A 1 - Andes Physics Tutor
... 6. Referring to the Interactive Figure (a dump truck with a bed that tilts until a box rested there starts to slip), suppose the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the crate and the truck bed are 0.407 and 0.326, respectively. (a) Determine the angle at which the crate begins to sl ...
... 6. Referring to the Interactive Figure (a dump truck with a bed that tilts until a box rested there starts to slip), suppose the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the crate and the truck bed are 0.407 and 0.326, respectively. (a) Determine the angle at which the crate begins to sl ...
PHYS 1114: Physics I
... An arc of a circle is a "portion" of the circumference of the circle. The length of an arc is simply the length of its "portion" of the circumference. Actually, the circumference itself can be considered an arc length. The length of an arc (or arc length) is traditionally symbolized by s. ...
... An arc of a circle is a "portion" of the circumference of the circle. The length of an arc is simply the length of its "portion" of the circumference. Actually, the circumference itself can be considered an arc length. The length of an arc (or arc length) is traditionally symbolized by s. ...
Force Mass Acceleration - kcpe-kcse
... Explain why the acceleration of a freely falling body near the Earth’s surface is about 10 m/s2. Copy Figure 2 (all parts) on page 141 and explain the velocitytime for an object falling in a fluid. Your explanation should include what is meant by (a) ‘drag force’ and (b) ‘terminal velocity’. Copy an ...
... Explain why the acceleration of a freely falling body near the Earth’s surface is about 10 m/s2. Copy Figure 2 (all parts) on page 141 and explain the velocitytime for an object falling in a fluid. Your explanation should include what is meant by (a) ‘drag force’ and (b) ‘terminal velocity’. Copy an ...
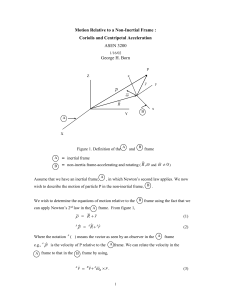
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
pp03
... • Newton’s second law of motion ∑F = ma • When the force fulfill Newton's first law of motion, ma = 0 a=0 therefore, the particle is moving in constant velocity or at rest ...
... • Newton’s second law of motion ∑F = ma • When the force fulfill Newton's first law of motion, ma = 0 a=0 therefore, the particle is moving in constant velocity or at rest ...
Motion and Speed Classwork Name
... 78. Answers will vary. 79. A force will cause acceleration if it is unbalanced. 80. 1000 N / 100 kg = 10 m/s2 81. slow down b/c more mass. 1000 N/ 500 kg = 2 m/s2 82. 0.314 kg (164 m/s2) = 51.5 N 83. 50 kg (4 m/s2) = 200 N 84. push harder because more mass, 70 kg (4 m/s2) = 280N 85. Your friend’s bo ...
... 78. Answers will vary. 79. A force will cause acceleration if it is unbalanced. 80. 1000 N / 100 kg = 10 m/s2 81. slow down b/c more mass. 1000 N/ 500 kg = 2 m/s2 82. 0.314 kg (164 m/s2) = 51.5 N 83. 50 kg (4 m/s2) = 200 N 84. push harder because more mass, 70 kg (4 m/s2) = 280N 85. Your friend’s bo ...
Solutions Guide - Blue Valley Schools
... be forces acting on the object as long as the vector sum of the forces is zero. ...
... be forces acting on the object as long as the vector sum of the forces is zero. ...
Friction
... Intergranular fracture in a nickel-chromium alloy, viewed under the scanning electron microscope. ...
... Intergranular fracture in a nickel-chromium alloy, viewed under the scanning electron microscope. ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.