1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equilibrium & revision
... A) The tension in the robe is equal to her weight B) The tension in the robe is equal to her mass times her acceleration C) Her acceleration is downward and equal to g (9.8 m/s2) D) Her acceleration is zero E) Her acceleration is equal to her velocity squared divided by the length of the swing. ...
... A) The tension in the robe is equal to her weight B) The tension in the robe is equal to her mass times her acceleration C) Her acceleration is downward and equal to g (9.8 m/s2) D) Her acceleration is zero E) Her acceleration is equal to her velocity squared divided by the length of the swing. ...
Forces HW-1
... (b) If the parachutist comes to rest in a shorter distance, the acceleration will be greater so the net force will be greater, so the force of the ground on the parachutist will therefore be greater. You must provide an equation that shows acceleration’s dependence on stopping distance. (a) = 5146 ...
... (b) If the parachutist comes to rest in a shorter distance, the acceleration will be greater so the net force will be greater, so the force of the ground on the parachutist will therefore be greater. You must provide an equation that shows acceleration’s dependence on stopping distance. (a) = 5146 ...
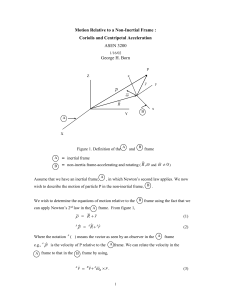
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT ap ...
... equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT ap ...
Chap. 7 Momentum - Coal City Unit District #1
... Newton’s 3rd Law: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
Force and Energy
... 1 A body at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line remains in that state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an outside force. If you are moving at constant speed in a circle, are you accelerating? ...
... 1 A body at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line remains in that state of rest or motion unless acted upon by an outside force. If you are moving at constant speed in a circle, are you accelerating? ...
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 4
... Consider the forces acting on your foot, when your feet are spread apart at an angle θ, as shown in the figure to the right. The frictional force, F~f , preventing you from sliding points to the right, the normal force F~N points vertically, while the force of your weight, F~W , points at an angle, ...
... Consider the forces acting on your foot, when your feet are spread apart at an angle θ, as shown in the figure to the right. The frictional force, F~f , preventing you from sliding points to the right, the normal force F~N points vertically, while the force of your weight, F~W , points at an angle, ...
Friction, Circular Motion, Drag Forces 5
... Example 5-9: Moon’s centripetal acceleration. The Moon’s nearly circular orbit about the Earth has a radius of about 384,000 km and a period T of 27.3 days. Determine the acceleration of the Moon toward the Earth. ...
... Example 5-9: Moon’s centripetal acceleration. The Moon’s nearly circular orbit about the Earth has a radius of about 384,000 km and a period T of 27.3 days. Determine the acceleration of the Moon toward the Earth. ...
Part I
... they correspond to the low frequency, long wavelength limit of the more general lattice vibrations we have been considering up to now. • At a given frequency and in a given direction in a crystal it is possible to transmit 3 different kinds of sound waves, differing in their direction of polarizatio ...
... they correspond to the low frequency, long wavelength limit of the more general lattice vibrations we have been considering up to now. • At a given frequency and in a given direction in a crystal it is possible to transmit 3 different kinds of sound waves, differing in their direction of polarizatio ...
Total Time
... distance between the dominoes. Write your predictions. Repeat steps 2 & 3 several times using distances between the dominoes that are smaller and larger than the distance used in your first setup. Use the same number of dominoes in each trial. Calculate the average speed for each trial by dividing t ...
... distance between the dominoes. Write your predictions. Repeat steps 2 & 3 several times using distances between the dominoes that are smaller and larger than the distance used in your first setup. Use the same number of dominoes in each trial. Calculate the average speed for each trial by dividing t ...
Chapter 1 Matter in Motion
... Given an object in motion, calculate its speed (distance/time). Interpret a line graph representing an object’s motion in terms of distance over time (speed) using metric units. Explain every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. Recognize an object’s weight is a m ...
... Given an object in motion, calculate its speed (distance/time). Interpret a line graph representing an object’s motion in terms of distance over time (speed) using metric units. Explain every object exerts a gravitational force of attraction on every other object. Recognize an object’s weight is a m ...
Balloon Racer Unit Overview Unit Title: Force and Motion Lesson
... Remember: F=ma, if F goes up then "a" goes up, if "m" goes up "a" goes down. In this activity the effects of friction (drag) and air resistance are ignored. Work with a colleague to test this investigation in advance, so you can judge difficulties that may arise. Management of classroom space, m ...
... Remember: F=ma, if F goes up then "a" goes up, if "m" goes up "a" goes down. In this activity the effects of friction (drag) and air resistance are ignored. Work with a colleague to test this investigation in advance, so you can judge difficulties that may arise. Management of classroom space, m ...
Chapter 5
... • In motion through air at the speed of a tossed tennis ball or faster, the resisting force is approximately proportional to v2 rather than v. It is then called air drag or simply drag. Airplanes, falling raindrops, and bicyclists all experience air drag. The air drag on a typical car is negligible ...
... • In motion through air at the speed of a tossed tennis ball or faster, the resisting force is approximately proportional to v2 rather than v. It is then called air drag or simply drag. Airplanes, falling raindrops, and bicyclists all experience air drag. The air drag on a typical car is negligible ...
Physics v. 2016
... the resulting acceleration using Newton’s Second Law of Motion. Use Newton’s Third Law to explain forces as interactions between bodies. 3.2.P .B1. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of objects. 3.2.P .B6. PATTERNS, SCALE MODELS, CONSTANCY/CHANGE Use Newton’ ...
... the resulting acceleration using Newton’s Second Law of Motion. Use Newton’s Third Law to explain forces as interactions between bodies. 3.2.P .B1. Use force and mass to explain translational motion or simple harmonic motion of objects. 3.2.P .B6. PATTERNS, SCALE MODELS, CONSTANCY/CHANGE Use Newton’ ...
Document
... Consider a block of mass “m” which is suspended from a fixed beam by means of a string. The string is assumed to be light and inextensible. The string is stretched, since it is being pulled at both ends by the block and the beam. The string must be being pulled by oppositely directed forces of the s ...
... Consider a block of mass “m” which is suspended from a fixed beam by means of a string. The string is assumed to be light and inextensible. The string is stretched, since it is being pulled at both ends by the block and the beam. The string must be being pulled by oppositely directed forces of the s ...