Stacey Carpenter
... Friction always acts opposite to the direction of force or motion. If there is no force in a direction, there is no friction in the opposite direction. There are two main kinds of friction, static and sliding. Both increase if the force between the two objects increases. For example, a heavier objec ...
... Friction always acts opposite to the direction of force or motion. If there is no force in a direction, there is no friction in the opposite direction. There are two main kinds of friction, static and sliding. Both increase if the force between the two objects increases. For example, a heavier objec ...
Dynamics Notes/Labs/HW
... two objects. A single object does not have a force by default, as the force is defined through the interaction of two objects. Remember that all physical quantities are measured in units. The unit of force is called the newton (N), where 1 N = (1 kg)(1 m/s2). d) How could you label this force arrow ...
... two objects. A single object does not have a force by default, as the force is defined through the interaction of two objects. Remember that all physical quantities are measured in units. The unit of force is called the newton (N), where 1 N = (1 kg)(1 m/s2). d) How could you label this force arrow ...
Force, Momentum and Impulse
... De nition 1: Newton's First Law of Motion An object will remain in a state of rest or continue traveling at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced (net) force. Let us consider the following situations: An ice skater pushes herself away from the side of the ice rink and skates across t ...
... De nition 1: Newton's First Law of Motion An object will remain in a state of rest or continue traveling at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced (net) force. Let us consider the following situations: An ice skater pushes herself away from the side of the ice rink and skates across t ...
Calculus-Based Physics I
... to be read/said: ‘x’ equals minus ‘b’, plus-or-minus the square root of ‘b’ squared minus four ‘a’ ‘c’, all over two ‘a’. So, how do you know when you have to use the quadratic formula? There is a good chance that you need it when the square of the variable for which you are solving, appears in the ...
... to be read/said: ‘x’ equals minus ‘b’, plus-or-minus the square root of ‘b’ squared minus four ‘a’ ‘c’, all over two ‘a’. So, how do you know when you have to use the quadratic formula? There is a good chance that you need it when the square of the variable for which you are solving, appears in the ...
Ch 05 Applying Newtons Laws
... 13) A 400-kg box is lifted vertically upward with constant velocity by means of two cables pulling at 40.0° on either side of the vertical direction. What is the tension in each cable? A) 231 N B) 400 N C) 800 N D) 2560 N E) 3920 N Answer: D Var: 1 14) A 10.0-kg picture is held in place by two wire ...
... 13) A 400-kg box is lifted vertically upward with constant velocity by means of two cables pulling at 40.0° on either side of the vertical direction. What is the tension in each cable? A) 231 N B) 400 N C) 800 N D) 2560 N E) 3920 N Answer: D Var: 1 14) A 10.0-kg picture is held in place by two wire ...
1 A car engine applies a force of 65 kN, how much work is done by
... 92. A 255 N force is applied to a 46 kg box that is located on a flat horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the surface is 0.3. a. Sketch a free-body diagram and show all the applied forces. b. Find the acceleration of the box c. How far the box will go in 10 s? ...
... 92. A 255 N force is applied to a 46 kg box that is located on a flat horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the surface is 0.3. a. Sketch a free-body diagram and show all the applied forces. b. Find the acceleration of the box c. How far the box will go in 10 s? ...
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
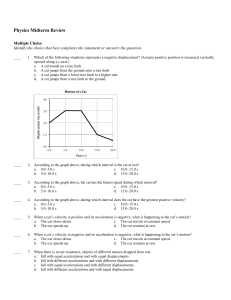
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
time of completion - Clayton State University
... 9.The driver of a truck slams on the brakes when he sees tree blocking the road. The truck slows down uniformly with an acceleration of -5.60 m/s2 for 4.20 s. If the truck was moving at 27.0 m/s the moment the driver sees the tree, a. With what speed does the truck hit the tree? V = V0 + a t V = (27 ...
... 9.The driver of a truck slams on the brakes when he sees tree blocking the road. The truck slows down uniformly with an acceleration of -5.60 m/s2 for 4.20 s. If the truck was moving at 27.0 m/s the moment the driver sees the tree, a. With what speed does the truck hit the tree? V = V0 + a t V = (27 ...
Friction - Study 4ur Success
... Contact forces − A contact force on an object arises due to contact with some other object − solid or fluid. Example− force of friction Friction − Friction is the property due to which force is set up at the surface of contact of the two bodies preventing any relative motion between them. ...
... Contact forces − A contact force on an object arises due to contact with some other object − solid or fluid. Example− force of friction Friction − Friction is the property due to which force is set up at the surface of contact of the two bodies preventing any relative motion between them. ...
Chapter 11 Equilibrium - Farmingdale State College
... rotates in a counterclockwise direction. Even though the first condition of equilibrium holds, the body is not in complete equilibrium because the seesaw has tilted. It is obvious that the first condition of equilibrium is not sufficient to describe equilibrium. The first condition takes care of the ...
... rotates in a counterclockwise direction. Even though the first condition of equilibrium holds, the body is not in complete equilibrium because the seesaw has tilted. It is obvious that the first condition of equilibrium is not sufficient to describe equilibrium. The first condition takes care of the ...
03_PearsonPhysics_ch03_1
... affect the motion of an object. When a driver suddenly applies the brakes, the seat belts of all occupants lock. If the vehicle collides head-on with another vehicle, airbags may become deployed. Both seat belts and airbags are designed to stop the forward motion of motorists during a head-on collis ...
... affect the motion of an object. When a driver suddenly applies the brakes, the seat belts of all occupants lock. If the vehicle collides head-on with another vehicle, airbags may become deployed. Both seat belts and airbags are designed to stop the forward motion of motorists during a head-on collis ...
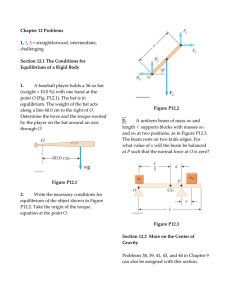
Chapter 12 Problems
... (a) By what distance will the rod compress the concrete when the original tension in the rod is released? (b) The rod will still be under what tension T2? (c) The rod will then be how much longer than its unstressed length? (d) When the concrete was poured, the rod should have been stretched by what ...
... (a) By what distance will the rod compress the concrete when the original tension in the rod is released? (b) The rod will still be under what tension T2? (c) The rod will then be how much longer than its unstressed length? (d) When the concrete was poured, the rod should have been stretched by what ...
Physics
... 39. A car travels 85 km in the first hour of a trip. The car continues to travel for 2 more hours and travels 200 km. What was the average speed of the car for the trip? a. 39 km/h b. 95 km/h c. 115 km/h d. 285 km/h 40. A runner rounding a curve on a track at a constant speed is an example of what t ...
... 39. A car travels 85 km in the first hour of a trip. The car continues to travel for 2 more hours and travels 200 km. What was the average speed of the car for the trip? a. 39 km/h b. 95 km/h c. 115 km/h d. 285 km/h 40. A runner rounding a curve on a track at a constant speed is an example of what t ...
Force - Montville.net
... Objects can speed up, slow down, and change direction while they move. In short, they accelerate. A famous scientist, Sir Isaac Newton, wondered how and why this occurs. Theories about acceleration existed, but Newton did not find them very convincing. His skepticism led him to some of the most impo ...
... Objects can speed up, slow down, and change direction while they move. In short, they accelerate. A famous scientist, Sir Isaac Newton, wondered how and why this occurs. Theories about acceleration existed, but Newton did not find them very convincing. His skepticism led him to some of the most impo ...
Chapter 4: Circular Motion
... direction of the object’s acceleration and the direction of the sum of the forces exerted on it by other objects. However, this knowledge is not enough to answer the questions posed at the beginning of the chapter, as we do not know how to determine the magnitude of object’s acceleration. First, let ...
... direction of the object’s acceleration and the direction of the sum of the forces exerted on it by other objects. However, this knowledge is not enough to answer the questions posed at the beginning of the chapter, as we do not know how to determine the magnitude of object’s acceleration. First, let ...
Simple Machines: Pulley
... amount of substance of an object. In the metric system, mass is measured in kilograms (kg). There is a platinum-iridium cylinder kept at the international Bureau of Weights and Measures in France that by definition has the mass of 1 kg. The mass of other objects can be found through the use of an eq ...
... amount of substance of an object. In the metric system, mass is measured in kilograms (kg). There is a platinum-iridium cylinder kept at the international Bureau of Weights and Measures in France that by definition has the mass of 1 kg. The mass of other objects can be found through the use of an eq ...
chapter 3 part 1
... identified: the distinction between forces that act on an object and forces that act by the object. This leads to his Third Law of Motion: For every force by a first object on a second object, there is a force by the second object on the first object with the same magnitude but in the opposite direc ...
... identified: the distinction between forces that act on an object and forces that act by the object. This leads to his Third Law of Motion: For every force by a first object on a second object, there is a force by the second object on the first object with the same magnitude but in the opposite direc ...
02-12-2014 Forces and Wind
... - Balance between Pressure Gradient Force and Coriolis Force LOW PGF ...
... - Balance between Pressure Gradient Force and Coriolis Force LOW PGF ...
Chap05_Main
... which acts when there is no motion between the two surfaces, was opposing the motion. But static friction has a limit. Once the force is greater than this maximum static friction, the refrigerator begins moving. Then, kinetic friction, the force acting between the surfaces in relative motion, begins ...
... which acts when there is no motion between the two surfaces, was opposing the motion. But static friction has a limit. Once the force is greater than this maximum static friction, the refrigerator begins moving. Then, kinetic friction, the force acting between the surfaces in relative motion, begins ...
Newtons Lesson 10
... 5. When a person stands on a bathroom scale while on the elevator, what is his weight when the elevator is at rest? 6. Moving at constant speed? 7. What is the net force acting on the person? 8. What is the acceleration of the person? Elevator Accelerating Upward: 9. When the elevator accelerates up ...
... 5. When a person stands on a bathroom scale while on the elevator, what is his weight when the elevator is at rest? 6. Moving at constant speed? 7. What is the net force acting on the person? 8. What is the acceleration of the person? Elevator Accelerating Upward: 9. When the elevator accelerates up ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.