chapter14
... Assume the density is the same throughout the fluid. This means it is an incompressible liquid. The three forces are: Downward force on the top, P0A Upward on the bottom, PA Gravity acting downward, Mg The mass can be found from the density: M = ρ V = ρ A h. ...
... Assume the density is the same throughout the fluid. This means it is an incompressible liquid. The three forces are: Downward force on the top, P0A Upward on the bottom, PA Gravity acting downward, Mg The mass can be found from the density: M = ρ V = ρ A h. ...
Ch_3 Presentation
... Mass and Weight are not the same thing... Once again; mass is the amount of matter an object is composed of. Weight is the effect gravity has on an objects mass. If the Moon is said to have 1/5th the gravity of Earth, than what would be the weight of a 500lb object on the surface of the moon? Would ...
... Mass and Weight are not the same thing... Once again; mass is the amount of matter an object is composed of. Weight is the effect gravity has on an objects mass. If the Moon is said to have 1/5th the gravity of Earth, than what would be the weight of a 500lb object on the surface of the moon? Would ...
Physical Science Chapter 2
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion aka F=ma Force = mass x acceleration ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion aka F=ma Force = mass x acceleration ...
Physical Science: Test Force
... B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the force of friction 3. Which of the four main types of forces is the weakest? A. Electromagnetic ...
... B. Kinetic C. Sliding D. Inelastic E. Static 2. What is the unbalanced force that slows down a ball rolling across the floor? A. the force of gravity C. the force of inertia B. the force of momentum D. the force of friction 3. Which of the four main types of forces is the weakest? A. Electromagnetic ...
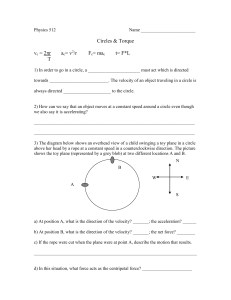
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
Forces and Motion Jeopardy
... A winding road is a series of inclined planes. How does a winding road make it easier for vehicles to travel up a hill? ...
... A winding road is a series of inclined planes. How does a winding road make it easier for vehicles to travel up a hill? ...
Forces Physical Science Chapter 2
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • The motion of all objects depends on the total of all forces acting on the object. • We call the total of all forces the net force. • Reminder – add forces acting in same direction, subtract, when in opposite ...
... Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • The motion of all objects depends on the total of all forces acting on the object. • We call the total of all forces the net force. • Reminder – add forces acting in same direction, subtract, when in opposite ...
Forces
... Detecting Motion • When gravity pulls an item downward, Newton’s third law states that the item is also pulling upward on the Earth. Since the Earth has such a large mass, its acceleration is so small, that we can’t see it. ...
... Detecting Motion • When gravity pulls an item downward, Newton’s third law states that the item is also pulling upward on the Earth. Since the Earth has such a large mass, its acceleration is so small, that we can’t see it. ...
Newton`s Laws powerpoint
... The air pushes up as gravity pulls down Dependent upon the shape and surface area of the object When the air resistance equals the force of gravity, terminal velocity is reached, and the object stops accelerating and falls at a constant speed Terminal velocity is the highest velocity that an object ...
... The air pushes up as gravity pulls down Dependent upon the shape and surface area of the object When the air resistance equals the force of gravity, terminal velocity is reached, and the object stops accelerating and falls at a constant speed Terminal velocity is the highest velocity that an object ...
Study guide for Chapter 2 Test: Forces
... The top speed an object reaches when being pulled downward by gravity. It occurs when gravity and air resistance (fluid friction) equal each other. When terminal velocity is reached, acceleration is at zero. Inertia ...
... The top speed an object reaches when being pulled downward by gravity. It occurs when gravity and air resistance (fluid friction) equal each other. When terminal velocity is reached, acceleration is at zero. Inertia ...
Chapter 6. Fluid Mechanics
... effected at that point, it should be clear that weight can be a source of pressure. For example, the pressure in the earth’s atmosphere decreases as one goes to higher altitude as the weight of the, or the amount of, fluid above is reduced. Similarly, an increase in pressure is felt by a diver who d ...
... effected at that point, it should be clear that weight can be a source of pressure. For example, the pressure in the earth’s atmosphere decreases as one goes to higher altitude as the weight of the, or the amount of, fluid above is reduced. Similarly, an increase in pressure is felt by a diver who d ...
1 Chapter 4: Forces and the Laws of Motion pages 119 144 Date __
... Freebody diagrams are diagrams to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. The tail of the arrow is attached to the object on which the force is acting. The size of the arrow reflects the __________________ of the force and the direction of the arrow shows the ...
... Freebody diagrams are diagrams to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. The tail of the arrow is attached to the object on which the force is acting. The size of the arrow reflects the __________________ of the force and the direction of the arrow shows the ...
Forces And Motion
... • Weight is the mass (kg) of an object multiplied by the acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s2). – The weight of an object depends on the gravitational pull of the location in the universe. – The gravitational pull on the Moon is only 1/6 of Earth’s ...
... • Weight is the mass (kg) of an object multiplied by the acceleration of gravity (9.8 m/s2). – The weight of an object depends on the gravitational pull of the location in the universe. – The gravitational pull on the Moon is only 1/6 of Earth’s ...
Gravity
... an object in motion tends to stay in motion until a force is exerted on it. 3______________________This is the combining of two or more forces on an object. 4______________________When two forces go against each other but are not equal. 5______________________When two forces work against each other ...
... an object in motion tends to stay in motion until a force is exerted on it. 3______________________This is the combining of two or more forces on an object. 4______________________When two forces go against each other but are not equal. 5______________________When two forces work against each other ...
Homework 10 - NMSU Physics
... inner ear. The outward force per unit area on your eardrum is greater than the inward force per unit area; therefore, your eardrum moves outward. b. As you climb down, the outside pressure becomes greater than the pressure in your inner ear. The outward force per unit area on your eardrum is less th ...
... inner ear. The outward force per unit area on your eardrum is greater than the inward force per unit area; therefore, your eardrum moves outward. b. As you climb down, the outside pressure becomes greater than the pressure in your inner ear. The outward force per unit area on your eardrum is less th ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... One way is to increase the force. If the mass is constant, acceleration and force change in the same way. So to increase the acceleration of the wagon, you increase the force used to pull it. Another way to increase acceleration is to change the mass. According to the equation, acceleration and ma ...
... One way is to increase the force. If the mass is constant, acceleration and force change in the same way. So to increase the acceleration of the wagon, you increase the force used to pull it. Another way to increase acceleration is to change the mass. According to the equation, acceleration and ma ...
Buoyancy
In science, buoyancy (pronunciation: /ˈbɔɪ.ənᵗsi/ or /ˈbuːjənᵗsi/; also known as upthrust) is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. This pressure difference results in a net upwards force on the object. The magnitude of that force exerted is proportional to that pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid.For this reason, an object whose density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is either less dense than the liquid or is shaped appropriately (as in a boat), the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a reference frame which either has a gravitational field or is accelerating due to a force other than gravity defining a ""downward"" direction (that is, a non-inertial reference frame). In a situation of fluid statics, the net upward buoyancy force is equal to the magnitude of the weight of fluid displaced by the body.The center of buoyancy of an object is the centroid of the displaced volume of fluid.