding off Hemisphere A small point like object of mass m rests on top of a sphere of radius R. The object is released from the top of the sphere with a negligible speed and it slowly starts to slide. Find an expression for the angle θf with respect to the vertical at which t ...
... Worked Example: Block Sliding off Hemisphere A small point like object of mass m rests on top of a sphere of radius R. The object is released from the top of the sphere with a negligible speed and it slowly starts to slide. Find an expression for the angle θf with respect to the vertical at which t ...
Chapter 8C -- Conservation of Energy
... provides an example of energy in nature. The potential energy of the water at the top is converted into kinetic energy at the bottom. ...
... provides an example of energy in nature. The potential energy of the water at the top is converted into kinetic energy at the bottom. ...
Activity 13 - cloudfront.net
... Drag the Table icon to the run you want to consider to view a table of your Kinetic Energy values. 7. Click the Σ button to view max, min, mean, and standard deviation values. 8. Record the Max (maximum) value for KE(J) in the Data Section. IMPORTANT: If your cart did not start from rest, also recor ...
... Drag the Table icon to the run you want to consider to view a table of your Kinetic Energy values. 7. Click the Σ button to view max, min, mean, and standard deviation values. 8. Record the Max (maximum) value for KE(J) in the Data Section. IMPORTANT: If your cart did not start from rest, also recor ...
Hunting oscillation

Hunting oscillation is a self-oscillation, usually unwanted, about an equilibrium. The expression came into use in the 19th century and describes how a system ""hunts"" for equilibrium. The expression is used to describe phenomena in such diverse fields as electronics, aviation, biology, and railway engineering.