21-1 Creating and Measuring Electric Fields
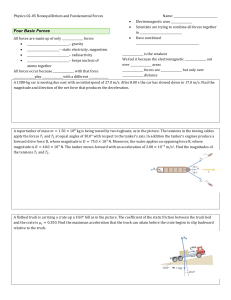
... experiences a force of 0.60 N acting at an angle of 10o. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the location of the test charge? ...
... experiences a force of 0.60 N acting at an angle of 10o. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the location of the test charge? ...
Newton`s Laws Notetakers
... A body at rest will remain at rest, a body in motion will remain in motion, traveling with a constant velocity in a straight line, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. INERTIA = a measure of a body’s ability to resist changes in velocity. (the greater the mass of a body, the less it will accelerat ...
... A body at rest will remain at rest, a body in motion will remain in motion, traveling with a constant velocity in a straight line, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. INERTIA = a measure of a body’s ability to resist changes in velocity. (the greater the mass of a body, the less it will accelerat ...
Document
... perpendicularly to a magnetic field. The conductor experiences a magnetic force per unit length of 0.12 N/m in the negative y direction. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field in the region through which the current passes. • A wire carries a steady current of 2.40A. A straight ...
... perpendicularly to a magnetic field. The conductor experiences a magnetic force per unit length of 0.12 N/m in the negative y direction. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field in the region through which the current passes. • A wire carries a steady current of 2.40A. A straight ...
The principle of constancy of the speed of Light in free-space
... 6,12) were made (finally without success) to develop theories that would explain all the observed facts without this postulate. The first postulate is evidently one, which stands on the firm ground of reasonableness. But the same is not true for the second one. It is difficult to accept the idea of ...
... 6,12) were made (finally without success) to develop theories that would explain all the observed facts without this postulate. The first postulate is evidently one, which stands on the firm ground of reasonableness. But the same is not true for the second one. It is difficult to accept the idea of ...
Holt Physics-Chapter 4: Forces and The Laws of Motion
... more objects that are in contact and at rest. 2. Kinetic Friction is the friction experienced by two or more objects that are in contact and are moving relative to each other. 3. Kinetic friction is less than static friction 4. Friction must always be considered in order to exactly calculate net for ...
... more objects that are in contact and at rest. 2. Kinetic Friction is the friction experienced by two or more objects that are in contact and are moving relative to each other. 3. Kinetic friction is less than static friction 4. Friction must always be considered in order to exactly calculate net for ...
Elements of Physics
... is held in its orbit by the Earth's gravity 3. major tool of physics 4. astronomer who concluded the sun was the center of the universe 5. for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction is the 6. his theory showed that gravity affects light 7. total quantity of an object's matter 8. univer ...
... is held in its orbit by the Earth's gravity 3. major tool of physics 4. astronomer who concluded the sun was the center of the universe 5. for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction is the 6. his theory showed that gravity affects light 7. total quantity of an object's matter 8. univer ...
Magnetic fields
... We know B since we applied it. E is determined from V and the width of the artery d E=V/d ...
... We know B since we applied it. E is determined from V and the width of the artery d E=V/d ...
LINEAR KINETICS (Part 1)
... Newton’s First Law can be restated to predict what will happen to the “system”: In the absence of _______ forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant (in both ________ and _________). Example #1: A 100 kg running back carries the ball forward with a speed of 9 m/s. H ...
... Newton’s First Law can be restated to predict what will happen to the “system”: In the absence of _______ forces acting on a system, the total momentum of the system remains constant (in both ________ and _________). Example #1: A 100 kg running back carries the ball forward with a speed of 9 m/s. H ...
Fundamental interaction
Fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions in physical systems that don't appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four conventionally accepted fundamental interactions—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear. Each one is understood as the dynamics of a field. The gravitational force is modeled as a continuous classical field. The other three are each modeled as discrete quantum fields, and exhibit a measurable unit or elementary particle.Gravitation and electromagnetism act over a potentially infinite distance across the universe. They mediate macroscopic phenomena every day. The other two fields act over minuscule, subatomic distances. The strong nuclear interaction is responsible for the binding of atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear interaction also acts on the nucleus, mediating radioactive decay.Theoretical physicists working beyond the Standard Model seek to quantize the gravitational field toward predictions that particle physicists can experimentally confirm, thus yielding acceptance to a theory of quantum gravity (QG). (Phenomena suitable to model as a fifth force—perhaps an added gravitational effect—remain widely disputed). Other theorists seek to unite the electroweak and strong fields within a Grand Unified Theory (GUT). While all four fundamental interactions are widely thought to align at an extremely minuscule scale, particle accelerators cannot produce the massive energy levels required to experimentally probe at that Planck scale (which would experimentally confirm such theories). Yet some theories, such as the string theory, seek both QG and GUT within one framework, unifying all four fundamental interactions along with mass generation within a theory of everything (ToE).