Summary of Chapters 1-3 Equations of motion for a uniformly acclerating object
... A mass at rest on a ramp. Gravity applies a 100 N gravitational force to an object at rest on a 15° ramp. Component of gravity pulls the mass down the the ramp ...
... A mass at rest on a ramp. Gravity applies a 100 N gravitational force to an object at rest on a 15° ramp. Component of gravity pulls the mass down the the ramp ...
what happens when an object changes direction
... straight line, circular, erratic? How does the ball change its motion if you hit it on the side with your hand or a club? Draw a conclusion about whether a force must be applied to the object while it moves to get it to change direction. b)Using such a ball is also a good approach for experimenting ...
... straight line, circular, erratic? How does the ball change its motion if you hit it on the side with your hand or a club? Draw a conclusion about whether a force must be applied to the object while it moves to get it to change direction. b)Using such a ball is also a good approach for experimenting ...
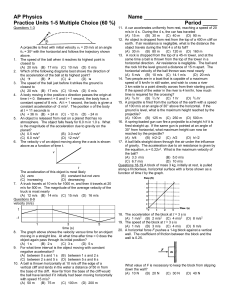
AP Physics
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
... m/s in 4 s. During the 4 s, the car has traveled (A) 15 m (B) 30 m (C) 40 m (D) 90 m 12. An object is dropped from rest from the top of a 400 m cliff on earth. If air resistance is negligible, what is the distance the object travels during the first 4 s of its fall? (A) 30 m (B) 80 m (C) 120 m (D) 1 ...
Rigid Body - GEOCITIES.ws
... Set the turntable rotating with an angular velocity Drop a small mass to the platform, changes to a lower value ’ If there is no frictional couple, the angular momentum is conserved, I = I’ ’ = (I + mr2) ’ ...
... Set the turntable rotating with an angular velocity Drop a small mass to the platform, changes to a lower value ’ If there is no frictional couple, the angular momentum is conserved, I = I’ ’ = (I + mr2) ’ ...
Elements of Physics
... l. Newton showed the is held in its orbit by the Earth's gravity 3. major tool of physics 4. astronomer who concluded the sun was the center of the universe 5. for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction is the 6. his theory showed that gravity affects light 7. total quantity of an obje ...
... l. Newton showed the is held in its orbit by the Earth's gravity 3. major tool of physics 4. astronomer who concluded the sun was the center of the universe 5. for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction is the 6. his theory showed that gravity affects light 7. total quantity of an obje ...
Unbalanced Forces & Acceleration
... • The forces that two objects exert on each other are called force pairs. • The pairs are opposite in direction. ...
... • The forces that two objects exert on each other are called force pairs. • The pairs are opposite in direction. ...
Conservation Of Momentum
... system – two or more objects that interact with each other during an event. They experience equal and opposite forces during the event, so they have the same impulse. event – the physical interaction between two or more objects during which an impulse occurs. collisions and explosions. Events are de ...
... system – two or more objects that interact with each other during an event. They experience equal and opposite forces during the event, so they have the same impulse. event – the physical interaction between two or more objects during which an impulse occurs. collisions and explosions. Events are de ...
Kinetic energy of rolling.
... Torque is calculated with respect to (about) a point. Changing the point can change the torque’s magnitude and direction. ...
... Torque is calculated with respect to (about) a point. Changing the point can change the torque’s magnitude and direction. ...
Question 7 - Flipped Physics
... mass m by a cord that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown above. If the masses of the cord and the pulley are negligible, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the descending block? (A) Zero (B) g/4 (C) g/3 (D) 2g/3 (E) g 18. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left al ...
... mass m by a cord that passes over a frictionless pulley, as shown above. If the masses of the cord and the pulley are negligible, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the descending block? (A) Zero (B) g/4 (C) g/3 (D) 2g/3 (E) g 18. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left al ...
Acceleration due to gravity
... Here, the parameters vo and g are, respectively, the initial velocity and the acceleration. Galileo first demonstrated this result when he dropped cannonballs of different masses (weights) from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to show that although they had different masses, when dropped together, they lan ...
... Here, the parameters vo and g are, respectively, the initial velocity and the acceleration. Galileo first demonstrated this result when he dropped cannonballs of different masses (weights) from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to show that although they had different masses, when dropped together, they lan ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Explain terminal speed and velocity. Use motion graphs and free-body diagrams to illustrate falling objects. Explain how acceleration rates change for falling objects as they approach terminal velocity. 10. Evaluate differences in how object fall through the atmosphere. 11. Explain the two component ...
... Explain terminal speed and velocity. Use motion graphs and free-body diagrams to illustrate falling objects. Explain how acceleration rates change for falling objects as they approach terminal velocity. 10. Evaluate differences in how object fall through the atmosphere. 11. Explain the two component ...
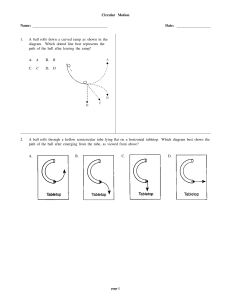
Reading - The Centripetal Force Requirement
... an unbalanced force can change the direction of velocity but not its magnitude still indicates that the velocity has changed and therefore, by definition, the object has accelerated. ...
... an unbalanced force can change the direction of velocity but not its magnitude still indicates that the velocity has changed and therefore, by definition, the object has accelerated. ...