A) kg × m s2 B) kg × m 2 C) kg × m s2 D) kg2 × m s2 1. A force of 1
... has the same texture as surface A, but twice the area of surface A ...
... has the same texture as surface A, but twice the area of surface A ...
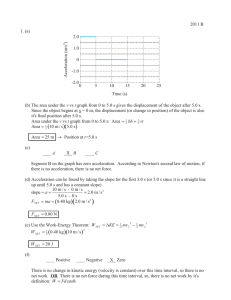
2011 B 1. (a) 2.0 0
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
... (b) Using the chalk, mark a starting line on the track. Using a tape metric measure or a meter stick, measure 10 m distances (marked by a chalk-line) up to, and including, 100 m (which is the finish line). Position one student, who has the starter's pistol, at the starting line. The ten other studen ...
AHSGE Review
... Zookeepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the lion’s upward acceleration is 0.657 m/s2. What is the unbalanced force necessary to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? ...
... Zookeepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the lion’s upward acceleration is 0.657 m/s2. What is the unbalanced force necessary to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? ...
Lecture 16
... • We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origi ...
... • We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origi ...
MOTION THE LAWS OF NEWTON
... Write your own song, rap, poem or story about Newton’s Laws of Motion. Your composition must include the following: 1. Explanation of Law 1 2. Example of Law 1 from everyday life 3. Explanation of Law 2 ( must include the equation F=m*a) 4. Example of Law 2 from everyday life 5. Explanation of Law 3 ...
... Write your own song, rap, poem or story about Newton’s Laws of Motion. Your composition must include the following: 1. Explanation of Law 1 2. Example of Law 1 from everyday life 3. Explanation of Law 2 ( must include the equation F=m*a) 4. Example of Law 2 from everyday life 5. Explanation of Law 3 ...
motion - Images
... All matter is in constant motion • Motion is any change in position • Relative Motion is used to recognize a change in position by using a point of reference – An object changes positions if it moves relative to a reference point ...
... All matter is in constant motion • Motion is any change in position • Relative Motion is used to recognize a change in position by using a point of reference – An object changes positions if it moves relative to a reference point ...
Physics Semester Exam Study Guide January 2013 Answer Section
... 57. Which of the following is an area of physics that studies motion and its causes? 58. What is a term for the quantity Ft, where F is an applied force and t is the time interval over which the force is applied? ...
... 57. Which of the following is an area of physics that studies motion and its causes? 58. What is a term for the quantity Ft, where F is an applied force and t is the time interval over which the force is applied? ...
For this basic module we simply take the suitable backbone... " This module is the newest and updated version. The module... Introduction to Materials
... First we notice that while the individual fly moves around quite fast, its vector velocity vi averaged over time t,t, must be zero as long as the swarm as an ensemble doesn't move.
In other words, the flies, on average, move just as often to the left as to the right, etc. The net current produc ...
... First we notice that while the individual fly moves around quite fast, its vector velocity vi averaged over time t,
Final Review Powerpoint
... changes as a function of TIME (t). The rate at which Displacement changes is also called VELOCITY. Thus if we use our derivative we can find out how fast the object is traveling at t = 2 second. Since dx/dt = 3kt2=3(1)(2)2= 12 m/s ...
... changes as a function of TIME (t). The rate at which Displacement changes is also called VELOCITY. Thus if we use our derivative we can find out how fast the object is traveling at t = 2 second. Since dx/dt = 3kt2=3(1)(2)2= 12 m/s ...
AP Physics C IB
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
... Ex. Apparent weight of a 72 kg person in an elevator given by the scale reading (normal force). Find the apparent weight when a) the elevator is at rest or moving at a constant velocity b) accelerating upward at 3.20 m/s2 and c) accelerating downward at 3.20 m/s2. ...
Physics Review
... 1. What is the formula you use to find the speed of an object? speed=distance/time 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving and velocity is the same except it takes in to consideration a certain direction the object is moving. 3. An obj ...
... 1. What is the formula you use to find the speed of an object? speed=distance/time 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving and velocity is the same except it takes in to consideration a certain direction the object is moving. 3. An obj ...
Measurments
... established is an adaptation of the metric system, and it is called the SI system of units. (The abbreviation SI comes from the system’s French name “Système International.”) In this system, the units of length, mass, and time are the meter, kilogram, and second, respectively [Kms] ...
... established is an adaptation of the metric system, and it is called the SI system of units. (The abbreviation SI comes from the system’s French name “Système International.”) In this system, the units of length, mass, and time are the meter, kilogram, and second, respectively [Kms] ...
Rotation Torque, Rolling, & Angular Momentum
... Instantaneous angular velocity is derivative of function for angular position: (t) Angular acceleration is the derivative of velocity: (t) The same acceleration-a/displacement-d/velocity-v equations (from kinematics) are used for // s (the arc length) = r …taking the derivative of above: v=r, ...
... Instantaneous angular velocity is derivative of function for angular position: (t) Angular acceleration is the derivative of velocity: (t) The same acceleration-a/displacement-d/velocity-v equations (from kinematics) are used for // s (the arc length) = r …taking the derivative of above: v=r, ...
AP Physics C - Heritage High School
... • If a force is internal to a system the total momentum of the system does not change • Only external forces will cause acceleration or a change in momentum. • Usually we can expand the system so that all ...
... • If a force is internal to a system the total momentum of the system does not change • Only external forces will cause acceleration or a change in momentum. • Usually we can expand the system so that all ...
Jeopardy
... $500 Answer from Velocity How quick can Chuck Norris get in bed after turning off the light ? ...
... $500 Answer from Velocity How quick can Chuck Norris get in bed after turning off the light ? ...