DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF GUIDED
... division multiplexed (WDM) related applications. In display applications TOFs have been being used as color filters (CF) to separate primary colors from incident white light. In this study, two types of TOFs have been designed and fabricated: 1) thermo-optic tunable optical filters (TOTOF) working i ...
... division multiplexed (WDM) related applications. In display applications TOFs have been being used as color filters (CF) to separate primary colors from incident white light. In this study, two types of TOFs have been designed and fabricated: 1) thermo-optic tunable optical filters (TOTOF) working i ...
3 PROGRAMMABLE APODIZERS AND FRESNEL LENSES pupils
... look at Table 3.2 we can see that the first minimum for the clear aperture is at ρ=0.60. Using this position as a reference, we determine if the other filters exhibit a transverse apodizing or hyperresolving performance. The bigger value is ρ=0.81 for the filter t(r)=1-r2 , and the smaller value is ...
... look at Table 3.2 we can see that the first minimum for the clear aperture is at ρ=0.60. Using this position as a reference, we determine if the other filters exhibit a transverse apodizing or hyperresolving performance. The bigger value is ρ=0.81 for the filter t(r)=1-r2 , and the smaller value is ...
Point spread function engineering in confocal scanning microscopy
... proposed [1]. Confocal scanning microscopes (CSM’s) are imaging systems in which the monochromatic light proceeding from a point source is focused onto a point of a 3D specimen by a high NA objective. Afterwards, the light emitted/reflected by the sample is collected by the same objective, passes th ...
... proposed [1]. Confocal scanning microscopes (CSM’s) are imaging systems in which the monochromatic light proceeding from a point source is focused onto a point of a 3D specimen by a high NA objective. Afterwards, the light emitted/reflected by the sample is collected by the same objective, passes th ...
Handbook of Optical Filters
... substrate) is usually composed of a material with low autofluorescence such as UV-grade fused silica. Most microscopes have a slider or turret that can hold from two to four individual filter cubes. It must be noted that the filters in each cube are a matched set, and one should avoid mixing filters ...
... substrate) is usually composed of a material with low autofluorescence such as UV-grade fused silica. Most microscopes have a slider or turret that can hold from two to four individual filter cubes. It must be noted that the filters in each cube are a matched set, and one should avoid mixing filters ...
Handbook of Optical Filters for Fluorescence Microscopy
... Several factors influence the amount of fluorescence emitted by a stained specimen with a given amount of excitation intensity. These include 1) the dye concentration within stained sections of the specimen, and the thickness of the specimen; 2) the extinction coefficient of the dye; 3) the quantum ...
... Several factors influence the amount of fluorescence emitted by a stained specimen with a given amount of excitation intensity. These include 1) the dye concentration within stained sections of the specimen, and the thickness of the specimen; 2) the extinction coefficient of the dye; 3) the quantum ...
Sidelobe decline in single-photon 4Pi microscopy by Toraldo rings
... Following the Toraldo’s method we have designed a pupil filter that consists of seven annular zones. As shown in Fig. 4 the zones have no absorption, having each pair of neighboring zones opposite phases. The normalized radii for the zones are r1 ¼ 0:41; r2 ¼ 0:56; r3 ¼ 0:73; r4 ¼ 0:83; r5 ¼ 0:91; r ...
... Following the Toraldo’s method we have designed a pupil filter that consists of seven annular zones. As shown in Fig. 4 the zones have no absorption, having each pair of neighboring zones opposite phases. The normalized radii for the zones are r1 ¼ 0:41; r2 ¼ 0:56; r3 ¼ 0:73; r4 ¼ 0:83; r5 ¼ 0:91; r ...
Optimally designed narrowband guided
... Since the introduction of narrowband reflectance filters using subwavelength periodic grating nanostructures [1–3], guided-mode resonance (GMR) filters (as they have come to be called, but also known as photonic crystal slabs or photonic crystal surfaces) have found application in label-free biodete ...
... Since the introduction of narrowband reflectance filters using subwavelength periodic grating nanostructures [1–3], guided-mode resonance (GMR) filters (as they have come to be called, but also known as photonic crystal slabs or photonic crystal surfaces) have found application in label-free biodete ...
Exemption Renewal Request Form
... cadmium and lead. Fluorescence spectroscopy is an analytical technique that is used for analysis of some types of organic substances, molecular biology (e.g. cell and tissue analysis), medical research, cancer detection and other medical diagnostic procedures and industrial applications such as semi ...
... cadmium and lead. Fluorescence spectroscopy is an analytical technique that is used for analysis of some types of organic substances, molecular biology (e.g. cell and tissue analysis), medical research, cancer detection and other medical diagnostic procedures and industrial applications such as semi ...
TAP 313 - 1: Polarisation of waves
... Light from a hot filament lamp is unpolarised (or rather, is emitted in randomly changing directions of polarisation). A polarising filter made of polaroid polarises the light. The filter passes components vibrating parallel to a special direction, and removes components vibrating perpendicular to t ...
... Light from a hot filament lamp is unpolarised (or rather, is emitted in randomly changing directions of polarisation). A polarising filter made of polaroid polarises the light. The filter passes components vibrating parallel to a special direction, and removes components vibrating perpendicular to t ...
Understanding Microscopy And Filtering Techniques
... additional 76.5mm of space between the tube lens and objective is optimal, but it is common to only use about 56.5mm of space between #55-743 and #58-329 since each adapter adds about 10mm of space. With this 56.5mm of space, use extension tubes or add other optical components such as beamsplitters, ...
... additional 76.5mm of space between the tube lens and objective is optimal, but it is common to only use about 56.5mm of space between #55-743 and #58-329 since each adapter adds about 10mm of space. With this 56.5mm of space, use extension tubes or add other optical components such as beamsplitters, ...
Parfocal and Critical Focus Zone
... best focal point (i.e. the center of the CFZ) by projecting a fitted calibration from two defocused images at different focus points OUTSIDE the CFZ. The conundrum is that there is a reproducible focus offset between the green filter and the others within the classically defined CFZ. Thus, all filte ...
... best focal point (i.e. the center of the CFZ) by projecting a fitted calibration from two defocused images at different focus points OUTSIDE the CFZ. The conundrum is that there is a reproducible focus offset between the green filter and the others within the classically defined CFZ. Thus, all filte ...
Lecture0006c - Purdue University Cytometry Laboratories
... materials. If you want to use any of these slides, you may do so if you credit each slide with the author’s name. It is illegal to post this lecture on CourseHero or any other site Some of these slides are modified from Dr. Bob Murphy [RFM] ...
... materials. If you want to use any of these slides, you may do so if you credit each slide with the author’s name. It is illegal to post this lecture on CourseHero or any other site Some of these slides are modified from Dr. Bob Murphy [RFM] ...
Document
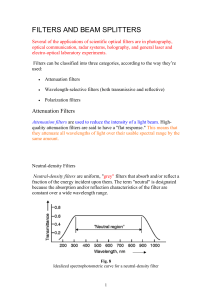
... outside the pass band, most interference filters incorporate some absorptive elements as well as dielectric layers ...
... outside the pass band, most interference filters incorporate some absorptive elements as well as dielectric layers ...
Optics - Filter Properties & manipulation of light in flow cytometry
... outside the pass band, most interference filters incorporate some absorptive elements as well as dielectric layers ...
... outside the pass band, most interference filters incorporate some absorptive elements as well as dielectric layers ...
Colorful Liquid Crys tal Fil ter Abstract Color filters are very important
... Colorful Liquid Crys tal Fil ter Abstract Color filters are very important components for optical equipment. Basically,color filters are made of high-density glass or isinglass. They can select a certain part of aspectrum before further processed.However,the transmitting spectral band is usually fix ...
... Colorful Liquid Crys tal Fil ter Abstract Color filters are very important components for optical equipment. Basically,color filters are made of high-density glass or isinglass. They can select a certain part of aspectrum before further processed.However,the transmitting spectral band is usually fix ...
A Simple Classroom Demonstration of Natural Convection
... setup, including the use of striped filters, is the same as in Fig. 1, except that a focusing lens increases the brightness of the projected image by collecting and distributing the light from the projector lamp. The smaller filter (point S) is attached to the surface of the overhead projector, and ...
... setup, including the use of striped filters, is the same as in Fig. 1, except that a focusing lens increases the brightness of the projected image by collecting and distributing the light from the projector lamp. The smaller filter (point S) is attached to the surface of the overhead projector, and ...
DISPERSIVE BIREFRINGENT FILTERS Pochi YEH 1. Introduction
... retardation between the components of the light polarized parallel to the fast and slow axes of the crystal when radiation passes through it. Since the phase retardation introduced by a wave plate is proportional to the birefringence of the crystal. It is desirable to have crystals with large birefr ...
... retardation between the components of the light polarized parallel to the fast and slow axes of the crystal when radiation passes through it. Since the phase retardation introduced by a wave plate is proportional to the birefringence of the crystal. It is desirable to have crystals with large birefr ...
OPTICAL FILTER COATINGS
... Optics interference filters enable rapid and accurate measurement of the amplitude of specific spectral lines. This combination has an enormous throughput advantage since the collecting area of filters is very large compared to instrumental slits. Additionally, interference filters enable the viewin ...
... Optics interference filters enable rapid and accurate measurement of the amplitude of specific spectral lines. This combination has an enormous throughput advantage since the collecting area of filters is very large compared to instrumental slits. Additionally, interference filters enable the viewin ...
teacher`s notes
... Half of the light gets through the first filter. Half of that light – the appropriate component – gets through the next. Half of that light gets through the third. 12) Unpolarized light is sent toward filters at 0, 20, 40 and then 80. What percentage of the light gets through? (Show your steps.) ...
... Half of the light gets through the first filter. Half of that light – the appropriate component – gets through the next. Half of that light gets through the third. 12) Unpolarized light is sent toward filters at 0, 20, 40 and then 80. What percentage of the light gets through? (Show your steps.) ...
Chromatic Dispersion
... the phase consist of spherical droplets of one phase in the other. In fact, one will have droplets of each phase within the other. Because it’s unlikely that two liquids suited to this purpose will have the same density, one will typically sit atop the other. There will be an effective dispersion on ...
... the phase consist of spherical droplets of one phase in the other. In fact, one will have droplets of each phase within the other. Because it’s unlikely that two liquids suited to this purpose will have the same density, one will typically sit atop the other. There will be an effective dispersion on ...
Plasmonic waveguide filters with nanodisk resonators
... filter can be demonstrated. The transmission spectrum can also be calculated using the method shown in Ref 1. **Note: The slight difference in the peak wavelengths (compared to reference) is due to the different metal model used. ...
... filter can be demonstrated. The transmission spectrum can also be calculated using the method shown in Ref 1. **Note: The slight difference in the peak wavelengths (compared to reference) is due to the different metal model used. ...
Coherence and Combining Filters
... Wc is the maximum separation of two points across the wavefront at a fixed time such that the two points still have a well-defined phase relationship (and hence are able to produce interference fringes) ...
... Wc is the maximum separation of two points across the wavefront at a fixed time such that the two points still have a well-defined phase relationship (and hence are able to produce interference fringes) ...
PolarView™ ND filter
... High performance digital cameras are normally designed to be sensitive in low light conditions, increasing the risk of over exposure in bright ambient light. To ensure optimal image exposure over a wide range of lighting conditions, the well-equipped photographer often carries a number of ND filters ...
... High performance digital cameras are normally designed to be sensitive in low light conditions, increasing the risk of over exposure in bright ambient light. To ensure optimal image exposure over a wide range of lighting conditions, the well-equipped photographer often carries a number of ND filters ...
Photographic filter

In photography and videography, a filter is a camera accessory consisting of an optical filter that can be inserted into the optical path. The filter can be of a square or oblong shape and mounted in a holder accessory, or, more commonly, a glass or plastic disk in a metal or plastic ring frame, which can be screwed into the front of or clipped onto the camera lens.Filters modify the images recorded. Sometimes they are used to make only subtle changes to images; other times the image would simply not be possible without them. In monochrome photography coloured filters affect the relative brightness of different colours; red lipstick may be rendered as anything from almost white to almost black with different filters. Others change the colour balance of images, so that photographs under incandescent lighting show colours as they are perceived, rather than with a reddish tinge. There are filters that distort the image in a desired way, diffusing an otherwise sharp image, adding a starry effect, etc. Supplementary close-up lenses may be classified as filters. Linear and circular polarising filters reduce oblique reflections from non-metallic surfaces.Many filters absorb part of the light available, necessitating longer exposure. As the filter is in the optical path, any imperfections—non-flat or non-parallel surfaces, reflections (minimised by optical coating), scratches, dirt—affect the image.There is no universal standard naming system for filters. The Wratten numbers adopted in the early twentieth century by Kodak, then a dominant force in film photography, are used by several manufacturers. Colour correction filters are often identified by a code of the form CC50Y—CC for colour correction, 50 for the strength of the filter, Y for yellow.Optical filters are used in various areas of science, including in particular astronomy; they are essentially the same as photographic filters, but in practice often need far more accurately controlled optical properties and precisely defined transmission curves than filters exclusively for photographic use. Photographic filters sell in larger quantities at correspondingly lower prices than many laboratory filters. The article on optical filters has material relevant to photographic filters.In digital photography the majority of filters used with film cameras have been rendered redundant by digital filters applied either in-camera or during post processing. Exceptions include the ultraviolet (UV) Ultra typically used to protect the front surface of the lens, the neutral density (ND) filter, the polarising filter and the infra red (IR) filter. The neutral density filter permits effects requiring wide apertures or long exposures to be applied to brightly lit scenes, while the graduated neutral density filter is useful in situations where the scene's dynamic range exceeds the capability of the sensor. Not using optical filters in front of the lens has the advantage of avoiding the reduction of image quality caused by the presence of an extra optical element in the light path and may be necessary to avoid vignetting when using wide-angle lenses.