Newtons 2nd Law Ws
... A force of 50 N to the right is applied to each ball Ball C It will Double the acceleration because the mass is the same ...
... A force of 50 N to the right is applied to each ball Ball C It will Double the acceleration because the mass is the same ...
Planetary Properties - University of Dayton
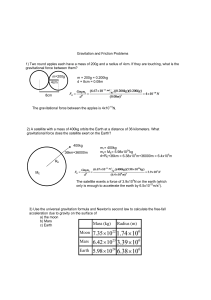
... of moons, or orbiting satellites sent from earth. From Newton’s Laws, the acceleration of the orbiting object (assuming a circular orbit) is Note: the speed can easily be determined from knowledge of the radius of the orbit and the period. In one period, the object must travel a distance equal to th ...
... of moons, or orbiting satellites sent from earth. From Newton’s Laws, the acceleration of the orbiting object (assuming a circular orbit) is Note: the speed can easily be determined from knowledge of the radius of the orbit and the period. In one period, the object must travel a distance equal to th ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... Caution: This is a vector equation used for a instant. We will use it in component form. In the rectangular coordinate axis: ...
... Caution: This is a vector equation used for a instant. We will use it in component form. In the rectangular coordinate axis: ...
Dynamics
... 4. Frictional Force - produced when one surface moves over another; acts in a direction resisting motion. 5. Gravitation Force produced by attraction of any two objects, acts downward on Earth ...
... 4. Frictional Force - produced when one surface moves over another; acts in a direction resisting motion. 5. Gravitation Force produced by attraction of any two objects, acts downward on Earth ...
Q ~ ~ ~ ~ # $ ~ ( 3 0 %... 1. (5%)
... compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. (b) Find the temperatures at points B and C. (c) Assuming that the specific heat does not depend on temperature, so that Einl=31?RT/2,find the internal energy at points A, B, and C. (d) Tab ...
... compressed isobarically (constant pressure) to its original state. (a) Find the number of moles in the sample. (b) Find the temperatures at points B and C. (c) Assuming that the specific heat does not depend on temperature, so that Einl=31?RT/2,find the internal energy at points A, B, and C. (d) Tab ...
PPA6_Lecture_Ch_05
... 3. For muzzle velocity, compare predicted with actual and explain any differences using the physics you know. 4. For v vs. t graph, describe the change in velocity 5. Explain possible reasons for this v vs. t behavior using what you know about gasses and physics. 6. Due Tuesday 15 Dec at beginning o ...
... 3. For muzzle velocity, compare predicted with actual and explain any differences using the physics you know. 4. For v vs. t graph, describe the change in velocity 5. Explain possible reasons for this v vs. t behavior using what you know about gasses and physics. 6. Due Tuesday 15 Dec at beginning o ...
Gravity
... THIRD Law states: force on Earth = force on cookies SECOND Law states: acceleration = force divided by mass Mass of Earth = 1025 x mass of cookies Therefore, acceleration of cookies = 1025 x acceleration of Earth. (Cookies reach a high speed while the Earth hardly budges.) ...
... THIRD Law states: force on Earth = force on cookies SECOND Law states: acceleration = force divided by mass Mass of Earth = 1025 x mass of cookies Therefore, acceleration of cookies = 1025 x acceleration of Earth. (Cookies reach a high speed while the Earth hardly budges.) ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.