Lunar Base Supply Egg Drop - NSTA Learning Center
... rocket moving. Once moving, the rocket will keep moving in a straight line unless it is acted upon by another unbalanced force. ...
... rocket moving. Once moving, the rocket will keep moving in a straight line unless it is acted upon by another unbalanced force. ...
Newton`s Laws - Issaquah Connect
... Support forces – upward supporting force Book at rest on a desk Forces = gravity or weight (-), desk (+) (support force) Equilibrium for moving objects (Dynamic equilibrium) Object at rest =equilibrium Object moving at a constant speed in the same direction = equilibrium 3.3 Mass is a measure of ine ...
... Support forces – upward supporting force Book at rest on a desk Forces = gravity or weight (-), desk (+) (support force) Equilibrium for moving objects (Dynamic equilibrium) Object at rest =equilibrium Object moving at a constant speed in the same direction = equilibrium 3.3 Mass is a measure of ine ...
Astronomy
... Symmetry in Forces 4.5. Normal, Tension, and Other Examples of Forces Define normal and tension forces. Apply Newton's laws of motion to solve problems involving a variety of forces. Use trigonometric identities to resolve weight into components. Practice - 4.5 Incline Planes Without Friction ...
... Symmetry in Forces 4.5. Normal, Tension, and Other Examples of Forces Define normal and tension forces. Apply Newton's laws of motion to solve problems involving a variety of forces. Use trigonometric identities to resolve weight into components. Practice - 4.5 Incline Planes Without Friction ...
Circular Motion and the Law of Gravity
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0° on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0°. It moves t ...
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0° on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0°. It moves t ...
Newton and Friction
... Newton and Friction Quick Fact Study Sheet Newton’s Laws 1) An object in motion will remain in motion unless an unbalanced force acts on it. If an object is moving at constant velocity, there is no acceleration or net force. Mass and inertia are proportional, the higher the mass the higher the inert ...
... Newton and Friction Quick Fact Study Sheet Newton’s Laws 1) An object in motion will remain in motion unless an unbalanced force acts on it. If an object is moving at constant velocity, there is no acceleration or net force. Mass and inertia are proportional, the higher the mass the higher the inert ...
chapter 5 test - aubreyisd.net
... CHAPTER 4 & 5 REVIEW 1. Determine if each of the following equations represents a direct variation. If the equation is direct then find the constant of variation. (A) 2 y 5 x 1 (B) 5 x 6 y 0 (C) y 13 x Yes, 1/3 Not a representation Yes, 5/6 2. Find the rate of change for each situation: (A ...
... CHAPTER 4 & 5 REVIEW 1. Determine if each of the following equations represents a direct variation. If the equation is direct then find the constant of variation. (A) 2 y 5 x 1 (B) 5 x 6 y 0 (C) y 13 x Yes, 1/3 Not a representation Yes, 5/6 2. Find the rate of change for each situation: (A ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
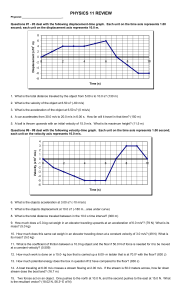
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
Lecture 6
... – Experiment: If NO NET FORCE is applied to an object moving at a constant speed in straight line, it will continue moving at the same speed in a straight line! – If I succeed in having you overcome the wrong, ancient misconception & understand the correct view, one of the main goals of the ...
... – Experiment: If NO NET FORCE is applied to an object moving at a constant speed in straight line, it will continue moving at the same speed in a straight line! – If I succeed in having you overcome the wrong, ancient misconception & understand the correct view, one of the main goals of the ...
Action / Reaction forces
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
3. - Cobb Learning
... Additional Example 1C: Solving Equations by Multiplying and Dividing Solve each equation. Write the answer in simplest form. ...
... Additional Example 1C: Solving Equations by Multiplying and Dividing Solve each equation. Write the answer in simplest form. ...
78AM-1
... 5. A rod of length L and mass M is pivoted at one end to constitute a pendulum. Determine its period of oscillation and calculate its length if the period is desired to be 1 second. If the rod was instead suspended from a point at one quarter of its length, what would be the expression for the peri ...
... 5. A rod of length L and mass M is pivoted at one end to constitute a pendulum. Determine its period of oscillation and calculate its length if the period is desired to be 1 second. If the rod was instead suspended from a point at one quarter of its length, what would be the expression for the peri ...
Review of Physics 20
... Physics 30 Review of Physics 20 Essentials Welcome to Physics 30. The Physics 30 course builds on a number of ideas and skills that you learned in Physics 20. Physics 30 requires that the following ideas and skills are well understood: ...
... Physics 30 Review of Physics 20 Essentials Welcome to Physics 30. The Physics 30 course builds on a number of ideas and skills that you learned in Physics 20. Physics 30 requires that the following ideas and skills are well understood: ...
Physics
... motion in which motion everywhere in the universe can be explained by the same few rules. Note that his mathematical analysis of gravitational force and motion showed that planetary orbits had to be the very ellipses that Johannes Kepler had proposed two generations earlier. Describe how Newton’s sy ...
... motion in which motion everywhere in the universe can be explained by the same few rules. Note that his mathematical analysis of gravitational force and motion showed that planetary orbits had to be the very ellipses that Johannes Kepler had proposed two generations earlier. Describe how Newton’s sy ...
Law of conservation of linear momentum
... Law of inertia, law of acceleration, law of action and reaction Law of inertia: A body is at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion unless made to change its state by external forces Inertia is a property of matter by which it remains at rest or continues moving uniformly in a straight line unless ac ...
... Law of inertia, law of acceleration, law of action and reaction Law of inertia: A body is at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion unless made to change its state by external forces Inertia is a property of matter by which it remains at rest or continues moving uniformly in a straight line unless ac ...
Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in
... - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or m ...
... - Acceleration of an object in a free fall on the Earth: = 9.8 m/s2 3 Forces that affect Motion 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or m ...
Day23,Oct24: Time Varying Fields
... alliance between these two fields is rooted deep in relativity theory. (You can turn a static charge into a dynamic one simply by moving relative to it, thus turning E fields into B fields.) • The divergence equations and the boundary conditions stay the same for time-dependent fields. The curl chan ...
... alliance between these two fields is rooted deep in relativity theory. (You can turn a static charge into a dynamic one simply by moving relative to it, thus turning E fields into B fields.) • The divergence equations and the boundary conditions stay the same for time-dependent fields. The curl chan ...
File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
... resistance or wind) then the bowling ball will fall first. ...
... resistance or wind) then the bowling ball will fall first. ...