f F = mg X
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force ❑ They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law ❑ Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force ❑ They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law ❑ Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
Slides for Chapters 9, 10, 11 and Review
... motion (about some axis passing through center of mass) and translation motion (of the center of mass). ...
... motion (about some axis passing through center of mass) and translation motion (of the center of mass). ...
Pressure gradient
... - Use these properties of turbulent flows in the Navier Stokes equations -The only terms that have products of fluctuations are the advection terms - All other terms remain the same, e.g., u t u t u ' t u t ...
... - Use these properties of turbulent flows in the Navier Stokes equations -The only terms that have products of fluctuations are the advection terms - All other terms remain the same, e.g., u t u t u ' t u t ...
Motion in one and two dimensions
... All motions are relative.The motion (velocity) of an object depends on which frame of reference is used to measure it. We say the measured velocity is relative to the chosen frame of reference. Usually the ground is the preferred choice as the reference frame and very often it is not specifically me ...
... All motions are relative.The motion (velocity) of an object depends on which frame of reference is used to measure it. We say the measured velocity is relative to the chosen frame of reference. Usually the ground is the preferred choice as the reference frame and very often it is not specifically me ...
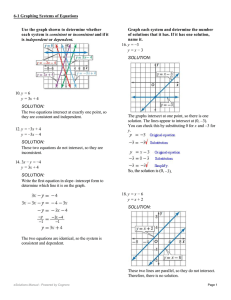
Solving Two-Step Equations 3.5
... 5. IN YOUR OWN WORDS How can you use algebra tiles to solve a two-step equation? 6. When solving the equation 4x + 1 = −11, what is the first step? 7. REPEATED REASONING Solve the equation 2x − 75 = −25. How do your steps compare with the strategy of working backwards in Activity 4? ...
... 5. IN YOUR OWN WORDS How can you use algebra tiles to solve a two-step equation? 6. When solving the equation 4x + 1 = −11, what is the first step? 7. REPEATED REASONING Solve the equation 2x − 75 = −25. How do your steps compare with the strategy of working backwards in Activity 4? ...
11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion Any vibrating system where the
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Monday, April 1, 2013
... 4. You must show the detail of your OWN work in order to obtain any credit. Monday, April 1, 2013 ...
... 4. You must show the detail of your OWN work in order to obtain any credit. Monday, April 1, 2013 ...
Force and Acceleration in Circular Motion
... acceleration. For circular motion at constant speed, the velocity is always tangential to the circular path, and therefore its direction is continuously changing even though its magnitude is constant. Therefore, the object has an acceleration. It can be shown that the magnitude of the acceleration v ...
... acceleration. For circular motion at constant speed, the velocity is always tangential to the circular path, and therefore its direction is continuously changing even though its magnitude is constant. Therefore, the object has an acceleration. It can be shown that the magnitude of the acceleration v ...
ID_newton4_060906 - Swift
... Students may be confused by this because they know that more massive objects weigh more. While this is true, it is important to distinguish between weight and mass. Mass is intrinsic to matter, but weight is the force of gravity on that mass. Remember, F=ma. The acceleration due to gravity does not ...
... Students may be confused by this because they know that more massive objects weigh more. While this is true, it is important to distinguish between weight and mass. Mass is intrinsic to matter, but weight is the force of gravity on that mass. Remember, F=ma. The acceleration due to gravity does not ...
The conservation laws in the field theoretical representation of
... not really belong to the field and is only meant to avoid a singularity. Rather, here it represents an actual field quantity which is determined by the field equations. Similarly, the zero divergence of the matter tensor is no longer a heuristic principle for obtaining the dynamics in addition to th ...
... not really belong to the field and is only meant to avoid a singularity. Rather, here it represents an actual field quantity which is determined by the field equations. Similarly, the zero divergence of the matter tensor is no longer a heuristic principle for obtaining the dynamics in addition to th ...
fundamental topics in physics
... when the electric field of the incident beam is polarised perpendicular to the plane of incidence. i and t are the angles of incidence and transmission respectively. (i) Use equation (1) to show that the reflected beam is in phase with the incident beam when n1 > n2, and that the two beams are out ...
... when the electric field of the incident beam is polarised perpendicular to the plane of incidence. i and t are the angles of incidence and transmission respectively. (i) Use equation (1) to show that the reflected beam is in phase with the incident beam when n1 > n2, and that the two beams are out ...
Unit 4 - Wsfcs
... 5. For what values of s does T(s) make sense in the context of the problem? Ex: Sally can paint a classroom in 7 hours. John can paint a classroom in 5 hours. How long will it take them to paint a classroom if they work together? A.CED.2 Create equations in two or more variables to represent relatio ...
... 5. For what values of s does T(s) make sense in the context of the problem? Ex: Sally can paint a classroom in 7 hours. John can paint a classroom in 5 hours. How long will it take them to paint a classroom if they work together? A.CED.2 Create equations in two or more variables to represent relatio ...
Lecture 14ba
... • Newton’s 1st Law (rotational language version): “A rotating body will continue to rotate at a constant angular velocity unless an external TORQUE acts.” • Clearly, to understand this, we need to define the concept of TORQUE. • Newton’s 2nd Law (rotational language version): Also needs torque. ...
... • Newton’s 1st Law (rotational language version): “A rotating body will continue to rotate at a constant angular velocity unless an external TORQUE acts.” • Clearly, to understand this, we need to define the concept of TORQUE. • Newton’s 2nd Law (rotational language version): Also needs torque. ...