What is time to top?
... Q4 A lead ball and an aluminum ball, each 1 in. in diameter, are released simultaneously and allowed to fall to the ground. Due to its greater density, the lead ball has a substantially larger mass than the aluminum ball. Which of these balls, if either, has the greater acceleration due to gravity? ...
... Q4 A lead ball and an aluminum ball, each 1 in. in diameter, are released simultaneously and allowed to fall to the ground. Due to its greater density, the lead ball has a substantially larger mass than the aluminum ball. Which of these balls, if either, has the greater acceleration due to gravity? ...
EM Bullitin
... (1) Maxwell’s first equation for electrostatics, (2) Divergence theorem. (b) Write a detailed note on potential gradient (c) Derive the expression of curl. Also mention its physical interpretation (a) State and Explain Biot-Savart law. Derive an expression of magnetic field intensity for an infinite ...
... (1) Maxwell’s first equation for electrostatics, (2) Divergence theorem. (b) Write a detailed note on potential gradient (c) Derive the expression of curl. Also mention its physical interpretation (a) State and Explain Biot-Savart law. Derive an expression of magnetic field intensity for an infinite ...
force
... • In order to adequately describe nature, Newton invented Calculus at the same time • Laid out the fundamental principles of Classical Physics which dominated science until the advent of Quantum Mechanics in the 1920’s ...
... • In order to adequately describe nature, Newton invented Calculus at the same time • Laid out the fundamental principles of Classical Physics which dominated science until the advent of Quantum Mechanics in the 1920’s ...
Mid Year Review
... 2. A motorcyclist accelerates from 3.0 m/s to 27 m/s in 4.0 s. What is his acceleration? 6.0 m/s2 3. A car accelerates at 5.0 m/s2 from an initial velocity of 14 m/s. How long will it take to reach a velocity of 65 m/s? 10.2 s 4. A car accelerates form rest at 12.0 m/s2 for 14.0 s. a) How fast is it ...
... 2. A motorcyclist accelerates from 3.0 m/s to 27 m/s in 4.0 s. What is his acceleration? 6.0 m/s2 3. A car accelerates at 5.0 m/s2 from an initial velocity of 14 m/s. How long will it take to reach a velocity of 65 m/s? 10.2 s 4. A car accelerates form rest at 12.0 m/s2 for 14.0 s. a) How fast is it ...
Lecture II Simple One-Dimensional Vibrating Systems
... Dissipative processes/friction tends to lower the frequency of oscillation of a vibrating system, as can be seen from the relation 0 2 2 . Small damping corresponds to a slight decrease in the oscillation frequency from its “natural” un-damped value of k M . If we now imagine s ...
... Dissipative processes/friction tends to lower the frequency of oscillation of a vibrating system, as can be seen from the relation 0 2 2 . Small damping corresponds to a slight decrease in the oscillation frequency from its “natural” un-damped value of k M . If we now imagine s ...
FREE PDF - Perkins eLearning
... Now, the desk pushes back against the person with a force of the same size. This reaction force will cause the rolling chair to move backwards. Notice that the two forces act on different objects. The action force acts on the desk. The reaction force acts on the person. Newton’s Third Law Newton’s t ...
... Now, the desk pushes back against the person with a force of the same size. This reaction force will cause the rolling chair to move backwards. Notice that the two forces act on different objects. The action force acts on the desk. The reaction force acts on the person. Newton’s Third Law Newton’s t ...
Circular Motion - Effingham County Schools
... a downward force that causes the see saw to twist. The force is more effective at causing the twist if it is greater OR if it is further from the point of rotation. ...
... a downward force that causes the see saw to twist. The force is more effective at causing the twist if it is greater OR if it is further from the point of rotation. ...
Slide 1 - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
... Time of collision is short enough that external forces may be ignored Inelastic collision: momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not Completely inelastic collision: objects stick ...
321 Exam: Part 1 (Closed book/notes)
... b. Since the fuel is 50% deuterium, D-D reactions will occur in addition to the desired D-T reactions. This results in emission of both 2.54 MeV D-D neutrons and 14 MeV D-T neutrons. Assume the D-T fusion burn occurs at 100 keV and at the compression density given in part a. Set up an expression for ...
... b. Since the fuel is 50% deuterium, D-D reactions will occur in addition to the desired D-T reactions. This results in emission of both 2.54 MeV D-D neutrons and 14 MeV D-T neutrons. Assume the D-T fusion burn occurs at 100 keV and at the compression density given in part a. Set up an expression for ...
Acceleration - Cloudfront.net
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...
Tuesday, June 6, 2006
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained ...
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained ...
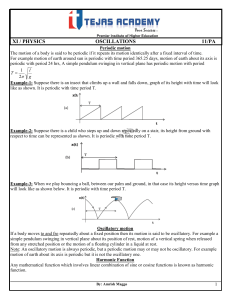
AP1 Oscillations
... EK: 3.B.3 Restoring forces can result in oscillatory motion. When a linear restoring force is exerted on an object displaced from an equilibrium position, the object will undergo a special type of motion called simple harmonic motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potenti ...
... EK: 3.B.3 Restoring forces can result in oscillatory motion. When a linear restoring force is exerted on an object displaced from an equilibrium position, the object will undergo a special type of motion called simple harmonic motion. 4.C.1 The energy of a system includes its kinetic energy, potenti ...
Name Reading Science – Newton`s Laws and Roller Coasters In
... Newton’s second law is the law of force and acceleration. That law states that the acceleration of an object depends on the object’s mass and magnitude of the force acting upon it (F=ma). You feel this second law when you start going down the hills. The coaster cars and your body have mass. The grav ...
... Newton’s second law is the law of force and acceleration. That law states that the acceleration of an object depends on the object’s mass and magnitude of the force acting upon it (F=ma). You feel this second law when you start going down the hills. The coaster cars and your body have mass. The grav ...
Lecture11(CavitiesI) 2015 - Indico
... The drift tubes, which have no field inside them, also contain the magnets to focus the beam. Energy gain from accelerating potential differences between end of drift tubes, but the phase shift between drift tube gaps is 360o. Alternate tubes need not be earthed and each gap appears to the particle ...
... The drift tubes, which have no field inside them, also contain the magnets to focus the beam. Energy gain from accelerating potential differences between end of drift tubes, but the phase shift between drift tube gaps is 360o. Alternate tubes need not be earthed and each gap appears to the particle ...
here.
... • The zeroth law of classical mechanics can be regarded as saying that the trajectory r(t) of a particle is a (twice) differentiable function of time. This is a law that applies to planets, pendulums etc. But it fails for Brownian motion (movement of pollen grains in water). It also fails for electr ...
... • The zeroth law of classical mechanics can be regarded as saying that the trajectory r(t) of a particle is a (twice) differentiable function of time. This is a law that applies to planets, pendulums etc. But it fails for Brownian motion (movement of pollen grains in water). It also fails for electr ...