Name - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
... If additional objects are involved, draw separate free body diagrams for each object ...
File - PHYSICS PHUN WITH MS.BEGUM
... an airplane flies at right angles to the wind, then the ground speed increases. (The hypotenuse of the triangle is bigger than the two vectors.) 69. All freely thrown objects in the air are considered projectiles. 70. A kilogram of iron and a kilogram of Styrofoam have the same mass. 71. The acceler ...
... an airplane flies at right angles to the wind, then the ground speed increases. (The hypotenuse of the triangle is bigger than the two vectors.) 69. All freely thrown objects in the air are considered projectiles. 70. A kilogram of iron and a kilogram of Styrofoam have the same mass. 71. The acceler ...
Momentum
... mass 60 kg, sit in a rowboat of mass 80 kg. With the boat initially at rest, the two people, who have been sitting at opposite ends of the boat 2.0 m apart from each other, now exchange seats. How far and in what direction will the boat move? (Hint: it can be shown that the net force acting on a sys ...
... mass 60 kg, sit in a rowboat of mass 80 kg. With the boat initially at rest, the two people, who have been sitting at opposite ends of the boat 2.0 m apart from each other, now exchange seats. How far and in what direction will the boat move? (Hint: it can be shown that the net force acting on a sys ...
FREE Sample Here
... Acknowledge the chief difference between Aristotle’s approach and that of Galileo. The big difference between these two giant intellects was the role of experiment—emphasized by Galileo. The legendary experiment at the Leaning Tower of Pisa is a good example. Interestingly, legend has it that many p ...
... Acknowledge the chief difference between Aristotle’s approach and that of Galileo. The big difference between these two giant intellects was the role of experiment—emphasized by Galileo. The legendary experiment at the Leaning Tower of Pisa is a good example. Interestingly, legend has it that many p ...
external forces. - Mahidol University
... Inertial frames are frames of reference that are not accelerating (i.e. not moving or moving at constant velocity) A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as bein ...
... Inertial frames are frames of reference that are not accelerating (i.e. not moving or moving at constant velocity) A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to the distant stars is the best approximation of an inertial frame, and for our purposes we can consider the Earth as bein ...
PhysicsNotes QRECT Video Version With MetaNumber Feb 19 2013.pdf
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
Momentum
... at the point of impact with zero momentum. If the green truck was moving at 10 m/s, how fast was the ...
... at the point of impact with zero momentum. If the green truck was moving at 10 m/s, how fast was the ...
Multiple Masses - The Lesson Locker
... The connecting coble or rope changes only the direction of the forces acting on the objects and has no effect on the magnitude of the forces. You can assign the direction of the motion as being from one end of the cable or rope to the other Se figure 10.12 page 482 ...
... The connecting coble or rope changes only the direction of the forces acting on the objects and has no effect on the magnitude of the forces. You can assign the direction of the motion as being from one end of the cable or rope to the other Se figure 10.12 page 482 ...
PhysicsNotes v1.pdf
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
... 3.2 Projectile motion in two dimensions using vectors r(t) = (x(t) , y(t) ) and v(t) = (vx(t) , vy(t)) ............ 11 3.3 Graphical view of motion in a river or with an air current using vectors graphically ........................... 11 3.4 More complex projectile problems ........................ ...
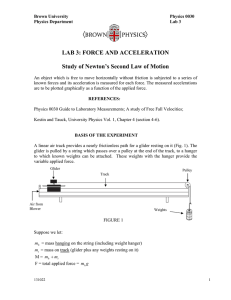
LAB 3: FORCE AND ACCELERATION Study of Newton`s Second
... mh (and therefore increases F without changing M). For each value of F, a is constant during the motion. Since M remains constant, Eq. (3) becomes the expression of a linear relationship between F and a in this experiment. It predicts that if each acceleration a is plotted as a function of the corre ...
... mh (and therefore increases F without changing M). For each value of F, a is constant during the motion. Since M remains constant, Eq. (3) becomes the expression of a linear relationship between F and a in this experiment. It predicts that if each acceleration a is plotted as a function of the corre ...
physics (classes xi –xii)
... Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel currentcarrying conductors – ...
... Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire, straight and toroidal solenoids. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel currentcarrying conductors – ...
II. Forces
... The force and weight are both measured in Newtons. Mass is measured in kilograms. Acceleration is measured in m/s/s (m/s2). 3. Free Fall a. A free-falling object is an object which is falling under the sole influence of gravity. b. Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. c. All free-f ...
... The force and weight are both measured in Newtons. Mass is measured in kilograms. Acceleration is measured in m/s/s (m/s2). 3. Free Fall a. A free-falling object is an object which is falling under the sole influence of gravity. b. Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. c. All free-f ...