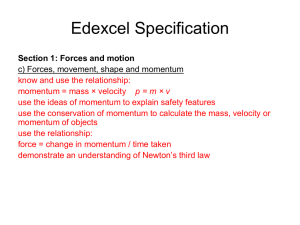
Chapter 2 - trinity
... this time. Changes in the landscape occur constantly as continents drift slowly over Earth’s surface. However, these changes are so gradual that you do not notice them. ...
... this time. Changes in the landscape occur constantly as continents drift slowly over Earth’s surface. However, these changes are so gradual that you do not notice them. ...
Notes on (algebra based) Physics
... Our immediate interest would be to predict the position of an object. The position of an object (in space), relative to another point, is unambiguously specified as x. The position is a function of time, that is, x(t). Newtonian mechanics, the subject of discussion, proposes a strategy to determine ...
... Our immediate interest would be to predict the position of an object. The position of an object (in space), relative to another point, is unambiguously specified as x. The position is a function of time, that is, x(t). Newtonian mechanics, the subject of discussion, proposes a strategy to determine ...
Chapter 10
... ❹ EVALUATE RESULT I know from experience that you have to pull harder to move a swing farther from its equilibrium position, and so my answer to part a makes sense. With regard to part b, when the swing is at rest at 45, the forces Frpc and FEpG on your friend make the same angle with the force Fsp ...
... ❹ EVALUATE RESULT I know from experience that you have to pull harder to move a swing farther from its equilibrium position, and so my answer to part a makes sense. With regard to part b, when the swing is at rest at 45, the forces Frpc and FEpG on your friend make the same angle with the force Fsp ...
ClassicalMechanics_4..
... Torque is provided by friction acting at the surface (otherwise the ball would just slide). Note that the normal force does not produce a torque (although it can with deformable surfaces and rolling friction). Semester 1 2008 ...
... Torque is provided by friction acting at the surface (otherwise the ball would just slide). Note that the normal force does not produce a torque (although it can with deformable surfaces and rolling friction). Semester 1 2008 ...
Exam Review
... 50. What force does Earth exert on a 80.0-kg astronaut at an altitude equivalent to 2.5 times Earth’s radius? 51. The gravitational field strength at the surface of a planet is 3.4 N/kg. If the planet’s mass is 7.2 1022 kg, what is its radius? 52. A driver carelessly ignores the reduced speed limi ...
... 50. What force does Earth exert on a 80.0-kg astronaut at an altitude equivalent to 2.5 times Earth’s radius? 51. The gravitational field strength at the surface of a planet is 3.4 N/kg. If the planet’s mass is 7.2 1022 kg, what is its radius? 52. A driver carelessly ignores the reduced speed limi ...
Lecture Presentation
... In the track and field event known as the hammer throw, an athlete spins a heavy mass in a circle at the end of a chain. Once the mass gets moving at a good clip, the athlete lets go of the chain. The mass flies off in a parabolic arc; the winner is the one who gets the maximum distance. For male at ...
... In the track and field event known as the hammer throw, an athlete spins a heavy mass in a circle at the end of a chain. Once the mass gets moving at a good clip, the athlete lets go of the chain. The mass flies off in a parabolic arc; the winner is the one who gets the maximum distance. For male at ...
Investigating Friction: Finding Safer Roofing
... 6. Zero the force sensor. a. Lay the force sensor on the table so that the support pole is horizontal. b. Click on the 0 ZERO button in the upper right of the top toolbar. 7. Secure a piece of roof shingle to a table or to the floor in a clear area. Place one shoe on the shingle, and securely attach ...
... 6. Zero the force sensor. a. Lay the force sensor on the table so that the support pole is horizontal. b. Click on the 0 ZERO button in the upper right of the top toolbar. 7. Secure a piece of roof shingle to a table or to the floor in a clear area. Place one shoe on the shingle, and securely attach ...
Static Friction
... Static friction is the force that is acting against the box. If you apply a light horizontal push that does not move the box, the static friction force is also small and directly opposite to your push. If you push harder, the friction force increases to match the magnitude of your push. There is a l ...
... Static friction is the force that is acting against the box. If you apply a light horizontal push that does not move the box, the static friction force is also small and directly opposite to your push. If you push harder, the friction force increases to match the magnitude of your push. There is a l ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.