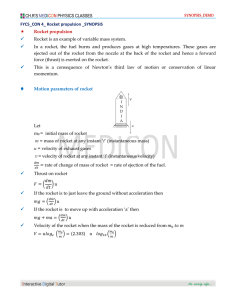
File - wentworth science
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
21 circ motion gravitation mc File
... downward (E) straight along the connecting string toward point P (the pivot) 27. A 4.0 kg mass is attached to one end of a rope 2 m long. If the mass is swung in a vertical circle from the free end of the rope, what is the tension in the rope when the mass is at its highest point if it is moving wit ...
... downward (E) straight along the connecting string toward point P (the pivot) 27. A 4.0 kg mass is attached to one end of a rope 2 m long. If the mass is swung in a vertical circle from the free end of the rope, what is the tension in the rope when the mass is at its highest point if it is moving wit ...
Newton`s Third Law of Motion CHECK YOUR ANSWER
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
ch07-4 - Physics-YISS
... Conceptual Example 4 Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Ans ...
... Conceptual Example 4 Is the Total Momentum Conserved? Imagine two balls colliding on a billiard table that is friction-free. Use the momentum conservation principle in answering the following questions. (a) Is the total momentum of the two-ball system the same before and after the collision? (b) Ans ...
Chapter 4 Kinematics In Two Dimensions
... displacement, velocity, and acceleration of a body are vector quantities, we did not write them in the traditional boldface type, characteristic of vectors. We took into account their vector character by noting that when the displacement, velocity, and acceleration were in the positive x- or y-direc ...
... displacement, velocity, and acceleration of a body are vector quantities, we did not write them in the traditional boldface type, characteristic of vectors. We took into account their vector character by noting that when the displacement, velocity, and acceleration were in the positive x- or y-direc ...
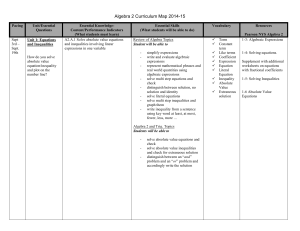
Pacing
... form of the equation identify the y-intercept as ( 0, c ) find the vertex of a parabola algebraically using the standard form of the equation identify the range of parabolas sketch a graph of a parabola after finding the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and the y-intercept use the calculator to find a ...
... form of the equation identify the y-intercept as ( 0, c ) find the vertex of a parabola algebraically using the standard form of the equation identify the range of parabolas sketch a graph of a parabola after finding the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and the y-intercept use the calculator to find a ...
2 - SVHSAlgebra1
... 2. One auto repair shop charges $30 for a diagnosis and $25 per hour for labor. Another auto repair shop charges $35 per hour for labor. For how many hours are the total charges for both of the shops the same? ANSWER ...
... 2. One auto repair shop charges $30 for a diagnosis and $25 per hour for labor. Another auto repair shop charges $35 per hour for labor. For how many hours are the total charges for both of the shops the same? ANSWER ...
July 2016 Exam Review
... Recall that the centripetal acceleration of the stone is v2/r, and if the speed is constant, then so is the centripetal acceleration. How can it be that the centripetal acceleration, which points towards the centre of the circle, is constant even though the direction of the weight force, which is do ...
... Recall that the centripetal acceleration of the stone is v2/r, and if the speed is constant, then so is the centripetal acceleration. How can it be that the centripetal acceleration, which points towards the centre of the circle, is constant even though the direction of the weight force, which is do ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
Understanding Circular Motion
... Experiment One: Speed (v) and Inward Acting Force (Fi) In this experiment you will keep the spinning radius constant and change the weight of the hanging mass. G. Find the mass of the rubber stopper and record in Table 1. H. Adjust the string so that the distance between the top of the tube and the ...
... Experiment One: Speed (v) and Inward Acting Force (Fi) In this experiment you will keep the spinning radius constant and change the weight of the hanging mass. G. Find the mass of the rubber stopper and record in Table 1. H. Adjust the string so that the distance between the top of the tube and the ...
Proposal-Use
... were explicit. In the first case, an object is moving with a constant velocity, most students viewed that there was a non-zero net force acting on the object in the direction of motion. Some students think that the net force will decrease in the direction of motion. In the second case, an object is ...
... were explicit. In the first case, an object is moving with a constant velocity, most students viewed that there was a non-zero net force acting on the object in the direction of motion. Some students think that the net force will decrease in the direction of motion. In the second case, an object is ...
Chapter 5 Forces
... • Newton’s Second Law – If there is a non-zero net force on a body, then it will accelerate. • Newton’s Second Law describes a Nonequilibrium Situation. • A Non-equilibrium Situation is one in which the acceleration of a body is not equal to zero. ...
... • Newton’s Second Law – If there is a non-zero net force on a body, then it will accelerate. • Newton’s Second Law describes a Nonequilibrium Situation. • A Non-equilibrium Situation is one in which the acceleration of a body is not equal to zero. ...