VIII
... becomes smaller than critical for some reason, the repelling forces between particles become too small to prevent their sticking together. For most soles the critical value of -potential is around 30 mV, under which the aggregative stability is lost. Electro kinetic potential is always a part of th ...
... becomes smaller than critical for some reason, the repelling forces between particles become too small to prevent their sticking together. For most soles the critical value of -potential is around 30 mV, under which the aggregative stability is lost. Electro kinetic potential is always a part of th ...
Teoría Total simplificada, Revista Chilena de Ingeniería, Vol. 16, Nº1
... Electromagnetic engineering is a branch of applied physics which is developing so fast that in the near future electromagnetic engineers will be indispensable in an important emerging area, that which is now known as Wave Structure Matter (WSM). The main reason for this is the penetration capacity o ...
... Electromagnetic engineering is a branch of applied physics which is developing so fast that in the near future electromagnetic engineers will be indispensable in an important emerging area, that which is now known as Wave Structure Matter (WSM). The main reason for this is the penetration capacity o ...
Liquid micro-droplet effects in a plasma
... This essay describes the current state of research into micrometre-scale liquid droplets in an ionised gas, usually referred to as a plasma. Such systems are a common occurrence in industrial processes, but have received little interest until recently. Electrostatic breakup is a significant mechanis ...
... This essay describes the current state of research into micrometre-scale liquid droplets in an ionised gas, usually referred to as a plasma. Such systems are a common occurrence in industrial processes, but have received little interest until recently. Electrostatic breakup is a significant mechanis ...
[SESSION-2012-2013] KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN Zonal Institute of Education & Training
... (non –evaluative)↓ Microscopic Explanation for Properties of Plasmas Plasmas have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume because the particles can move past one another. ...
... (non –evaluative)↓ Microscopic Explanation for Properties of Plasmas Plasmas have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume because the particles can move past one another. ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... • A different type of wave, called an electromagnetic wave, carries energy from the Sun to Earth. • An electromagnetic wave is a wave that can travel through empty space or through matter and is produced by charged particles that are in motion. ...
... • A different type of wave, called an electromagnetic wave, carries energy from the Sun to Earth. • An electromagnetic wave is a wave that can travel through empty space or through matter and is produced by charged particles that are in motion. ...
1) A 2) B 3) C 4) A and B 5) A and C 6) B and C 7) All of the movies
... 4. Redo the free-body diagrams for 3, 4, 5 under the assumption that the book's velocity is changing. 5. For #6, draw the free body diagram for the upper and the lower book and for the books as a single unit. ...
... 4. Redo the free-body diagrams for 3, 4, 5 under the assumption that the book's velocity is changing. 5. For #6, draw the free body diagram for the upper and the lower book and for the books as a single unit. ...
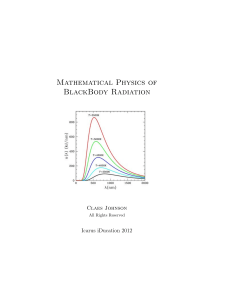
Mathematical Physics of BlackBody Radiation
... much support to Descartes’ idea but has not really any better theory and so the mystery of how soul and body interact remains to be resolved. What does then modern physics say about the interaction of light and matter? There are two competing theories depending on the nature of light as Deterministi ...
... much support to Descartes’ idea but has not really any better theory and so the mystery of how soul and body interact remains to be resolved. What does then modern physics say about the interaction of light and matter? There are two competing theories depending on the nature of light as Deterministi ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).






![[SESSION-2012-2013] KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN Zonal Institute of Education & Training](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008846751_1-2b4b3b69c179d4de9cadbe3a1137f0be-300x300.png)