to - GEOCITIES.ws
... We know that they are at the same location when the cross, so final positions are equal. ...
... We know that they are at the same location when the cross, so final positions are equal. ...
Rotational Energy and Momentum
... If no net external torques act on a system then the system’s angular momentum, L, remains constant. Speed and radius can change just as long as angular momentum is constant. ...
... If no net external torques act on a system then the system’s angular momentum, L, remains constant. Speed and radius can change just as long as angular momentum is constant. ...
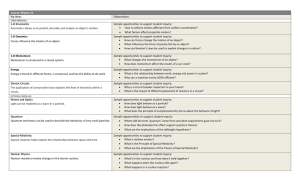
Equilibrium of a Particle
... Best representation of all the unknown forces (∑F) which acts on a body A sketch showing the particle “free” from the surroundings with all the forces acting on it Consider two common connections in this subject – Spring Cables and Pulleys ...
... Best representation of all the unknown forces (∑F) which acts on a body A sketch showing the particle “free” from the surroundings with all the forces acting on it Consider two common connections in this subject – Spring Cables and Pulleys ...
Forces Accelerate
... Finally, you learned that the unit of force is a Newton, N. One Newton (N) is defined as: N = kg x m/ s2 This is about the weight you feel in your hand when you hold a couple of apples. Can you see now why we multiplied mass in kg times 9.8 to find weight in Newtons? When you do the calculation you ...
... Finally, you learned that the unit of force is a Newton, N. One Newton (N) is defined as: N = kg x m/ s2 This is about the weight you feel in your hand when you hold a couple of apples. Can you see now why we multiplied mass in kg times 9.8 to find weight in Newtons? When you do the calculation you ...
17 M3 January 2006
... A body consists of a uniform solid circular cylinder C, together with a uniform solid hemisphere H which is attached to C. The plane face of H coincides with the upper plane face of C, as shown in Figure 2. The cylinder C has base radius r, height h and mass 3M. The mass of H is 2M. The point O is t ...
... A body consists of a uniform solid circular cylinder C, together with a uniform solid hemisphere H which is attached to C. The plane face of H coincides with the upper plane face of C, as shown in Figure 2. The cylinder C has base radius r, height h and mass 3M. The mass of H is 2M. The point O is t ...
Sect. 2.5 - TTU Physics
... Work & Energy • Definition: A particle is acted on by a total force F. The Work done on the particle in moving it from (arbitrary) position 1 to (arbitrary) position 2 in space is defined as line integral (limits from 1 to 2): W12 ∫ Fdr • By Newton’s 2nd Law (using chain rule of differentiation) ...
... Work & Energy • Definition: A particle is acted on by a total force F. The Work done on the particle in moving it from (arbitrary) position 1 to (arbitrary) position 2 in space is defined as line integral (limits from 1 to 2): W12 ∫ Fdr • By Newton’s 2nd Law (using chain rule of differentiation) ...
motion in two dimension
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 1. When it is acted on by an unbalanced force, an object will __________________________. 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object at rest, the object will ___________________________. 3. A change in velocity is called an _____________________________. 4. A large force will cause ______________ ...
... 1. When it is acted on by an unbalanced force, an object will __________________________. 2. When an unbalanced force acts on an object at rest, the object will ___________________________. 3. A change in velocity is called an _____________________________. 4. A large force will cause ______________ ...
Question Bank - India Study Channel
... (a) a book lying on a table (b) firing of bullet from a gun 25. Do action and reaction act on the same body or different bodies? How are they related in magnitude and direction? 26. A 2000 kg car traveling at 72 kmph ran into a concrete wall and stopped in 0.05 sec. What impulse did the wall exert o ...
... (a) a book lying on a table (b) firing of bullet from a gun 25. Do action and reaction act on the same body or different bodies? How are they related in magnitude and direction? 26. A 2000 kg car traveling at 72 kmph ran into a concrete wall and stopped in 0.05 sec. What impulse did the wall exert o ...
Circular Motion
... rotations per unit of time Example: Carousel horses travel at same rotational speed but different tangential speed ...
... rotations per unit of time Example: Carousel horses travel at same rotational speed but different tangential speed ...
Course: Physics 11 Big Ideas Elaborations: CORE MODULES: 1
... Elaborations: 1-D Kinematics vector: e.g., solve for vector components and vector addition projectile motion principles: vertical projectiles and simple 2-D projectiles (e.g., cannon being fired off cliff) the relationship between variables: Refer to the formula sheet 1-D Dynamics gravitational forc ...
... Elaborations: 1-D Kinematics vector: e.g., solve for vector components and vector addition projectile motion principles: vertical projectiles and simple 2-D projectiles (e.g., cannon being fired off cliff) the relationship between variables: Refer to the formula sheet 1-D Dynamics gravitational forc ...
Lectures in physics Part 1: Mechanics Przemysław Borys 7.11.2013
... terms of simple numbers. An example of such quantity is the velocity. It is not sufficient to say that a car moves at 50km/h, we need to supplement this idea by the direction he moves to. A quantity which consists of a magnitude and the direction information is called a vector. A vector can be of tw ...
... terms of simple numbers. An example of such quantity is the velocity. It is not sufficient to say that a car moves at 50km/h, we need to supplement this idea by the direction he moves to. A quantity which consists of a magnitude and the direction information is called a vector. A vector can be of tw ...
Document
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
drburtsphysicsnotes2 - hardingscienceinstitute
... What is the sum of the forces on you right now Assume you are not moving relative to other objects on earth (even though we are moving relative to the rest of the solar system) ...
... What is the sum of the forces on you right now Assume you are not moving relative to other objects on earth (even though we are moving relative to the rest of the solar system) ...