Chapter5_Final.doc
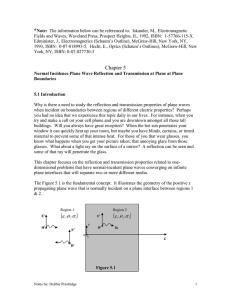
... The magnetic field distribution in front of a perfectly conducting boundary is illustrated in Figure 5.3, where we can observe that its first null occurs at z = 1 4 . This is the location of the maximum electric field (see Figure 5.2). By comparison, equations (5.13) & (5.16) shows that the electr ...
... The magnetic field distribution in front of a perfectly conducting boundary is illustrated in Figure 5.3, where we can observe that its first null occurs at z = 1 4 . This is the location of the maximum electric field (see Figure 5.2). By comparison, equations (5.13) & (5.16) shows that the electr ...
Part23 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... has a mass of 2 kg and an air resistance coefficient 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 from a helicopter 1,000 meters above the ground. Fgravity = mg = 2 kg * 9.8 m/s2 = 19.6 Nt. FAR = bv2 = 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 * [0 m/s]2 = 0 Nt. Using Newton’s Second Law, we can now calculate the initial acceleration: ...
... has a mass of 2 kg and an air resistance coefficient 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 from a helicopter 1,000 meters above the ground. Fgravity = mg = 2 kg * 9.8 m/s2 = 19.6 Nt. FAR = bv2 = 0.03 Nt-s2/m2 * [0 m/s]2 = 0 Nt. Using Newton’s Second Law, we can now calculate the initial acceleration: ...
Worked Examples from Introductory Physics Vol. I: Basic Mechanics
... Problem–solving can be very hard to learn, and students often confuse it with the algebra with which one finishes up a problem. But the level of mathematics and calculator skills required in a general physics course is not very great. Any student who has difficulty solving the equations we derive in ...
... Problem–solving can be very hard to learn, and students often confuse it with the algebra with which one finishes up a problem. But the level of mathematics and calculator skills required in a general physics course is not very great. Any student who has difficulty solving the equations we derive in ...
Preparing - broward.k12.fl.us
... •applying proper procedures for dealing with accidents and injuries in the physics laboratory Understand the use of mathematics (e.g., dimensional analysis, algebra, vector analysis, calculus) and mathematical modeling in physics. For example: •using mathematics to derive and solve equations •applyi ...
... •applying proper procedures for dealing with accidents and injuries in the physics laboratory Understand the use of mathematics (e.g., dimensional analysis, algebra, vector analysis, calculus) and mathematical modeling in physics. For example: •using mathematics to derive and solve equations •applyi ...
this PDF file - American International Journal of
... to be calculated within the framework of initial and boundary-value problems in a three-dimensional and unsteady statement in inhomogeneous dissipative media possessing similar time dispersion. It should be noted that these numerical codes are also expedient for calculation of fields not only in lin ...
... to be calculated within the framework of initial and boundary-value problems in a three-dimensional and unsteady statement in inhomogeneous dissipative media possessing similar time dispersion. It should be noted that these numerical codes are also expedient for calculation of fields not only in lin ...
Pacing Guide for Physics
... instantaneous acceleration. Interpret position-time graphs for motion with constant acceleration. Apply mathematical relationships among position, velocity, acceleration, and time to solve constant acceleration problems using an organized strategy. Define acceleration due to gravity and recognize it ...
... instantaneous acceleration. Interpret position-time graphs for motion with constant acceleration. Apply mathematical relationships among position, velocity, acceleration, and time to solve constant acceleration problems using an organized strategy. Define acceleration due to gravity and recognize it ...
Physics Regents Review Sheet
... _____ what three major particles atoms are made up of _____ how atoms become charged (positive or negative) _____ what an elementary charge is and where to find its value _____ how charged particles interact with one another _____ which particle is the ONLY one that’s allowed to transfer between ato ...
... _____ what three major particles atoms are made up of _____ how atoms become charged (positive or negative) _____ what an elementary charge is and where to find its value _____ how charged particles interact with one another _____ which particle is the ONLY one that’s allowed to transfer between ato ...
Writing Equations in Slope
... 11-3 Using Slopes and Intercepts If you know any two points on a line, or two solutions of a linear equation, you can find the slope of the line without graphing. The slope of a line through the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is as follows: ...
... 11-3 Using Slopes and Intercepts If you know any two points on a line, or two solutions of a linear equation, you can find the slope of the line without graphing. The slope of a line through the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is as follows: ...
Physics Review Assignment
... 6. Marissa and Summer are at the bottom of a canyon facing the canyon wall closest to them. They are 267m from the wall and the speed of sound is 340m/s at that location. How long after they shout will they hear their echo? (2 marks) ...
... 6. Marissa and Summer are at the bottom of a canyon facing the canyon wall closest to them. They are 267m from the wall and the speed of sound is 340m/s at that location. How long after they shout will they hear their echo? (2 marks) ...
Class IX Physics Reference Material for SA-I 2014-15
... 15. A car travels along a straight line for first half time with speed 40km/hr and the second half time with speed 60km/hr. Find the average speed of the car. 16. A body starts rolling over a horizontal surface with an initial velocity of 0.5m/s. Due to friction, its velocity decreases at the rate o ...
... 15. A car travels along a straight line for first half time with speed 40km/hr and the second half time with speed 60km/hr. Find the average speed of the car. 16. A body starts rolling over a horizontal surface with an initial velocity of 0.5m/s. Due to friction, its velocity decreases at the rate o ...
Review Questions
... The ratio of the larger moment of inertia to that of the smaller moment of inertia is ...
... The ratio of the larger moment of inertia to that of the smaller moment of inertia is ...