Review E: Simple Harmonic Motion and Mechanical Energy
... An object of mass m = 4.0 ×10−2 kg sitting on a frictionless surface is attached to one end of a spring. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall. Assume that the object is constrained to move horizontally along one dimension. The spring has spring constant k = 2.0 × 102 N/ m . The spring i ...
... An object of mass m = 4.0 ×10−2 kg sitting on a frictionless surface is attached to one end of a spring. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall. Assume that the object is constrained to move horizontally along one dimension. The spring has spring constant k = 2.0 × 102 N/ m . The spring i ...
Chapter 5 - KFUPM Faculty List
... is called classical or Newtonian mechanics. The fundamental relations of classical mechanics are contained in Newton’s Laws of motion that we will discuss three of them in this chapter. Newton’s First Law If a body is a rest, it stays at rest. If it is in motion with constant velocity, it will conti ...
... is called classical or Newtonian mechanics. The fundamental relations of classical mechanics are contained in Newton’s Laws of motion that we will discuss three of them in this chapter. Newton’s First Law If a body is a rest, it stays at rest. If it is in motion with constant velocity, it will conti ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. How would you write this la ...
... been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. How would you write this la ...
Are You suprised
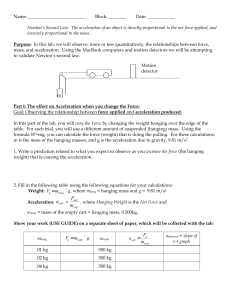
... 2. Fill in the following table using the following equations for your calculations: Weight: Fg = mhang ´ g , where mhang = hanging mass and g = 9.81 m/s2 Acceleration: acalc ...
... 2. Fill in the following table using the following equations for your calculations: Weight: Fg = mhang ´ g , where mhang = hanging mass and g = 9.81 m/s2 Acceleration: acalc ...
Velocity is - Noadswood Science
... Quick quiz • What can the motion be like of an object with BALANCED forces? (2 marks) • What can the motion be like of an object with UNBALANCED forces (2 marks) • How do you work out speed? • What does this distance time graph tell you about the journey? ...
... Quick quiz • What can the motion be like of an object with BALANCED forces? (2 marks) • What can the motion be like of an object with UNBALANCED forces (2 marks) • How do you work out speed? • What does this distance time graph tell you about the journey? ...
what is a force?
... The Second Law: – if the mass of an object does not change the acceleration of the object will increase when a larger force is applied. – If the same amount of force is exerted on the objects, then the acceleration of the larger mass will be ...
... The Second Law: – if the mass of an object does not change the acceleration of the object will increase when a larger force is applied. – If the same amount of force is exerted on the objects, then the acceleration of the larger mass will be ...
Newton`s Laws
... forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the first object is opposite to the direction of the force on the second object. ...
... forces acting on the two interacting objects. The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object. The direction of the force on the first object is opposite to the direction of the force on the second object. ...
2nd Term Exam - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... c) All points on the body are moving with the same linear velocity. d) Its center of rotation is at rest, i.e., not moving. 24. Consider two uniform solid spheres where both have the same diameter, but one has twice the mass of the other. The ratio of the larger moment of inertia to that of the smal ...
... c) All points on the body are moving with the same linear velocity. d) Its center of rotation is at rest, i.e., not moving. 24. Consider two uniform solid spheres where both have the same diameter, but one has twice the mass of the other. The ratio of the larger moment of inertia to that of the smal ...
document
... Question 3: Consider a heavy, 16 pound bowling ball at rest with a string tied to it, and the string is pulled with a constant force for one second, causing the ball to move across a nearly frictionless floor. Repeat this experiment with an 8 pound bowling ball, using the same force also for one se ...
... Question 3: Consider a heavy, 16 pound bowling ball at rest with a string tied to it, and the string is pulled with a constant force for one second, causing the ball to move across a nearly frictionless floor. Repeat this experiment with an 8 pound bowling ball, using the same force also for one se ...